Improving Electronic System Reliability with Proper PCB Design
In today’s digital age, electronic devices play a vital role in various aspects of our lives, emphasizing the importance of their reliability. The backbone of most electronic systems is the printed circuit board (PCB), which must be designed meticulously to ensure optimal performance. A well-designed PCB can enhance system reliability significantly, preventing issues like signal delays and noise interference.
1. Grounding Design Essentials
- Grounding Methods: Choosing between multi-point and single-point grounding depends on the system’s operating frequency. Multiple grounding points are ideal for frequencies above 10 MHz, while a single-point grounding method is more effective for circuits below 1 MHz.
- Analog-Digital Circuit Separation: To avoid interference, analog and digital circuits should be separated, with separate power terminals. Larger grounding areas for analog circuits help minimize noise coupling.
- Thicker Ground Wires: Using thicker ground wires with higher current-carrying capacity ensures stable operation and improved noise resistance. Opt for wires that are at least 3 mm wide.
2. Enhancing Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
- Routing Methods: Employing a “tic-tac-toe” routing pattern can reduce crosstalk between traces. Avoid long-distance parallel routing to minimize interference.
- Optimal Wire Width: Manage PCB trace inductance by using shorter, thicker traces to suppress interference effectively. For high-current signals, opt for shorter traces, while ICs and discrete components have specific trace width recommendations.
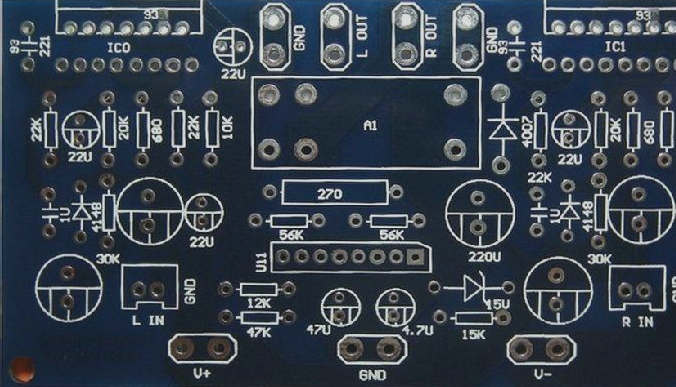
Design Considerations for Component Placement and PCB Dimensions
The Importance of PCB Size and Component Placement in Design
When designing a PCB, it is crucial to consider the size and placement of components to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. A board that is too large can lead to long traces, increasing impedance and noise resistance while also raising costs. To improve noise immunity, components that are functionally related should be placed close together.
For example, noise-sensitive devices like clock generators, crystal oscillators, and CPU clock inputs should be positioned in proximity to reduce interference. It is also essential to separate noise-sensitive circuits, low-power components, and high-current components from logic circuits to prevent signal degradation. Consider using separate PCBs for different sections for better isolation.
Key Considerations for Effective Heat Dissipation Design
Efficient heat dissipation is vital for maintaining the performance and longevity of electronic components. To optimize cooling, follow these guidelines:
- For natural convection cooling systems, orient integrated circuits vertically to enhance airflow.
- For forced air cooling systems, arrange devices horizontally to align with the airflow direction.
Consider the following points for effective heat dissipation:
- Arrange devices on the PCB based on their heat output and thermal dissipation capabilities. Place low-heat devices at the cooling airflow intake and high-heat devices at the downstream end.
- Position high-power components close to the board edge horizontally to minimize heat transfer and near the top vertically to reduce the impact on surrounding devices.
- Place temperature-sensitive components in cooler areas of the board, avoiding direct alignment with heat-generating components. Stagger devices horizontally for better thermal distribution.
- Optimize component placement and PCB layout for airflow path considerations. Avoid large empty spaces that disrupt airflow and prioritize areas of lower resistance.
If you have any inquiries regarding PCB design, feel free to reach out to us at info@wellcircuits.com.