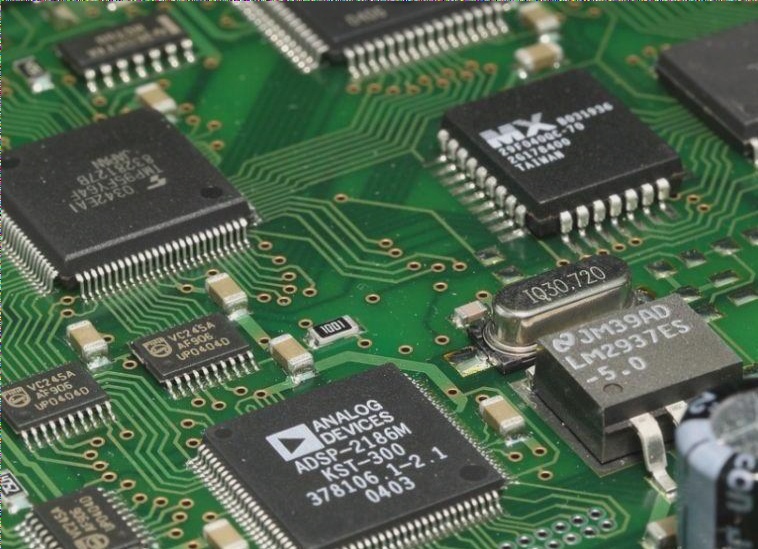
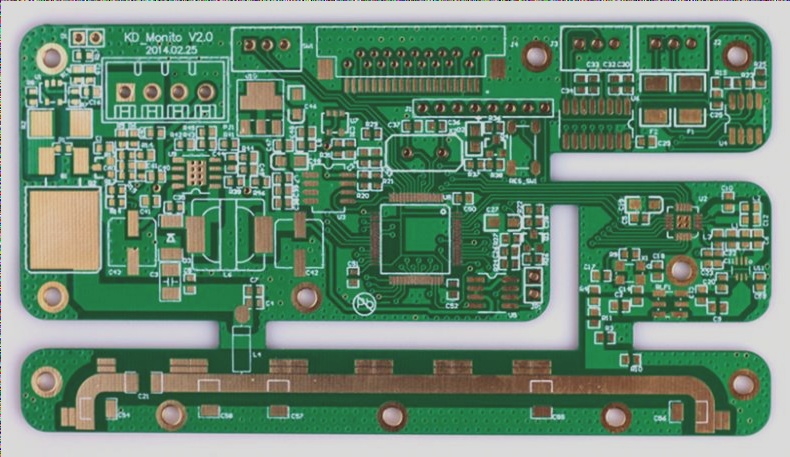
HDI PCBs: Revolutionizing Electronics with High-Density Interconnects
HDI (High-Density Interconnector) PCBs are transforming the landscape of printed circuit boards (PCBs) by offering a higher number of interconnections per unit area compared to traditional PCBs. These advanced boards boast high layer counts, fine line widths, and spaces, resulting in superior electrical performance and miniaturization.
Key Benefits of HDI PCBs:
- 1. Miniaturization: HDI rigid boards enable the reduction in size of electronic devices, enhancing their compactness and portability.
- 2. Enhanced Signal Integrity: The increased interconnections in HDI rigid boards allow for more efficient signal routing, reducing signal loss and improving signal integrity.
- 3. Cost-Effectiveness: HDI rigid boards offer cost savings due to their smaller size and weight.
- 4. Manufacturing Flexibility: Manufacturers can utilize various techniques, such as multi-layer lamination and through-hole plating, for enhanced PCB design and production flexibility.
Latest Advancements in HDI PCB Technology:
One of the primary reasons for the popularity of HDI rigid PCBs is their increased density. By leveraging microvia technology and blind vias, manufacturers can achieve higher component density, ultimately reducing the overall size of the printed circuit board and enabling the creation of more space-efficient electronic devices.
Moreover, HDI rigid boards can integrate multiple layers, allowing for more complex PCB designs compared to conventional technologies. While traditional PCBs are limited to five or six layers, HDI rigid boards can incorporate up to 24 layers, facilitating the integration of intricate circuitry and further reducing device size and weight.
Signal integrity is a critical focus for designers working on high-speed electronic devices. HDI rigid boards offer significant improvements in signal integrity through the use of microvias and blind vias, enabling shorter signal paths, reduced signal loss, and higher data transfer speeds. The controlled impedance of HDI rigid PCBs ensures consistent signal propagation, enhancing overall performance.
Advantages of HDI Rigid Boards:
- 1. Enhanced Mechanical Durability: The use of microvias and blind vias fortifies the structural integrity of HDI rigid PCBs, preventing delamination and cracking. The downsized components and increased layer count contribute to a more resilient design, ensuring extended lifespan and reliable performance, even in demanding applications.
- 2. Cost Savings: Contrary to common belief, HDI rigid PCBs can lead to cost savings for manufacturers. The higher density and improved signal integrity allow for the use of smaller components, reducing material costs and assembly complexities. Additionally, the shorter signal paths and smaller board sizes result in decreased power consumption, enhancing the cost-effectiveness of HDI rigid boards.
The Future of HDI PCB Technology:
As a superior trend in the PCB industry, HDI rigid boards continue to evolve to meet the increasing demands of electronic systems. With their ability to provide higher density, multilayer integration, improved signal integrity, enhanced mechanical durability, and cost reduction, HDI PCBs stand as the ideal choice for high-performance and compact electronic devices. Expect further advancements in HDI rigid PCB technology as technology progresses to address the evolving needs of the electronics industry.