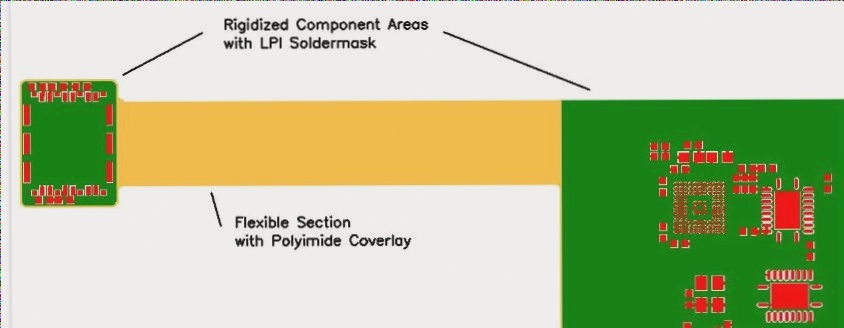
The Significance of Rigid-Flex PCB Design and Modern Tools
Manufacturing, assembly, testing, and logistics costs play a crucial role in projects utilizing Rigid-Flex PCB design techniques. Design and cost control are paramount in this process, emphasizing the need for mechanical expertise to integrate flexible designs seamlessly. However, this can be a time-consuming, expensive, and error-prone endeavor.
Traditional PCB design tools often overlook the complexities of folding and assembly in both rigid and flexible designs. Rigid-Flex PCB design requires a shift to 3D thinking, where designers must create designs that can fold, twist, and roll to meet mechanical specifications. Unfortunately, most conventional tools lack support for 3D circuit board design and bending simulations, making the process challenging.
Designers are forced to manually translate 3D designs into 2D formats, meticulously outlining soft design areas and ensuring no components interfere between rigid and flexible regions. This arduous process is compounded by numerous rules not supported by standard PCB design software.
Modern design tools with advanced 3D capabilities can simplify bending simulations for flexible components and define diverse layer stack designs, reducing reliance on mechanical CAD tools. By leveraging these tools, developers and manufacturers can collaborate effectively, accelerating the adoption of Rigid-Flex PCB technology.
Successful Rigid-Flex board production requires close collaboration between designers and manufacturers to establish design rules regarding layer count, material selection, hole size, bonding methods, and dimensional control. With the right tools, designers can optimize Rigid-Flex PCB designs from the outset, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs.
The evolution of Rigid-Flex PCB technologies is driven by industry trends and consumer demands for innovative solutions, particularly in mobile devices. Modern PCB design tools enable comprehensive simulation of rigid and flexible combinations, simplifying the design process and making Rigid-Flex PCB solutions more attractive and cost-effective.
Ultimately, informed choices in design can be the key to product success in the competitive market landscape.