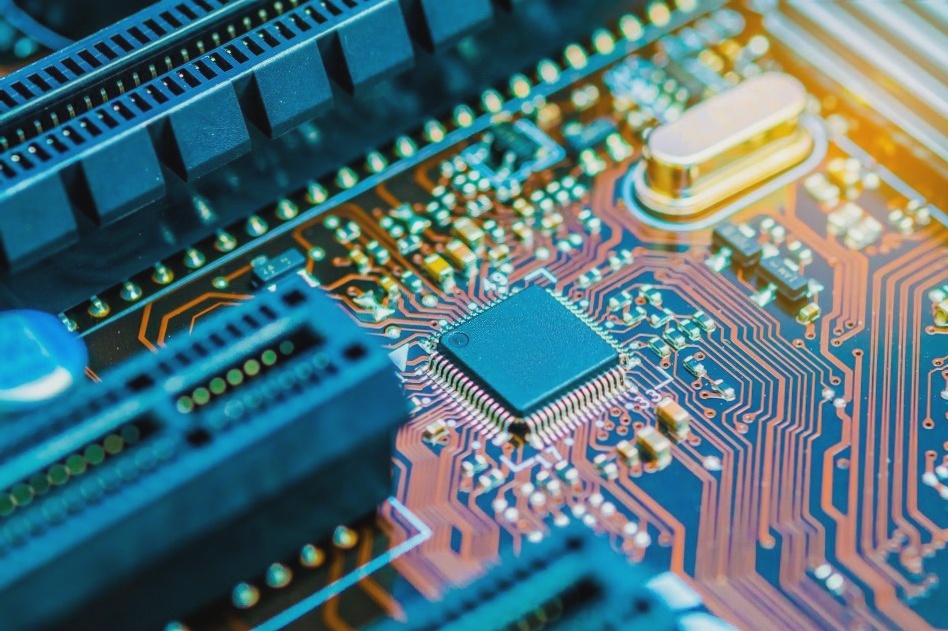
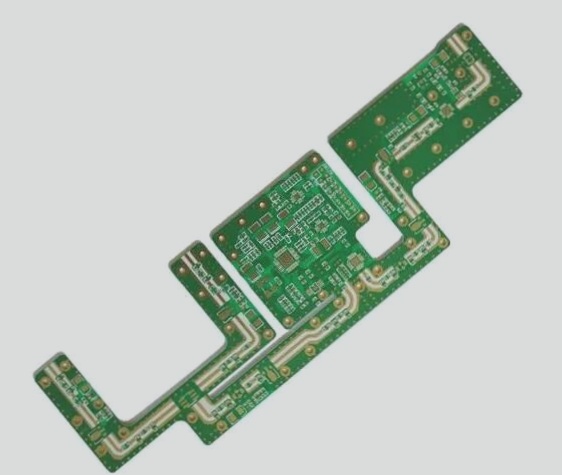
1. Usually, the style and manufacturing of a printed circuit board (PCB) are as crucial as the design of the main circuit itself. Manufacturers are increasingly employing compact, flexible PCBs to assemble and organize electronic circuits. A PCB may comprise one or more protective boards on which copper layers and conductive signal traces have been either etched or printed. Depending on the complexity of the circuit, PCB manufacturing typically involves anywhere from a single-layer PCB to eight layers, or even more.
2. Types of PCBs based on layers.
If you have a very basic circuit, your PCB supplier will likely suggest using a single-sided PCB. This is the simplest PCB type, as the entire circuit—comprising the electrical components and copper traces—is contained on a single protective board. A double-sided board accommodates a slightly more complex circuit than a single-sided board. As the name implies, both sides of the substrate are utilized for housing the wiring elements. Hole technology is typically employed in manufacturing double-sided or multilayered PCBs.
3. Complex printed circuit board manufacturing is achieved through multi-layered PCBs, which consist of multiple substrate sheets with insulating layers between each. Depending on the circuit’s complexity, these PCBs can range from two layers to four, eight, or even up to 42 layers in highly advanced applications.
4. Types of PCBs based on rigidity.
Different applications necessitate different types of PCBs. For instance, a rigid PCB is most prevalent and can be found in everyday consumer electronic items such as computers, televisions, and smartphones. Such a board, when bent beyond a certain limit, will crack or break. Another common type provided by PCB manufacturers is the flexible PCB. Circuits in such PCBs are built on thin, flexible insulating material, allowing the PCB to be bent and curved as desired without damaging the circuit or substrate. Flexible PCBs are used in medical devices, flexible heaters, and even devices like hearing aids.
5. The rigid-flex variety of PCBs combines rigid and flexible PCBs. These circuits are utilized in aerospace and military applications where a highly dense circuit is required. Rigid-flex PCBs help conserve significant space, resulting in electronic products that weigh much less.
6. Printed circuit board manufacturing can be tailored for a limited number of circuits or for large-volume production. It’s crucial to choose a PCB manufacturing company with a proven track record.
7. For the past few years, I have been writing articles on industrial products and technology, particularly passionate about exploring the various layers of PCBs. Dive into my articles to gain insights into circuit boards based on rigidity types and designs.
2. Types of PCBs based on layers.
If you have a very basic circuit, your PCB supplier will likely suggest using a single-sided PCB. This is the simplest PCB type, as the entire circuit—comprising the electrical components and copper traces—is contained on a single protective board. A double-sided board accommodates a slightly more complex circuit than a single-sided board. As the name implies, both sides of the substrate are utilized for housing the wiring elements. Hole technology is typically employed in manufacturing double-sided or multilayered PCBs.
3. Complex printed circuit board manufacturing is achieved through multi-layered PCBs, which consist of multiple substrate sheets with insulating layers between each. Depending on the circuit’s complexity, these PCBs can range from two layers to four, eight, or even up to 42 layers in highly advanced applications.
4. Types of PCBs based on rigidity.
Different applications necessitate different types of PCBs. For instance, a rigid PCB is most prevalent and can be found in everyday consumer electronic items such as computers, televisions, and smartphones. Such a board, when bent beyond a certain limit, will crack or break. Another common type provided by PCB manufacturers is the flexible PCB. Circuits in such PCBs are built on thin, flexible insulating material, allowing the PCB to be bent and curved as desired without damaging the circuit or substrate. Flexible PCBs are used in medical devices, flexible heaters, and even devices like hearing aids.
5. The rigid-flex variety of PCBs combines rigid and flexible PCBs. These circuits are utilized in aerospace and military applications where a highly dense circuit is required. Rigid-flex PCBs help conserve significant space, resulting in electronic products that weigh much less.
6. Printed circuit board manufacturing can be tailored for a limited number of circuits or for large-volume production. It’s crucial to choose a PCB manufacturing company with a proven track record.
7. For the past few years, I have been writing articles on industrial products and technology, particularly passionate about exploring the various layers of PCBs. Dive into my articles to gain insights into circuit boards based on rigidity types and designs.