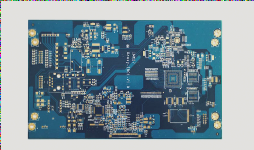
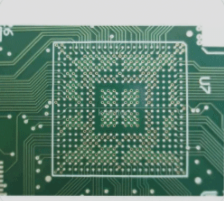
Types of Core Board PCBs
-
Classification Based on Number of Layers:
The PCB of the core board can be categorized into core single-sided, core double-sided, and core multilayer boards based on the number of layers. Common multilayer boards typically consist of 3 to 6 layers, while more complex multilayer boards can exceed ten layers.

-
Single-Sided Panel
On the most basic printed circuit board, components are concentrated on one side while the wiring is found on the opposite side. Since the wiring appears solely on one side, this type of printed circuit board is referred to as a single-sided board.
-
Double-Sided Panel
This type of PCB features wiring on both sides. To connect the circuits on either side, a proper circuit connection is necessary, known as a via.
-
Multilayer Board
To increase the available wiring area, multilayer boards incorporate multiple single or double-sided wiring boards. A multilayer board consists of several double-sided boards, each separated by an insulating layer and securely bonded together.
-
-
Classification by Core Material Type:
-
Flexible PCB
A flexible board is a printed circuit board made from a flexible substrate. Its main advantage is its ability to bend, facilitating the assembly of electrical components.
-
Rigid PCB
This type of board is constructed from paper-based materials or glass cloth, pre-impregnated with phenolic or epoxy resin. Copper foil is laminated on one or both surfaces and then cured.
-
Rigid-Flex PCB
A rigid-flex board is a printed circuit board that incorporates one or more rigid areas alongside flexible sections, created by laminating a rigid board with a flexible board.
-
The printed circuit board is a crucial electronic component and serves as the foundation for electronic components. Understanding the different types of core board PCBs is essential for designing and manufacturing electronic devices.