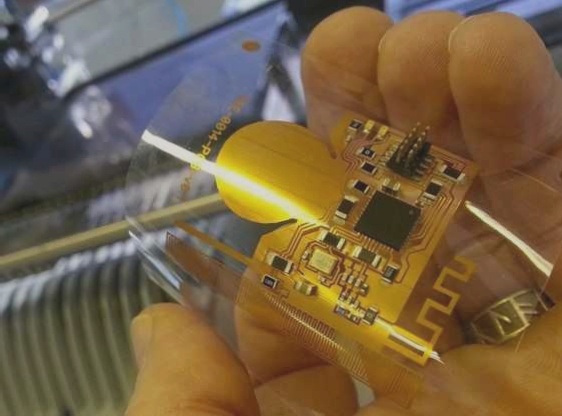
Benefits of Flexible PCBs in Electronic Products
- Replacement of multi-layer rigid boards and connectors with flexible printed circuits
- Substitution of rigid boards/ribbon cables with flexible PCBs
- Management of electromagnetic interference with protective layers
- Control of impedance with a complete ground layer
- Electrical connections through air gaps for narrow wiring areas
- Utilization of conductive rubber keypads for circuits
- Incorporation of heaters, temperature sensors, or wire antenna coils
- Use of flexible printed circuits as jumpers between rigid boards
- Bonding circuits to chassis or enclosure with pressure-sensitive conductive adhesive
Flexible PCBs offer innovative solutions to design and packaging challenges in electronic products. They are extensively used in military, aviation, medical, and commercial industries due to their unique advantages.
Recent advancements in flexible PCB technology have focused on enhancing flexibility, durability, and performance. Manufacturers are now developing flexible PCBs with increased bendability and resistance to environmental factors, making them ideal for applications in wearable technology, IoT devices, and automotive electronics.