Cold Solder Joint Issues in Electronics
Cold soldering is a common problem in electronics, especially in lesser-known brands. Unlike reputable brands, cold solder joints are more prevalent in inferior quality electronics. Cold soldering occurs when solder joints are made using incompletely melted solders, resulting in lumpy and coarse connections that may lead to electrical connectivity issues over time.
Understanding Soldering Process
In soldering, electronic components on a circuit board are connected using a conducting alloy that is melted and applied between connectors. This alloy, typically a lead and tin mixture, is heated with a soldering iron to create the connections. Cold soldering, characterized by imperfectly melted solders, can result from using substandard soldering materials.
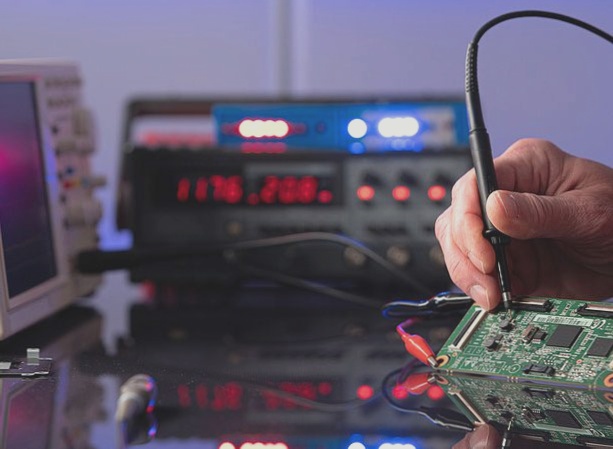
Detection and Testing of Cold Solder Joints
Cold soldering is often overlooked in rushed or bulk electronic projects, especially with freelance electricians. The lack of strict quality control in some brands can lead to cold soldering issues. Detecting cold solder joints is crucial to prevent component failure and potential PCB issues, which can result in rework and financial losses.
Importance of Testing
Proper testing methods, even for cold solder joints, are essential to ensure the reliability of electronic connections. Neglecting thorough testing can lead to business losses and client dissatisfaction due to faulty components and decreased payouts.
Standard Tests for Conductivity
- Visual inspection for lumpy or coarse solder joints
- Continuity testing to check electrical connectivity
- Microscopic examination for cracks or irregularities
By prioritizing quality soldering practices and thorough testing, electronics manufacturers can avoid the pitfalls associated with cold solder joints and ensure the longevity and reliability of their products.
How to Identify and Fix Cold Solder Joints on PCBs
1- Visual Inspection for Cold Solder Joints
Visual tests are a simple yet effective way to check for cold solder joints on PCBs. Look for lumpy, uneven soldering or joints that do not connect properly. Use tools like a magnifying glass to ensure a proper bond between edges.
If light passes through the joints or if you see rough solder blocks, it indicates a potential issue. Loose joints may detach when the board is tilted, while spilled solder can cause short circuits.
2- Testing with a Multimeter
- 2a- Resistance Testing: Use a multimeter set to 1000 ohms. A ‘zero’ reading between joints indicates a good connection.
- 2b- Continuity Testing: Switch the multimeter to continuity mode. A beep confirms a connected joint, while no sound suggests rework is needed.
These tests help ensure the functionality of solder joints despite cold soldering issues.
Repairing Cold Solder Joints
If cold joints are found, they can be repaired using the following methods:
- Distributed Cold Solder Joints: Commonly caused by movement during soldering, these joints appear concave and frosted. Keeping the work area stable can prevent this issue.
To prevent distributed cold solder joints, ensure a stable work surface or use a wall-mounted soldering vice for secure soldering.
Dealing with Normal Cold Solder Joints
Solving Cold Solder Joint Issues
- Identifying Cold Solder Joints: Recognizing a cold solder joint is straightforward. Inadequate heating or a dirty soldering iron tip are common causes.
One effective solution is to clean the soldering iron tip before each use and store it in a dust-free container. Ensuring proper heating of the soldering iron is also crucial.
Opting for SN96 solder, a lead-free alloy with a lower melting point, can be beneficial for smoother soldering.
Common Issues with Cold Solder Joints
Testing the conductivity of cold solder joints is essential to detect resistance. High resistance indicates incomplete alloy combustion, which can damage electronics and increase power consumption over time.
Incomplete circuits, overheating, and elevated power usage are typical consequences of high resistance in cold solder joints.
Best Soldering Practices
Cold soldering is costlier and less effective than hot soldering. To achieve optimal results, consider the following practices:
- Choose Quality Products: Invest in the right soldering tools for even and conductive joints.
- Use minimal solder to avoid excess.
- Store soldering equipment in a clean, dry environment.
- Ensure Proper Heating: Adequate heating results in smoother and more efficient solder joints.
- Consider using lead-free solder if cold soldering issues persist.
- Use a soldering gun for rapid heating.
- Solder on a stable work surface.
Conclusion
Soldering plays a crucial role in establishing electrical connections. To avoid cold soldering issues and ensure optimal joint performance, prioritize proper heating, cleanliness, and the use of quality materials in your soldering practices.