1. A circuit board drill is a sophisticated mechanical component essential for manufacturing printed circuit boards (PCBs).
2. In PCB production, precision is crucial, which is why specialized machinery is employed to guarantee accuracy, quality, and performance.

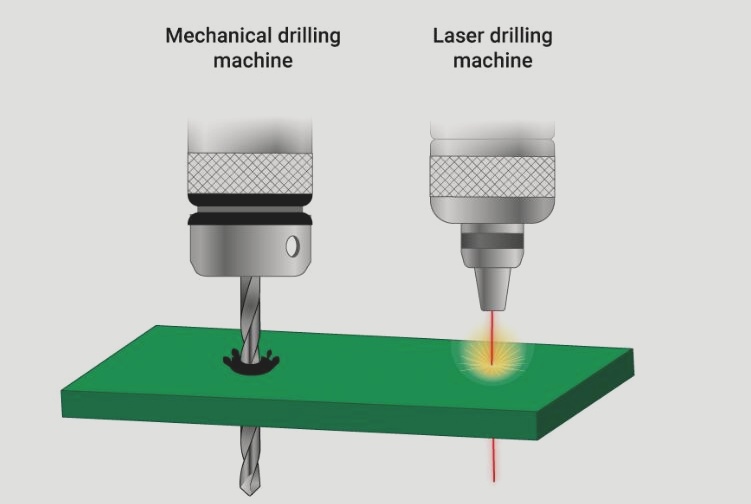
**Two Common Drilling Methods for Circuit Boards**
1. **Mechanical Drilling**
Mechanical drills have lower accuracy but are relatively simple to use. This technology allows the drill bit to penetrate with a minimum hole diameter of approximately 6 mils (0.006 inches).
**Limitations of Mechanical Drilling**
In softer materials like FR4, mechanical drills can perform about 800 impacts. For denser materials, the lifespan decreases to around 200 impacts. Neglecting this limitation can result in incorrect holes, potentially leading to circuit board scrapping.
2. **Laser Drilling**
Laser drills can create smaller holes with precision. This non-contact process involves using laser beams to remove material and control the drilling depth accurately, with a minimum diameter of 2 mils (0.002 inches).
**Limitations of Laser Drilling**
The circuit board’s copper, glass fiber, and resin have different optical properties, making it challenging for lasers to cut through effectively. Additionally, the cost of laser drilling is relatively high.
**Circuit Board Drilling Process**
After lamination, the laminate is placed on the material panel of the drilling machine. The panel helps reduce burr formation, which occurs when the drill bit penetrates the plate. Multiple stacks are aligned and covered with aluminum foil, which prevents burrs and dissipates heat from the drill bit. After drilling, the circuit board undergoes deburring and decontamination.
**Drill Bit Materials**
The quality of drilling hinges on the tool’s geometric shape. High-speed steel (HSS) and tungsten carbide (WC) are commonly used for drilling composite materials. For glass fiber reinforced polymer (GFRP), hard alloy tools are preferred for their extended tool life.
**Types of Holes in Circuit Board Drilling**
Various holes are drilled, including through holes (such as via holes, buried holes, blind holes, and micropores), component holes, and mechanical holes.
**Types of Circuit Board Drill Bits**
Drills include straight shank drills, fixed shank drills, and fixed shank undercut drills.
1) Straight shank drills are used for simple boards, with drilling depths up to 10 times the drill diameter. Drill sleeves can help avoid deviations in shallow substrates.
2) Modern CNC machines use fixed shank drills made from hard alloys, which automatically replace bits and offer high positioning accuracy. With large helix angles and efficient chip removal, these drills provide better drilling quality. Common drill stem diameters are 3.00mm and 3.175mm.
**Material and Characteristics of Drill Bits**
Circuit board drill bits are generally made from hard alloy due to the rapid wear on cutting tools caused by epoxy glass cloth-coated copper foil plates. These bits feature high hardness, wear resistance, strength, and long tool life.
2. In PCB production, precision is crucial, which is why specialized machinery is employed to guarantee accuracy, quality, and performance.
**Two Common Drilling Methods for Circuit Boards**
1. **Mechanical Drilling**
Mechanical drills have lower accuracy but are relatively simple to use. This technology allows the drill bit to penetrate with a minimum hole diameter of approximately 6 mils (0.006 inches).
**Limitations of Mechanical Drilling**
In softer materials like FR4, mechanical drills can perform about 800 impacts. For denser materials, the lifespan decreases to around 200 impacts. Neglecting this limitation can result in incorrect holes, potentially leading to circuit board scrapping.
2. **Laser Drilling**
Laser drills can create smaller holes with precision. This non-contact process involves using laser beams to remove material and control the drilling depth accurately, with a minimum diameter of 2 mils (0.002 inches).
**Limitations of Laser Drilling**
The circuit board’s copper, glass fiber, and resin have different optical properties, making it challenging for lasers to cut through effectively. Additionally, the cost of laser drilling is relatively high.
**Circuit Board Drilling Process**
After lamination, the laminate is placed on the material panel of the drilling machine. The panel helps reduce burr formation, which occurs when the drill bit penetrates the plate. Multiple stacks are aligned and covered with aluminum foil, which prevents burrs and dissipates heat from the drill bit. After drilling, the circuit board undergoes deburring and decontamination.
**Drill Bit Materials**
The quality of drilling hinges on the tool’s geometric shape. High-speed steel (HSS) and tungsten carbide (WC) are commonly used for drilling composite materials. For glass fiber reinforced polymer (GFRP), hard alloy tools are preferred for their extended tool life.
**Types of Holes in Circuit Board Drilling**
Various holes are drilled, including through holes (such as via holes, buried holes, blind holes, and micropores), component holes, and mechanical holes.
**Types of Circuit Board Drill Bits**
Drills include straight shank drills, fixed shank drills, and fixed shank undercut drills.
1) Straight shank drills are used for simple boards, with drilling depths up to 10 times the drill diameter. Drill sleeves can help avoid deviations in shallow substrates.
2) Modern CNC machines use fixed shank drills made from hard alloys, which automatically replace bits and offer high positioning accuracy. With large helix angles and efficient chip removal, these drills provide better drilling quality. Common drill stem diameters are 3.00mm and 3.175mm.
**Material and Characteristics of Drill Bits**
Circuit board drill bits are generally made from hard alloy due to the rapid wear on cutting tools caused by epoxy glass cloth-coated copper foil plates. These bits feature high hardness, wear resistance, strength, and long tool life.