**Multilayer FPC Soft Board**
Multilayer FPC soft boards, similar to rigid multilayer PCBs, are created through multilayer lamination technology. The simplest form of a multilayer FPC soft board is a three-layer flexible PCB, which consists of two copper shielding layers bonded to either side of a single-sided PCB. This three-layer flexible PCB exhibits electrical characteristics akin to those of coaxial or shielded wires. The most commonly utilized structure for multilayer FPC soft boards is a four-layer design, which employs metallized vias for interlayer connections. Typically, the two inner layers serve as the power layer and the ground layer.
The advantages of multilayer FPC flexible boards include a lightweight base film and outstanding electrical properties, such as a low dielectric constant. When using polyimide film as the substrate material, multilayer FPC soft boards can weigh about one-third less than rigid epoxy glass cloth multilayer PCBs. However, they do sacrifice some flexibility typically found in single-sided and double-sided FPC soft boards, as most of these products do not require such flexibility. Today, FPC manufacturers aim to provide insights into the classification of multilayer soft boards:
Multilayer FPC soft boards can be categorized into the following types:
1) A multilayer FPC soft board is constructed on a flexible insulating substrate, with the final product specified to maintain flexibility. This structure usually involves bonding the two sides of multiple single-sided or double-sided microstrip flexible PCBs together, while the central portion remains unbonded, allowing for a high degree of flexibility. To achieve the desired electrical characteristics, such as characteristic impedance performance and compatibility with the rigid PCB to which it connects, each circuit layer of the multilayer FPC soft board must incorporate signal lines on the ground plane. To ensure maximum flexibility, a thin, suitable coating, such as polyimide, is preferred over a thicker laminated cover layer on the wire layer.

1) The metallized holes facilitate the necessary interconnection across the z-planes between the flexible circuit layers. This type of multilayer FPC soft board is particularly well-suited for designs that demand flexibility, high reliability, and high density.
2) A multilayer PCB is constructed on a flexible insulating substrate, allowing the final product to maintain flexibility. This kind of multilayer FPC soft board is crafted from flexible insulating materials, such as polyimide film, which are laminated to form a multilayer structure. However, inherent flexibility is compromised after lamination. This type of FPC soft board is employed when designs require maximum utilization of the film’s insulating properties, including low dielectric constant, uniform medium thickness, reduced weight, and the capability for continuous processing. For instance, a multilayer PCB using polyimide film as the insulating material is approximately one-third lighter than a rigid PCB made with epoxy glass cloth.
3) A multilayer PCB is created on a flexible insulating substrate, where the final product is required to be shapeable but not continuously flexible. This type of multilayer FPC soft board is made from soft insulating materials. While it is constructed from soft materials, it faces limitations imposed by electrical design constraints. For example, to meet specific conductor resistance requirements, a thicker conductor may be necessary, or to achieve desired impedance or capacitance, a thicker conductor must be positioned between the signal layer and the ground layer. The insulation is already established in the finished application. The term “formable” refers to the ability of the multilayer FPC soft board component to be shaped into the necessary form while remaining inflexible during use. This type is utilized in the internal wiring of avionics units, where low conductor resistance in strip line or three-dimensional space designs is essential, and where capacitive coupling or circuit noise must be minimized. Additionally, the interconnection ends can be smoothly bent to 90°. The multilayer FPC soft board made from polyimide film meets these wiring requirements due to its high-temperature resistance, flexibility, and excellent electrical and mechanical properties. To accommodate all interconnections in this component, the wiring can be subdivided into several multilayer flexible circuit components, which are then bonded with adhesive tape to create a printed circuit board.
4) FPC multilayer soft and hard combined circuit boards (soft and hard combined boards) typically involve one or two rigid PCBs that incorporate the necessary FPC soft board to complete the assembly. The FPC soft board layer is laminated within a rigid multilayer PCB to fulfill specific electrical requirements or to extend beyond the rigid circuit, replacing the Z-plane circuit mounting capability. This type of product is extensively used in electronic devices where minimizing weight and volume is crucial, while ensuring high reliability, high-density assembly, and excellent electrical characteristics.
5) FPC multilayer flexible and rigid boards can also bond and press the ends of multiple single-sided or double-sided FPC flexible boards together to create a rigid section, while leaving the middle unbonded to maintain flexibility. The Z side of the rigid section is interconnected via metallized holes. Furthermore, the flexible circuit can be laminated into the rigid multilayer board. This type of PCB is increasingly employed in applications that require ultra-high packaging density, outstanding electrical characteristics, high reliability, and stringent volume constraints.
6) A series of hybrid multilayer FPC soft board components has been designed for military avionics. In these contexts, weight and volume are critical factors. To adhere to specified weight and volume limits, the internal packaging density must be exceptionally high. In addition to achieving high circuit density, minimizing crosstalk and noise requires all signal transmission lines to be shielded. Using shielded separate wires is often impractical for economical system packaging. Consequently, a hybrid multilayer FPC soft board is utilized to facilitate interconnection. This component includes shielded signal lines integrated into the flat stripline FPC soft board, which is also a crucial part of the rigid PCB. In high-stress operating conditions, the completed PCB forms a 90° S-shaped bend, providing a means for z-plane interconnection while alleviating stress-strain effects on solder joints during vibration in the x, y, and z planes.
If you have any PCB manufacturing needs, please do not hesitate to contact me.Contact me
Multilayer FPC soft boards, similar to rigid multilayer PCBs, are created through multilayer lamination technology. The simplest form of a multilayer FPC soft board is a three-layer flexible PCB, which consists of two copper shielding layers bonded to either side of a single-sided PCB. This three-layer flexible PCB exhibits electrical characteristics akin to those of coaxial or shielded wires. The most commonly utilized structure for multilayer FPC soft boards is a four-layer design, which employs metallized vias for interlayer connections. Typically, the two inner layers serve as the power layer and the ground layer.
The advantages of multilayer FPC flexible boards include a lightweight base film and outstanding electrical properties, such as a low dielectric constant. When using polyimide film as the substrate material, multilayer FPC soft boards can weigh about one-third less than rigid epoxy glass cloth multilayer PCBs. However, they do sacrifice some flexibility typically found in single-sided and double-sided FPC soft boards, as most of these products do not require such flexibility. Today, FPC manufacturers aim to provide insights into the classification of multilayer soft boards:
Multilayer FPC soft boards can be categorized into the following types:
1) A multilayer FPC soft board is constructed on a flexible insulating substrate, with the final product specified to maintain flexibility. This structure usually involves bonding the two sides of multiple single-sided or double-sided microstrip flexible PCBs together, while the central portion remains unbonded, allowing for a high degree of flexibility. To achieve the desired electrical characteristics, such as characteristic impedance performance and compatibility with the rigid PCB to which it connects, each circuit layer of the multilayer FPC soft board must incorporate signal lines on the ground plane. To ensure maximum flexibility, a thin, suitable coating, such as polyimide, is preferred over a thicker laminated cover layer on the wire layer.
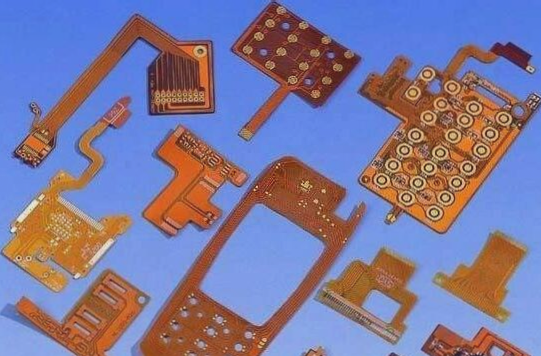
1) The metallized holes facilitate the necessary interconnection across the z-planes between the flexible circuit layers. This type of multilayer FPC soft board is particularly well-suited for designs that demand flexibility, high reliability, and high density.
2) A multilayer PCB is constructed on a flexible insulating substrate, allowing the final product to maintain flexibility. This kind of multilayer FPC soft board is crafted from flexible insulating materials, such as polyimide film, which are laminated to form a multilayer structure. However, inherent flexibility is compromised after lamination. This type of FPC soft board is employed when designs require maximum utilization of the film’s insulating properties, including low dielectric constant, uniform medium thickness, reduced weight, and the capability for continuous processing. For instance, a multilayer PCB using polyimide film as the insulating material is approximately one-third lighter than a rigid PCB made with epoxy glass cloth.
3) A multilayer PCB is created on a flexible insulating substrate, where the final product is required to be shapeable but not continuously flexible. This type of multilayer FPC soft board is made from soft insulating materials. While it is constructed from soft materials, it faces limitations imposed by electrical design constraints. For example, to meet specific conductor resistance requirements, a thicker conductor may be necessary, or to achieve desired impedance or capacitance, a thicker conductor must be positioned between the signal layer and the ground layer. The insulation is already established in the finished application. The term “formable” refers to the ability of the multilayer FPC soft board component to be shaped into the necessary form while remaining inflexible during use. This type is utilized in the internal wiring of avionics units, where low conductor resistance in strip line or three-dimensional space designs is essential, and where capacitive coupling or circuit noise must be minimized. Additionally, the interconnection ends can be smoothly bent to 90°. The multilayer FPC soft board made from polyimide film meets these wiring requirements due to its high-temperature resistance, flexibility, and excellent electrical and mechanical properties. To accommodate all interconnections in this component, the wiring can be subdivided into several multilayer flexible circuit components, which are then bonded with adhesive tape to create a printed circuit board.
4) FPC multilayer soft and hard combined circuit boards (soft and hard combined boards) typically involve one or two rigid PCBs that incorporate the necessary FPC soft board to complete the assembly. The FPC soft board layer is laminated within a rigid multilayer PCB to fulfill specific electrical requirements or to extend beyond the rigid circuit, replacing the Z-plane circuit mounting capability. This type of product is extensively used in electronic devices where minimizing weight and volume is crucial, while ensuring high reliability, high-density assembly, and excellent electrical characteristics.
5) FPC multilayer flexible and rigid boards can also bond and press the ends of multiple single-sided or double-sided FPC flexible boards together to create a rigid section, while leaving the middle unbonded to maintain flexibility. The Z side of the rigid section is interconnected via metallized holes. Furthermore, the flexible circuit can be laminated into the rigid multilayer board. This type of PCB is increasingly employed in applications that require ultra-high packaging density, outstanding electrical characteristics, high reliability, and stringent volume constraints.
6) A series of hybrid multilayer FPC soft board components has been designed for military avionics. In these contexts, weight and volume are critical factors. To adhere to specified weight and volume limits, the internal packaging density must be exceptionally high. In addition to achieving high circuit density, minimizing crosstalk and noise requires all signal transmission lines to be shielded. Using shielded separate wires is often impractical for economical system packaging. Consequently, a hybrid multilayer FPC soft board is utilized to facilitate interconnection. This component includes shielded signal lines integrated into the flat stripline FPC soft board, which is also a crucial part of the rigid PCB. In high-stress operating conditions, the completed PCB forms a 90° S-shaped bend, providing a means for z-plane interconnection while alleviating stress-strain effects on solder joints during vibration in the x, y, and z planes.
If you have any PCB manufacturing needs, please do not hesitate to contact me.Contact me