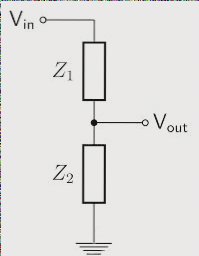
Types of PCB Resist Coating Methods
- Screen Printing Method:
- Dry Film/Sensitization Method:
- Liquid Resist Sensitization Method:
The screen printing method involves directly printing circuit patterns onto copper foil surfaces. It is widely used for low-cost PCB mass production, with a precision of 0.2 to 0.3mm line width/spacing.
The dry film method can achieve line-width patterns of 70-80μm, suitable for precision patterns below 0.3mm. Batch production can yield graphics with line widths of 30-40μm under optimal conditions.
When selecting a dry film, compatibility with the copper foil board and process must be established through experimentation to ensure high pass rates during mass production of PCBs.
Key Considerations for Dry Film Application
- Three-Layer Structure:
- Equipment and Process:
- Stability and Exposure:
- Line Width Considerations:
- Drying and Baking:
The dry film consists of a protective film, a photoresist film, and a release film. Proper removal and application are crucial for successful PCB production.
The dry film comes in roll form, making equipment and processes straightforward. Manual lamination is preferred over automated systems due to higher linear speed.
After application, the dry film should rest for 15-20 minutes before exposure to ensure stability and optimal results.
For circuit patterns with line widths less than 30μm, dry film may not be suitable for mass production. Liquid photoresist is preferred for finer lines.
After coating with liquid photoresist, meticulous control of drying and baking conditions is essential to ensure optimal resist film performance.