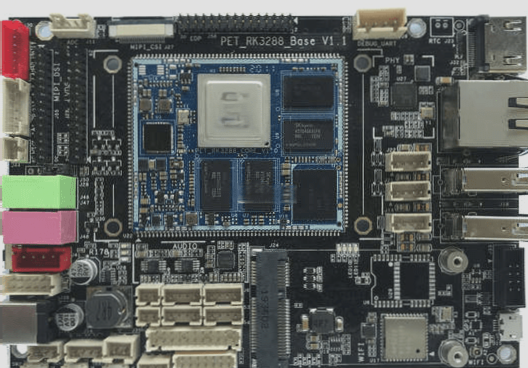
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) vs. Printed Wire Board (PWB): What’s the Difference?
Introduction
Printed Wire Board (PWB) and PCB are terms commonly used in the electronics industry to refer to insulated substrates with conductor patterns. While they are often used interchangeably, there are subtle differences between the two.
Definition
PWB, also known as Printed Wire Board, is a semi-finished product that acts as a substrate for electronic components. It forms the foundation for creating electronic circuits by connecting conductors.
On the other hand, PCB, or Printed Circuit Board, refers to the entire substrate of a PWB equipped with electronic components, forming a complete circuit board.
Differences
One key difference lies in the technology used. PWBs rely on manual circuit drawing and etching, while PCBs involve computer-aided design for circuit creation.
PCBs are more advanced, with components printed point-to-point on insulated boards, enhancing circuit operation efficiency.
Materials Used
Both PCBs and PWBs consist of conductive and non-conductive layers. Commonly used conductive materials include copper, silver, and gold, with copper being the most cost-effective and widely used due to its strong conductivity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while PWBs and PCBs share similarities, such as their function as electronic substrates, their manufacturing processes and technological advancements set them apart. Understanding the nuances between PWBs and PCBs is crucial in the electronics industry.

The Importance of Non-Conductive Layers in PCB Manufacturing
The non-conductive layer in a PCB is crucial as it is made of low-conductivity materials such as FR-4 and ceramic. FR-4 is a composite epoxy material that manufacturers use to enhance dielectric properties. On the other hand, ceramic substrates are favored for high-power applications due to their superior thermal conductivity.
Materials Used in PCB Manufacturing
Manufacturers utilize a variety of materials in PCB production to offer different levels of insulation and thermal conductivity. Common elements include fiberglass, plastic, copper tracks for electrical paths, adhesives for component fixation, and protective coatings against dust and moisture. The choice of materials depends on the intended use of the circuit board and the needs of the electronic components it will accommodate.
Difference Between PWB and PCB
PWB (Printed Wiring Board) acts as a foundation for components connected manually or via cables, allowing for easy design changes without replacing the entire board. In contrast, PCB (Printed Circuit Board) employs automated processes like etching and electroplating, enabling more components to be connected in a smaller space. While PCBs offer greater reliability and precision, any design modifications necessitate replacing the entire board.
Consumer Electronics and PCBs
In consumer electronics, PWB and PCB are sometimes used interchangeably. Both are essential for supporting and connecting electronic components in devices. However, they serve different purposes when it comes to completing circuits, with PCBs being more advanced and versatile due to their ability to support complex circuits and a wider range of components.