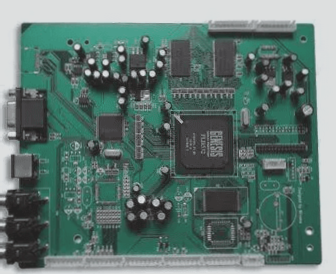
1. The main material of a PCB is a non-conductive base material, typically a cellulose substrate made by laminating insulating glass fiber cloth. This substrate is commonly referred to as FR-4, or Flame Retardant 4.
2. The FR-4 material offers excellent insulation, mechanical strength, and stability, making it suitable for meeting the requirements of most electronic products.

What are PCB boards made of?
Firstly, the main body of the circuit board is the substrate. A substrate is a flat sheet, usually made of materials such as glass fiber, plastic, or ceramics, covered with copper foil. The main function of copper foil is to provide electrical connections, connecting various electronic components. The shape and position of copper foil are usually determined based on design requirements.
Secondly, the electronic components on the circuit board are another important component of the circuit board. Electronic components are various electronic devices on a circuit board, such as capacitors, resistors, transistors, integrated circuits, and so on. They are connected with copper foil to form a circuit. The selection and arrangement of electronic components are an important part of circuit board design, which determines the performance and functionality of the circuit board.
Thirdly, the printed text and logo on the circuit board are also important components of the circuit board. Printed signs and text are usually used to identify various components and connection methods on a circuit board. These signs and text are usually printed on the circuit board using white ink.
Finally, the solder joints on the circuit board are also an important component of the circuit board. Welding points are the connection points between electronic components and copper foil, which are fixed and connected through welding technology. The quality and reliability of solder joints have a significant impact on the performance and lifespan of circuit boards.
Usually, PCBs are made of non-substrate materials with copper circuit layers. However, different types of PCBs have different structures. For example, although some printed circuit boards contain single-layer copper circuits, more advanced PCBs may contain 50 or more layers.
Printed circuit boards are made of various PCB materials and electronic components. Common PCB components include
1) Resistance
Resistors transmit current to generate voltage and dissipate electrical energy in the form of heat. They come in various materials.
2) Capacitor
The job of a capacitor is to maintain charge within the circuit board and then release it when more power is needed elsewhere in the circuit. The typical working principle of a capacitor is to collect opposite charges on two conductive layers separated by insulating materials.
3) Inductor
They are similar to capacitors because they store energy. However, they are typically used to block signals within a PCB, such as interference from another electronic device.
4) Transistor
A transistor is an amplifier. It is used to switch or control electronic signals in circuit boards. There are several different versions of transistors available, but the most common is bipolar transistors.
5) Diode
Diodes allow current to flow in one direction, but not in another direction. Therefore, diodes are used to prevent current from flowing in the wrong direction, thereby damaging circuit boards and devices. The most popular diode is LED (short for Light Emitting Diode).
6) Sensors
These devices are used to detect changes in environmental conditions and generate corresponding electrical signals. This signal is then sent to other components on the circuit board. Sensors convert physical elements such as light movement, air quality, or sound into electrical energy.
The PCB layers that make up the circuit board
1) Matrix layer
It is the basic layer of PCB, composed of glass fibers. FR4 is the most commonly used glass fiber. Some PCBs also come with phenolic and epoxides, which are cheaper and more durable compared to FR4. The properties of the substrate material determine the flexibility of the PCB board.
2) Copper layer
There is a thin layer of copper foil next to the substrate. Compound copper foil onto the board using heat and adhesive. In a double-sided PCB, both sides of the PCB are laminated with copper. The thickness of copper varies depending on the number of layers of the board, which can be defined in ounces per square foot. There is a thickness of 35 microns per square inch.
3) Solder mask layer
The solder mask layer exists above the copper layer. This layer is applied to the copper layer to insulate it and avoid direct contact with conductive materials. Therefore, we can say that solder resistance protects all circuits on the outer layer of the PCB. Some commonly used solder bumps are green, and there is also a red solder bump on the market.
4) Screen printing layer:
The silkscreen layer exists above the solder mask layer. It can help users add numbers and symbols to understand PCB boards. This screen-printed label provides a clear functional indication of each component and pin on the board. It is mainly used for white, but can also be found in various other colors such as gray, red, yellow, and black.
In summary, the PCB board is made of a substrate, electronic components, printed symbols and text, as well as solder joints. These parts work together to form the overall structure and functionality of the circuit board. In the development process of electronic technology, the design, manufacturing, and application of circuit boards have greatly developed, providing important support for the development of various electronic devices.
2. The FR-4 material offers excellent insulation, mechanical strength, and stability, making it suitable for meeting the requirements of most electronic products.

What are PCB boards made of?
Firstly, the main body of the circuit board is the substrate. A substrate is a flat sheet, usually made of materials such as glass fiber, plastic, or ceramics, covered with copper foil. The main function of copper foil is to provide electrical connections, connecting various electronic components. The shape and position of copper foil are usually determined based on design requirements.
Secondly, the electronic components on the circuit board are another important component of the circuit board. Electronic components are various electronic devices on a circuit board, such as capacitors, resistors, transistors, integrated circuits, and so on. They are connected with copper foil to form a circuit. The selection and arrangement of electronic components are an important part of circuit board design, which determines the performance and functionality of the circuit board.
Thirdly, the printed text and logo on the circuit board are also important components of the circuit board. Printed signs and text are usually used to identify various components and connection methods on a circuit board. These signs and text are usually printed on the circuit board using white ink.
Finally, the solder joints on the circuit board are also an important component of the circuit board. Welding points are the connection points between electronic components and copper foil, which are fixed and connected through welding technology. The quality and reliability of solder joints have a significant impact on the performance and lifespan of circuit boards.
Usually, PCBs are made of non-substrate materials with copper circuit layers. However, different types of PCBs have different structures. For example, although some printed circuit boards contain single-layer copper circuits, more advanced PCBs may contain 50 or more layers.
Printed circuit boards are made of various PCB materials and electronic components. Common PCB components include
1) Resistance
Resistors transmit current to generate voltage and dissipate electrical energy in the form of heat. They come in various materials.
2) Capacitor
The job of a capacitor is to maintain charge within the circuit board and then release it when more power is needed elsewhere in the circuit. The typical working principle of a capacitor is to collect opposite charges on two conductive layers separated by insulating materials.
3) Inductor
They are similar to capacitors because they store energy. However, they are typically used to block signals within a PCB, such as interference from another electronic device.
4) Transistor
A transistor is an amplifier. It is used to switch or control electronic signals in circuit boards. There are several different versions of transistors available, but the most common is bipolar transistors.
5) Diode
Diodes allow current to flow in one direction, but not in another direction. Therefore, diodes are used to prevent current from flowing in the wrong direction, thereby damaging circuit boards and devices. The most popular diode is LED (short for Light Emitting Diode).
6) Sensors
These devices are used to detect changes in environmental conditions and generate corresponding electrical signals. This signal is then sent to other components on the circuit board. Sensors convert physical elements such as light movement, air quality, or sound into electrical energy.
The PCB layers that make up the circuit board
1) Matrix layer
It is the basic layer of PCB, composed of glass fibers. FR4 is the most commonly used glass fiber. Some PCBs also come with phenolic and epoxides, which are cheaper and more durable compared to FR4. The properties of the substrate material determine the flexibility of the PCB board.
2) Copper layer
There is a thin layer of copper foil next to the substrate. Compound copper foil onto the board using heat and adhesive. In a double-sided PCB, both sides of the PCB are laminated with copper. The thickness of copper varies depending on the number of layers of the board, which can be defined in ounces per square foot. There is a thickness of 35 microns per square inch.
3) Solder mask layer
The solder mask layer exists above the copper layer. This layer is applied to the copper layer to insulate it and avoid direct contact with conductive materials. Therefore, we can say that solder resistance protects all circuits on the outer layer of the PCB. Some commonly used solder bumps are green, and there is also a red solder bump on the market.
4) Screen printing layer:
The silkscreen layer exists above the solder mask layer. It can help users add numbers and symbols to understand PCB boards. This screen-printed label provides a clear functional indication of each component and pin on the board. It is mainly used for white, but can also be found in various other colors such as gray, red, yellow, and black.
In summary, the PCB board is made of a substrate, electronic components, printed symbols and text, as well as solder joints. These parts work together to form the overall structure and functionality of the circuit board. In the development process of electronic technology, the design, manufacturing, and application of circuit boards have greatly developed, providing important support for the development of various electronic devices.