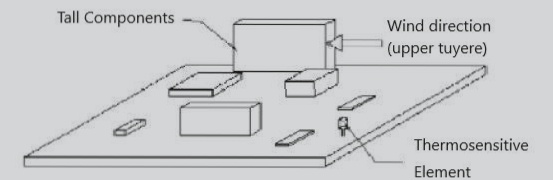
Reliability is a critical issue in PCB board manufacturing. The most effective approach is to design for reliability proactively rather than hoping for good performance retrospectively. Many factors influence reliability, with a significant number related to understanding how materials behave and interact during operation. Thus, studying material properties such as thermal expansion coefficient or transition temperature is essential. Choosing the wrong material can lead to numerous issues, including stress on components and joints.
What are the effective methods for digital image correlation in PCB manufacturing?
A valuable tool for enhancing the reliability process is Digital Image Correlation (DIC). This technology actively measures properties and provides reliable values. Whether for material selection, testing, monitoring, or simulation, you can rely on DIC to minimize errors. DIC is an optical method used to measure displacement and deformation. It involves applying a pattern of contrasting spots to a sample, which is then tracked to observe deformation. One advantage of DIC is that it does not require contact with the sample and can produce full-field displacement measurements, which are not possible with other methods. While a single camera can complete DIC, multiple cameras are needed for out-of-plane measurements. This technique is versatile and can be applied to various sample sizes.

Could you specify what aspects you’d like refined or any particular focus areas for this article?
What are the effective methods for digital image correlation in PCB manufacturing?
A valuable tool for enhancing the reliability process is Digital Image Correlation (DIC). This technology actively measures properties and provides reliable values. Whether for material selection, testing, monitoring, or simulation, you can rely on DIC to minimize errors. DIC is an optical method used to measure displacement and deformation. It involves applying a pattern of contrasting spots to a sample, which is then tracked to observe deformation. One advantage of DIC is that it does not require contact with the sample and can produce full-field displacement measurements, which are not possible with other methods. While a single camera can complete DIC, multiple cameras are needed for out-of-plane measurements. This technique is versatile and can be applied to various sample sizes.

Could you specify what aspects you’d like refined or any particular focus areas for this article?