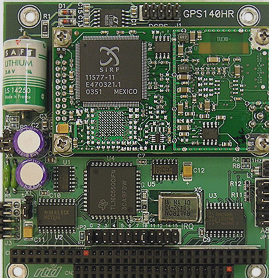
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) vs. Through-Hole Technology in PCB Assembly
- Most SMT chip components are reflow soldered, while through-hole components are wave soldered, though exceptions exist.
- In through-hole PCB assembly, components are manually inserted and wave soldered to form strong joints.
- For SMT components, solder paste is applied to pads, holding component leads in place.
- Reflow ovens are used in SMT assembly to create solid solder joints.
- Hybrid PCBs may require both wave and reflow soldering methods.
- Automatic pick-and-place machines are available for component handling.
The Advantages of SMT and Through-Hole Technologies
- SMT Benefits:
- 1. Size: SMT components are small, eliminating the need for drilling and providing a clean look suitable for compact electronics.
- 2. Availability: SMT components are increasingly replacing through-hole parts in PCBA assembly.
- 3. Performance: SMD integration in SMT allows for shorter signal paths, reducing signal flight time.
- 4. Cost-effectiveness: SMT parts are often more affordable compared to through-hole components.
- Through-Hole Advantages:
- 1. Availability: Larger through-hole components are easier to source for high-power applications.
- 2. Strength: Through-hole solder joints offer robustness, ideal for connectors and switches under pressure.
- 3. Power: Through-hole technology provides better mechanical strength for high-power circuits.