Environmental Challenges and Solutions for PCB Factories
Currently, the country’s focus on environmental protection and link governance poses challenges and opportunities for PCB factories. By prioritizing environmental concerns, FPC flexible circuit board products can lead the market and drive further development in the industry.
Addressing Environmental Challenges
- Innovation in Energy Conservation: PCB manufacturers should integrate Internet technology for automated monitoring and intelligent management in production processes to reduce energy consumption and emissions.
- Environmental Protection Informatization: Leveraging big data for monitoring pollution discharge and adopting eco-friendly technologies can help PCB factories identify and resolve environmental issues promptly.
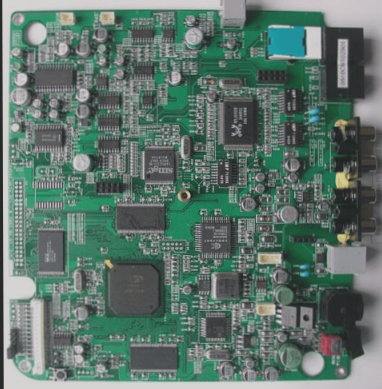
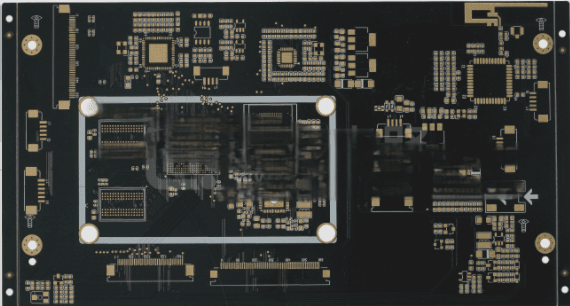
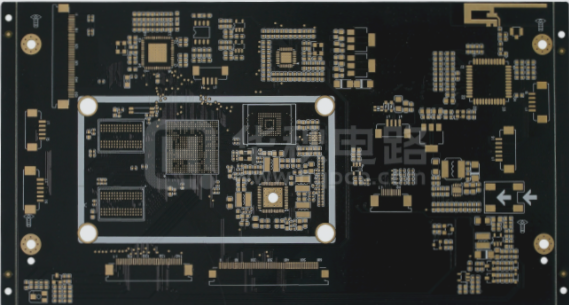
Quality Control in PCBA Patch Processing
Quality control is crucial at every stage of PCBA patch processing to ensure the final product meets high standards.
Stages of PCBA Patch Processing
- PCB Circuit Board Analysis: Analyzing the Gerber file and considering factors like hole spacing, signal interference, and impedance.
- Component Procurement: Ensuring quality through reliable channels and rigorous inspections of incoming materials.
- SMT Assembly Processing: Managing solder paste printing, reflow oven temperature, and conducting AOI testing to minimize defects.
- Plug-in Processing: Designing molds for wave soldering to produce quality products.
- Program Burning: Burning customer-provided programs into the main control IC for functional testing.
- PCBA Board Testing: Conducting ICT, FCT, aging tests, and other assessments to ensure product quality.
By following these steps and staying abreast of environmental advancements, PCB factories can navigate challenges and contribute to a greener, more efficient industry.