1. The process of transforming circuit boards from basic light boards to displaying intricate circuit graphics is quite complex.
2. Currently, the typical circuit board processing method employs the “graphic electroplating technique.”
3. This involves applying a lead-tin corrosion-resistant layer onto the copper foil areas that need to be preserved on the outer layer of the circuit board, specifically the circuit’s graphic elements.
4. Afterward, the remaining copper foil is chemically etched away.

The etching method involves removing copper foil outside the conductive circuit using an etching solution, while the carving method uses a carving machine for the same purpose. The former is a chemical process, more commonly used, whereas the latter is a physical process. Circuit board etching is a chemical process that employs concentrated sulfuric acid to corrode unwanted copper-clad circuit boards. In contrast, the carving method relies on physical techniques, utilizing specialized carving machines and cutting heads to carve copper-clad panels and create circuit wiring.
Factors Affecting Circuit Board Etching
1. Types of Etching Solution
Different etching solutions have varying chemical compositions, leading to different etching rates and coefficients. For instance, the etching coefficient of acidic copper chloride solutions is typically around 3, whereas alkaline copper chloride solutions can have an etching coefficient as high as 4. Recent studies indicate that nitric acid-based etching systems can achieve minimal side etching, with etched lines and sidewalls nearly perpendicular.
2. Etching Method
Soaking and bubbling etching can result in significant side corrosion, while splashing and spray etching produce less side corrosion, with spray etching being the most effective.
3. Density of Etching Solution
If the density of the alkaline etching solution is too low, side corrosion may increase. Choosing an etching solution with a higher copper concentration helps reduce side corrosion.
4. Etching Rate
A slow etching rate can exacerbate lateral corrosion. Enhancing etching quality is closely related to increasing the etching rate. Faster etching speeds reduce the board’s exposure time to the etching solution, resulting in less lateral etching and clearer, neater etched patterns.
5. pH Value of Etching Solution
A high pH value in an alkaline etching solution can lead to increased side corrosion. To minimize side corrosion, the pH value should generally be kept below 8.5.
6. Copper Foil Thickness
For etching thin wires with minimal lateral corrosion, using ultra-thin copper foil is ideal. Thinner line widths require thinner copper foil to minimize side etching, as the reduced thickness shortens the time the foil spends in the etching solution.
Circuit board etching allows for the identification of wires and component installation positions on the circuit board by removing unnecessary copper sheets and forming the actual circuit.
2. Currently, the typical circuit board processing method employs the “graphic electroplating technique.”
3. This involves applying a lead-tin corrosion-resistant layer onto the copper foil areas that need to be preserved on the outer layer of the circuit board, specifically the circuit’s graphic elements.
4. Afterward, the remaining copper foil is chemically etched away.
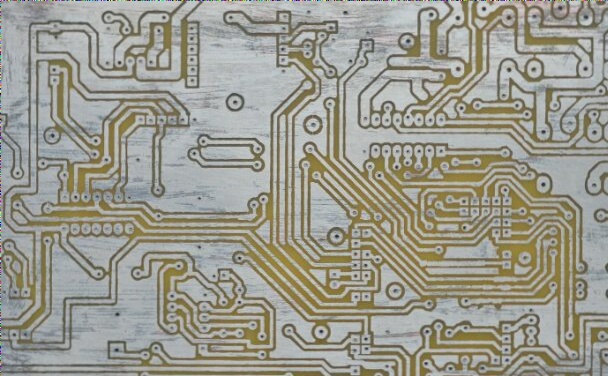
The etching method involves removing copper foil outside the conductive circuit using an etching solution, while the carving method uses a carving machine for the same purpose. The former is a chemical process, more commonly used, whereas the latter is a physical process. Circuit board etching is a chemical process that employs concentrated sulfuric acid to corrode unwanted copper-clad circuit boards. In contrast, the carving method relies on physical techniques, utilizing specialized carving machines and cutting heads to carve copper-clad panels and create circuit wiring.
Factors Affecting Circuit Board Etching
1. Types of Etching Solution
Different etching solutions have varying chemical compositions, leading to different etching rates and coefficients. For instance, the etching coefficient of acidic copper chloride solutions is typically around 3, whereas alkaline copper chloride solutions can have an etching coefficient as high as 4. Recent studies indicate that nitric acid-based etching systems can achieve minimal side etching, with etched lines and sidewalls nearly perpendicular.
2. Etching Method
Soaking and bubbling etching can result in significant side corrosion, while splashing and spray etching produce less side corrosion, with spray etching being the most effective.
3. Density of Etching Solution
If the density of the alkaline etching solution is too low, side corrosion may increase. Choosing an etching solution with a higher copper concentration helps reduce side corrosion.
4. Etching Rate
A slow etching rate can exacerbate lateral corrosion. Enhancing etching quality is closely related to increasing the etching rate. Faster etching speeds reduce the board’s exposure time to the etching solution, resulting in less lateral etching and clearer, neater etched patterns.
5. pH Value of Etching Solution
A high pH value in an alkaline etching solution can lead to increased side corrosion. To minimize side corrosion, the pH value should generally be kept below 8.5.
6. Copper Foil Thickness
For etching thin wires with minimal lateral corrosion, using ultra-thin copper foil is ideal. Thinner line widths require thinner copper foil to minimize side etching, as the reduced thickness shortens the time the foil spends in the etching solution.
Circuit board etching allows for the identification of wires and component installation positions on the circuit board by removing unnecessary copper sheets and forming the actual circuit.