Melt Deposition Modeling (FDM) in Additive Manufacturing
Melt Deposition Modeling (FDM), also known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), is a popular additive manufacturing process falling under material extrusion. In FDM, objects are built layer by layer using melted thermoplastic material. This technique utilizes a filament of thermoplastic polymer to create a wide range of products across industries like household appliances, electronics, automotive, healthcare, and more.
Working Principle of FDM
- A spool of thermoplastic filament is loaded into the 3D printer.
- The filament is melted in the extrusion head after reaching the required temperature.
- The melted material is extruded in fine threads and deposited layer by layer.
- Each layer is cooled and solidified to form the final object.
Key Features of FDM Printing
1. Warping
Warping is a common challenge in FDM due to material shrinkage during cooling. Maintaining consistent temperature and improving adhesion can help reduce warping. Avoiding large flat surfaces and using sacrificial material around delicate features can also mitigate warping issues.
2. Support Structures
Support structures are essential for printing overhangs or complex geometries. Designing parts that require minimal support can enhance surface quality and reduce post-processing work.
3. Fill Density and Shell Thickness
FDM prints often have low-density infill and solid outer layers. Adjusting fill density and shell thickness can impact the strength and durability of the printed object.
Advantages and Limitations of FDM
Advantages
- Cost-effective for customized parts and prototypes.
- Rapid turnaround times for quick prototyping and iteration.
- Supports a wide range of thermoplastic materials for various applications.
Limitations
- Lower dimensional accuracy and resolution compared to other 3D printing technologies.
Key Points about FDM 3D Printing
- FDM parts often show visible layering, requiring post-processing like sanding for a smooth finish.
- Layer-by-layer construction in FDM can lead to anisotropic properties, impacting mechanical strength based on layer direction.
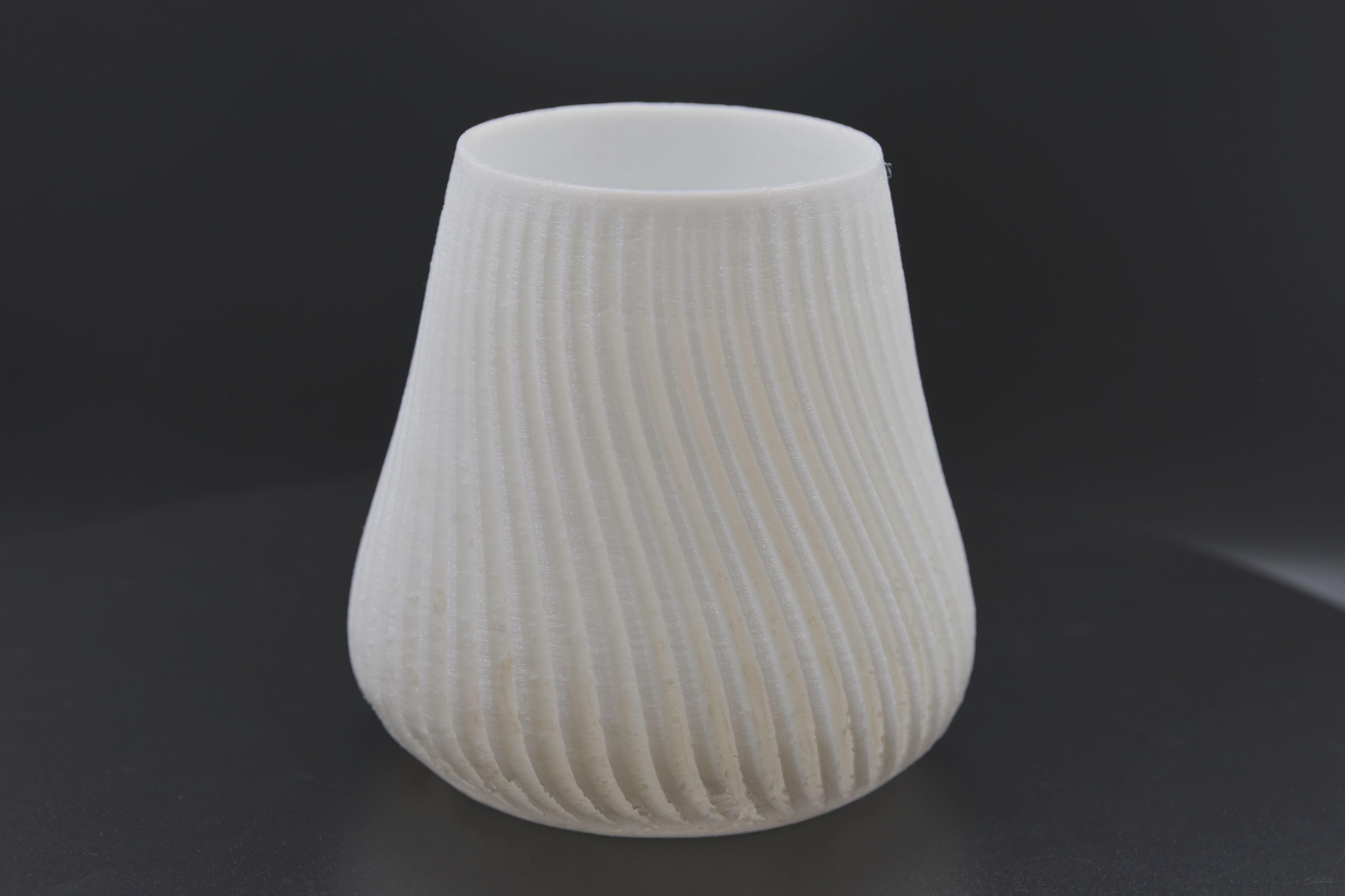
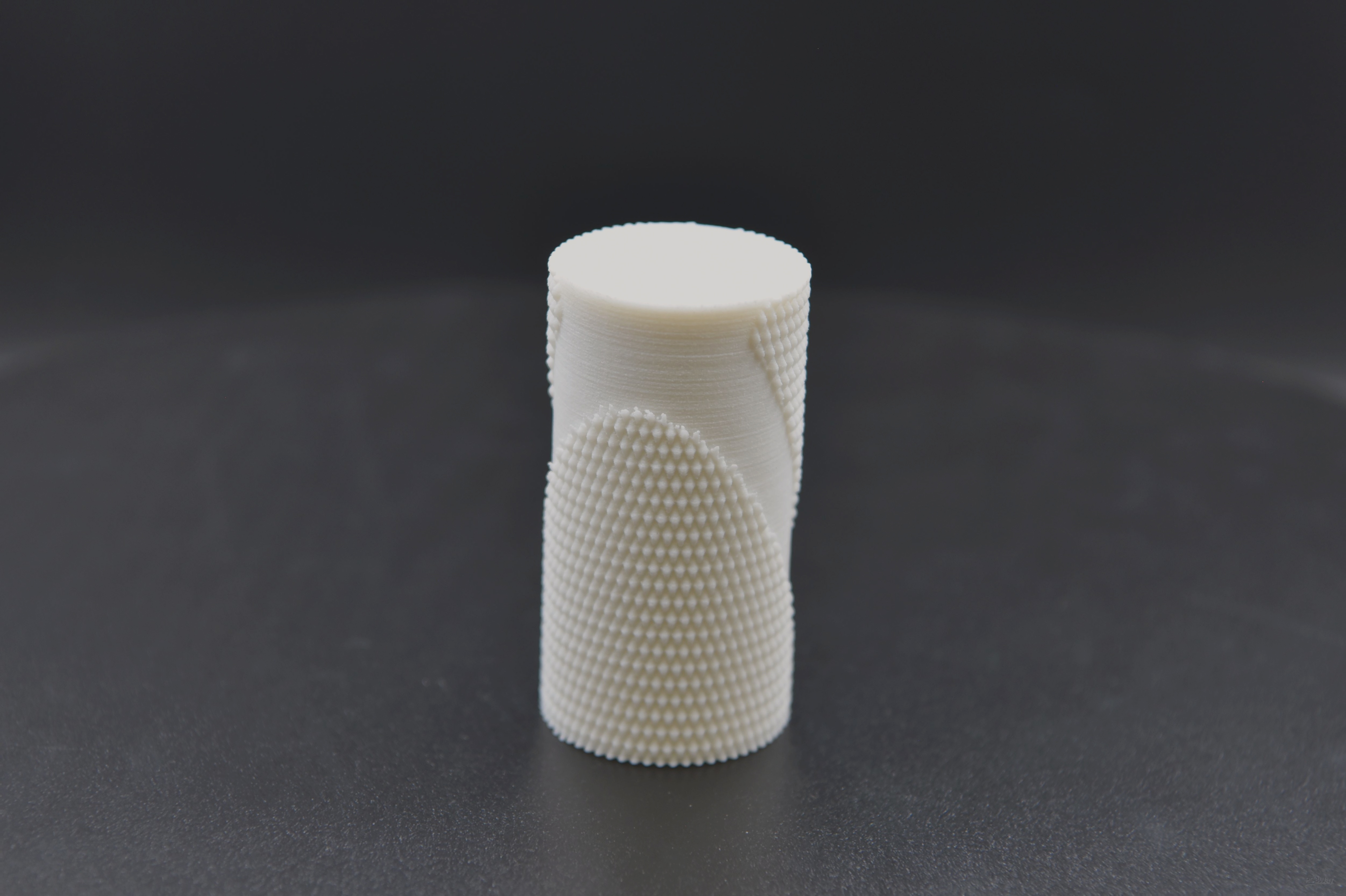
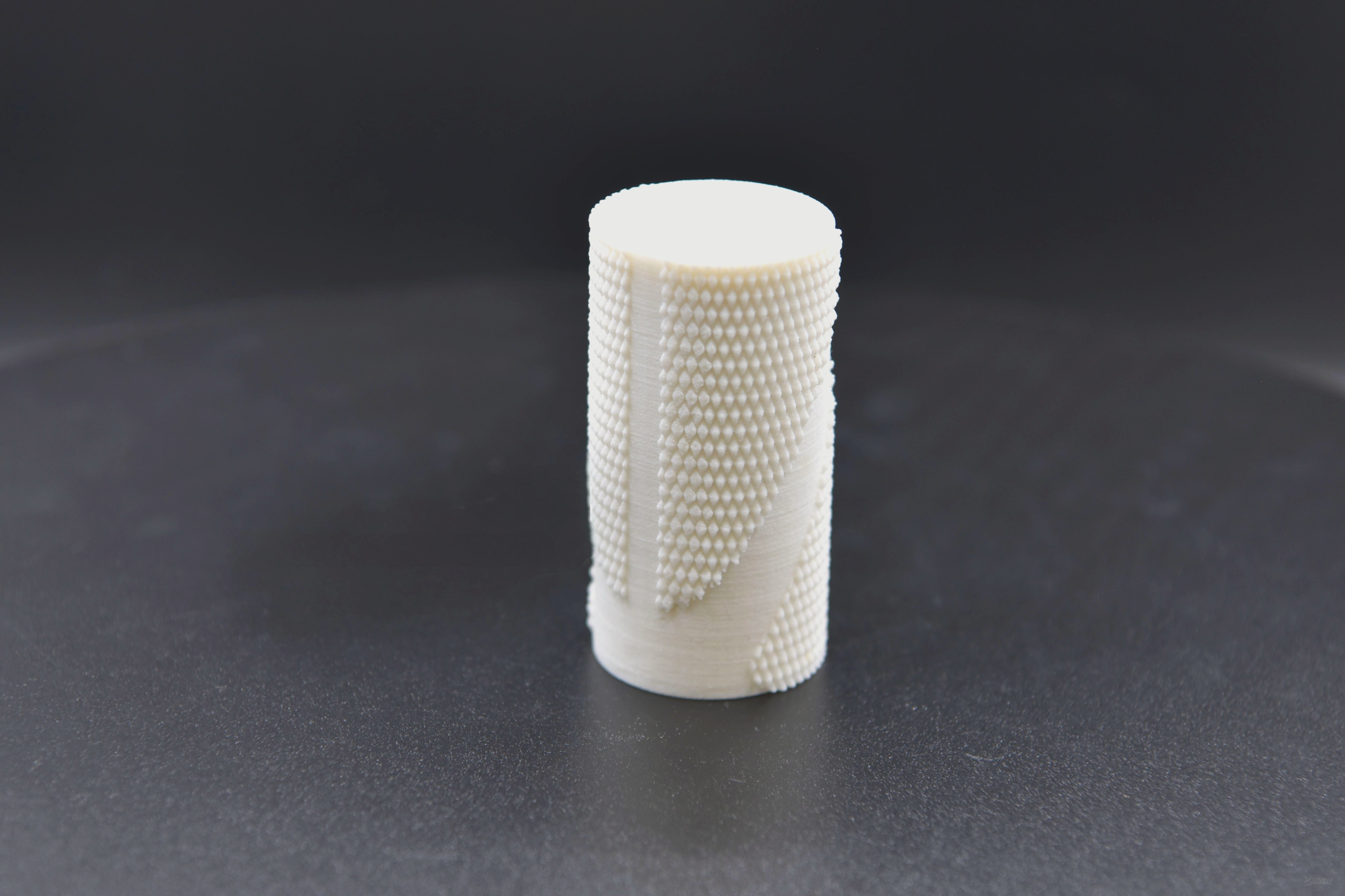
Check Out Our FDM Printed Products:



If you have any inquiries regarding PCBs or PCBA, don’t hesitate to reach out to us at info@wellcircuits.com.