Overview of Flexible Printed Circuits (FPCs):
Widespread Applications:
- Flexible printed circuits are commonly found in cars, VCRs, smart devices, SLR cameras, and advanced military and avionics systems.
Notable Application Example:
- In 1997, flexible-circuit technology was utilized in the rigid-flex wire harness on the Mars rover Sojourner.
Definition Challenges:
- There is an ongoing debate on what defines a flexible circuit, often confused with a bendy printed circuit.
Basic Materials for FPC Construction:
Part 1: Insulating Substrate:
- Flexible dielectric films like polyimide (PI), polyester (PET), and polytetrafluoroethylene are commonly used.
- Film thickness typically ranges from 0.0127-0.127mm (0.5-5mil).
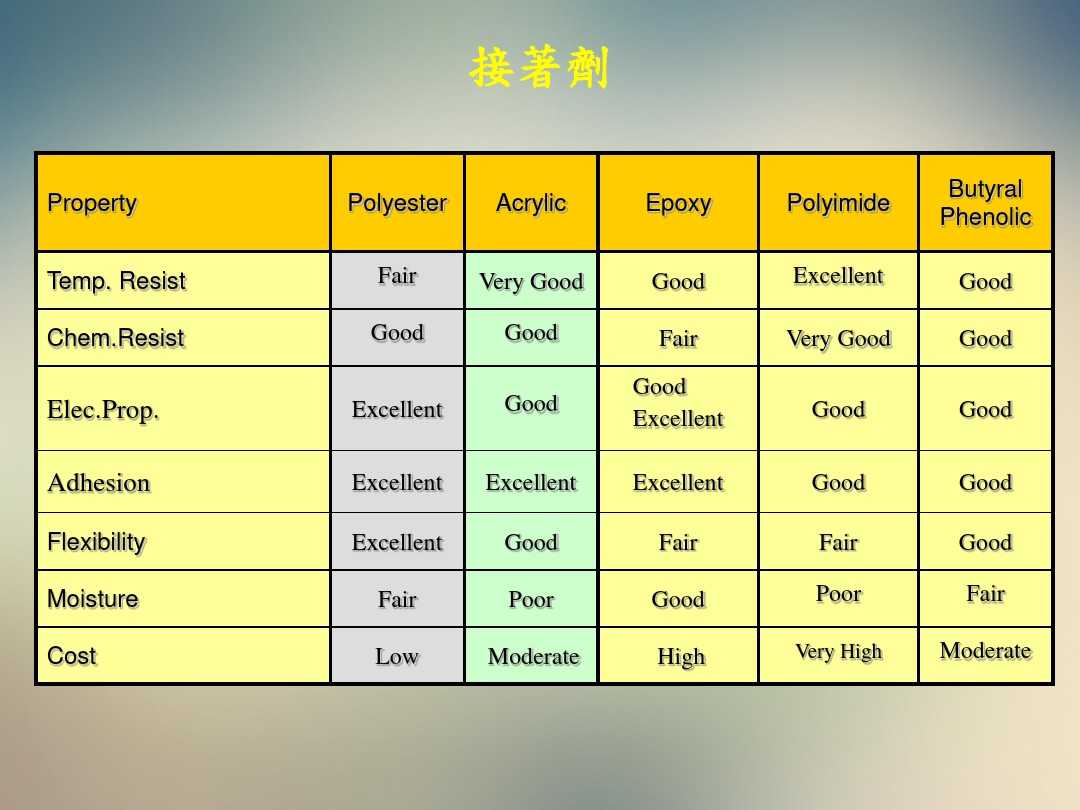
Part 2: Adhesive:
- Adhesive sheets are used to bond the film to metal foil or other films.
- Various types of adhesive, such as epoxy and acrylic, are used for different film substrates.
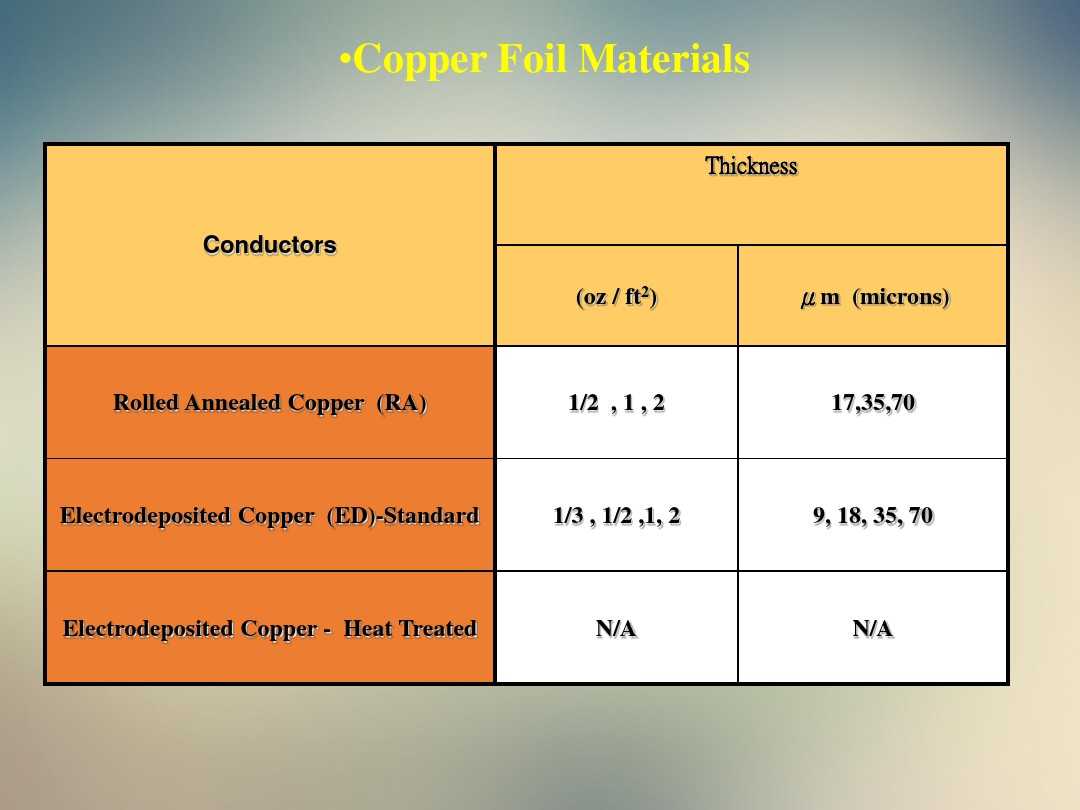
Part 3: Copper Foil:
- A conductive layer covers the insulating substrate, forming conductive lines through selective etching.
- Rolled and electrolytic copper foils with different thicknesses are employed.
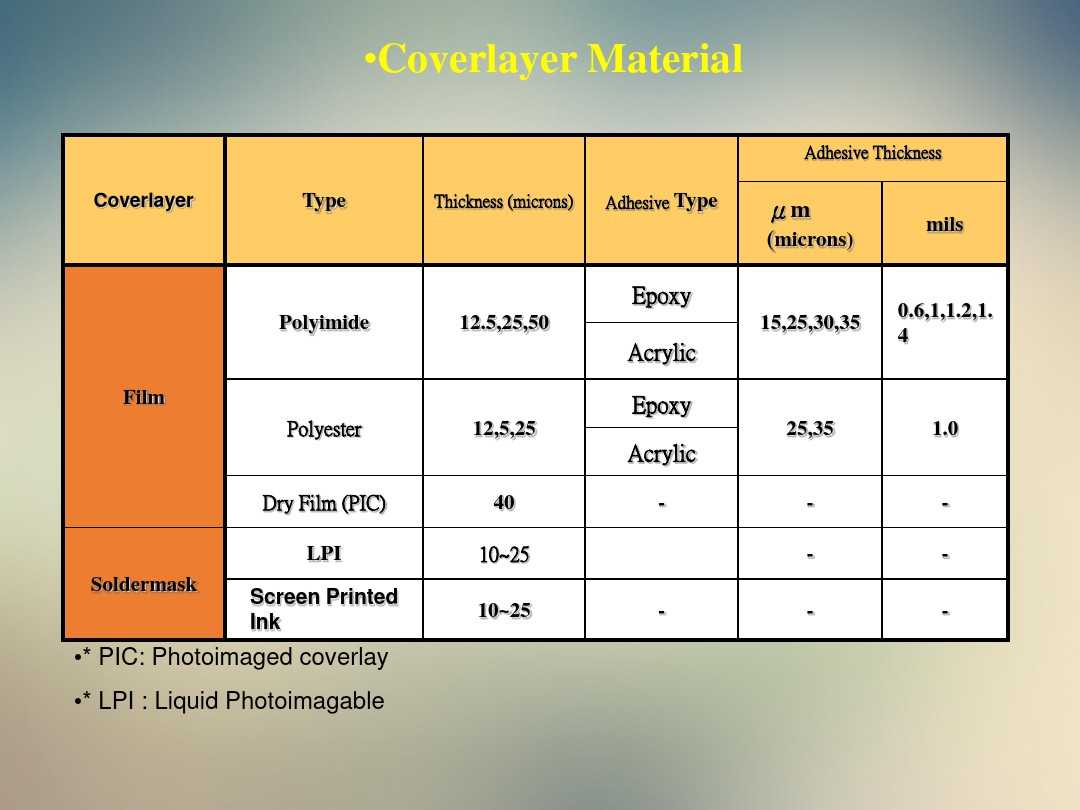
Part 4: Cover Layer:
- An insulating protective layer that enhances substrate strength.
- Types include dry film and photosensitive development for finer assembly.
Part 5: Stiffener:
- A reinforcement board that supports and strengthens the flexible film substrate.
- Materials used for stiffeners include polyester, polyimide, epoxy glass fiber cloth, phenolic paper, steel, and aluminum.
Company Highlight:
Wellcircuits:
- A high-quality flexible circuit board manufacturer based in China.
- Offers quick-turn prototyping services for various types of FPCs.
Note:
- Understanding the diverse materials used in FPC construction is crucial for optimal design and manufacturing. Contact WellCircuits for flexible PCB fabrication services.
Revolutionizing PCB Manufacturing with Cutting-Edge Materials
In the realm of PCB manufacturing, the choice of materials plays a pivotal role in determining the performance and reliability of electronic devices. Let’s delve into some of the latest advancements in materials that are reshaping the industry landscape:
1. FPC Copper Foil
One of the key components in flexible printed circuits (FPCs) is the copper foil, which serves as the conductive layer. The latest FPC copper foils offer enhanced conductivity and flexibility, allowing for the creation of intricate and compact circuit designs. Check out the image below to see this material in action:
2. Advanced Adhesive Materials
Adhesive materials are essential for bonding different layers of a PCB together. The newest adhesive formulations provide superior bonding strength, thermal stability, and moisture resistance, ensuring the longevity of the circuit board. Take a look at the image showcasing the cutting-edge adhesive material:
3. Innovative Coverlay Materials
Coverlay materials are used to protect the circuit traces on a PCB from environmental factors and mechanical damage. The latest coverlay materials offer exceptional dielectric properties, flexibility, and durability, safeguarding the integrity of the circuitry. Explore the image below to see the impact of these advanced materials: