Processing Technology and Application of FPC Flexible Boards
Introduction to FPC Flexible Boards
FPC flexible boards, also known as soft boards, are insulating substrates made from materials like polyimide or polyester film. They offer high reliability and excellent performance for electronic engineers’ design work.
Features of FPC Flexible Boards
- High wiring density
- Lightweight and thin
- Excellent bendability
Flexible circuit boards are the ultimate solution for miniaturization and mobility requirements in electronic products. They can be bent, wound, and folded freely, withstanding dynamic bends without damage. These boards significantly reduce the volume and weight of electronic products, ideal for high-density and reliable devices.

Types of FPC Flexible Boards
- Single-sided FPC
- Double-sided FPC
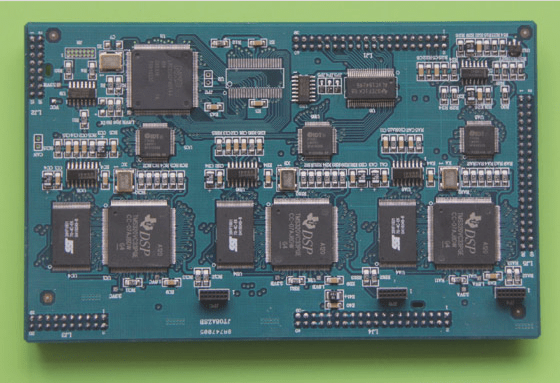
- Multi-layer FPC
Application Industry of FPC Flexible Boards
FPCs are widely used in aerospace, military, mobile communications, laptops, digital cameras, and more. They are common in computer hard disk drives and have substantial market potential in portable devices like mobile phones.
The Thermal and Mechanical Performance of Flexible Circuit Boards
Overview of Flexible Circuit Boards (FPCs)
FPCs, made from flexible copper clad laminate (FCCL), offer high reliability and flexibility. They are essential in electronic products like mobile phones, tablets, and laptops for manufacturing antennas and transmission lines.
Flexible Copper Clad Laminate (FCCL)
FCCL is created by bonding copper foil to flexible insulating materials like polyester or polyimide film. The insulating substrate, such as polyimide film, and copper foil conductor determine the board’s physical and electrical properties.
Performance Characterization of Insulating Substrates
Insulating substrates must meet high-frequency, high-speed transmission, and miniaturization needs. Materials like Modified PI and LCP cater to 5G network communication requirements, offering low dielectric constant, heat dissipation, and reliability.
Testing and Characterization
Accurate testing of thermal and mechanical parameters is crucial for determining use temperature, stability, moisture absorption, impact resistance, and heat dissipation. Characterizing properties of materials like polyimide and LCP is essential for practical applications.