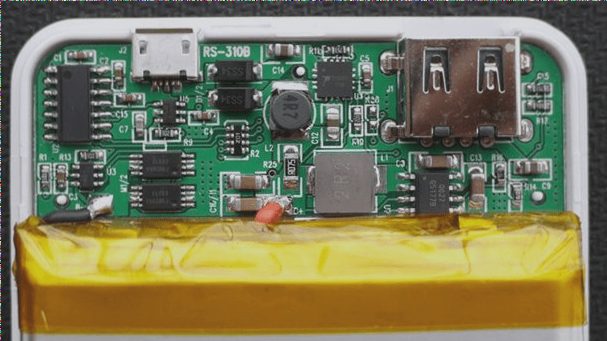
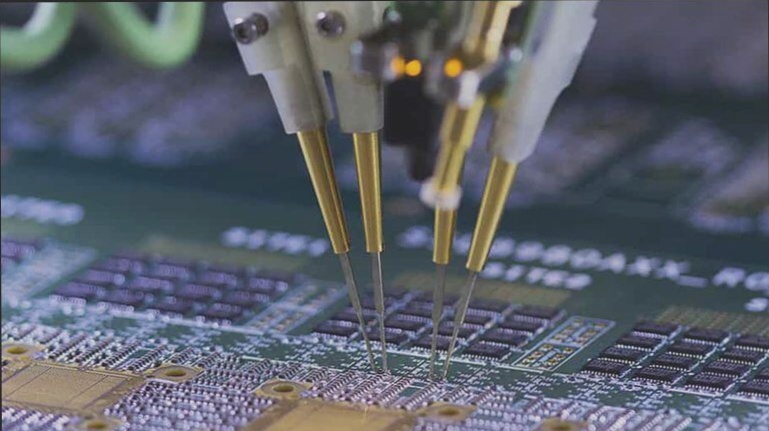
Processing materials are crucial for ensuring the quality and efficiency of SMT patch processing. When designing SMT patches and establishing production lines, selecting appropriate process materials according to the process flow and requirements is essential. These materials encompass solder, solder paste, adhesives, and other welding and patch materials, along with flux, cleaning agents, heat conversion media, and other process materials.
1. Solder and Solder Paste
Solder serves as a fundamental structural material in SMT chip processes. Different solder types are employed for various applications, facilitating the connection of metal surfaces of welded objects to form solder joints. Reflow soldering utilizes solder paste, a material that not only solders but also leverages its viscosity to pre-fix the SMC/SMD.
2. Flux
Flux stands out as a pivotal process material in chip processing, exerting significant influence on welding quality. It is indispensable across various welding processes, primarily functioning to assist in welding.
3. Adhesive
Adhesive serves as the bonding agent in SMT patches. In wave soldering processes, adhesive typically secures components onto the PCB beforehand. Even in cases of using reflow soldering for assembling SMD on both sides of the PCB, adhesive is frequently applied to the center of the PCB land pattern to reinforce SMD fixation, preventing shifts or falls during assembly operations.
4. Cleaning Agent
The cleaning agent plays a critical role in removing residues left on the board after the soldering process in SMT patching. Cleaning remains an integral part of the placement process under current technical conditions, with solvent cleaning emerging as the most effective method. SMT processing materials serve as the foundation of the placement process, with corresponding assembly process materials selected based on distinct assembly processes and procedures. At times, within the same assembly process, material usage may vary due to subsequent processes or assembly methods.
1. Solder and Solder Paste
Solder serves as a fundamental structural material in SMT chip processes. Different solder types are employed for various applications, facilitating the connection of metal surfaces of welded objects to form solder joints. Reflow soldering utilizes solder paste, a material that not only solders but also leverages its viscosity to pre-fix the SMC/SMD.
2. Flux
Flux stands out as a pivotal process material in chip processing, exerting significant influence on welding quality. It is indispensable across various welding processes, primarily functioning to assist in welding.
3. Adhesive
Adhesive serves as the bonding agent in SMT patches. In wave soldering processes, adhesive typically secures components onto the PCB beforehand. Even in cases of using reflow soldering for assembling SMD on both sides of the PCB, adhesive is frequently applied to the center of the PCB land pattern to reinforce SMD fixation, preventing shifts or falls during assembly operations.
4. Cleaning Agent
The cleaning agent plays a critical role in removing residues left on the board after the soldering process in SMT patching. Cleaning remains an integral part of the placement process under current technical conditions, with solvent cleaning emerging as the most effective method. SMT processing materials serve as the foundation of the placement process, with corresponding assembly process materials selected based on distinct assembly processes and procedures. At times, within the same assembly process, material usage may vary due to subsequent processes or assembly methods.