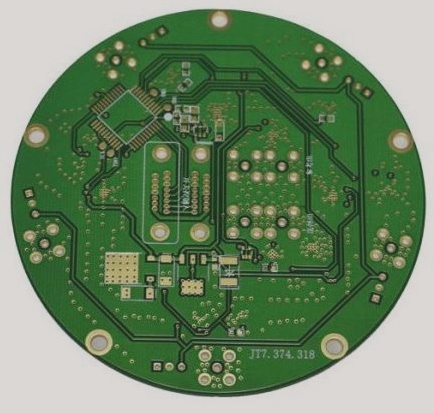
Many people believe that PCB design work is tedious. Each day involves routing thousands of wires on the board, various packages, and repeated wire pulling tasks. However, designers must make trade-offs between different design rules, taking into account performance, cost, craftsmanship, and other factors. They must also focus on creating a tidy and logical board layout. It is a task that requires more wisdom than it appears.
Let’s discuss how to develop good working habits when designing PCBs, which will result in more reasonable designs, easier production, and better performance.
(1) Create the Schematic Diagram
Many engineers prioritize layout work over creating a schematic diagram. However, the schematic diagram plays a crucial role in the subsequent circuit debugging process. It helps in identifying issues, communicating with colleagues, and providing a visual aid. Developing the habit of labeling the schematic diagram and marking areas that require attention during layout is beneficial for self-reminders and for others. Use a hierarchical schematic diagram to divide the circuit into different pages based on functionality and modules. This reduces workload and facilitates circuit reading or reuse in the future. Utilizing a proven design is less risky than creating a new circuit. Seeing all circuits densely packed on a drawing can be overwhelming.
(2) Set Rules
It is essential to set wiring rules in advanced PCB design software as well as in simple and user-friendly PCB tools. Humans are prone to errors, so setting rules to address common mistakes can prevent them. Proper rule setting enhances workflow regulation. As the complexity of the board increases, rule setting becomes more critical. Many EDA tools offer automatic wiring functions. Detailed rule settings allow the tools to design for you, leaving you time to enjoy a cup of coffee.
(3) Properly Arrange the Circuit Layout
Impatient engineers may rush to place components and start routing wires after importing the netlist into the PCB. However, a well-planned PCB layout makes wire routing easier and improves PCB performance. Follow the signal path when arranging the layout to ensure smooth signal transmission. Divide the board into different areas based on functional modules. Separate analog and digital components, power supply signals, heating devices, and susceptible devices. Avoid placing large components near the board’s edge and consider shielding radio frequency signals. Spending extra time optimizing the layout can save time during wire routing.
Let’s discuss how to develop good working habits when designing PCBs, which will result in more reasonable designs, easier production, and better performance.
(1) Create the Schematic Diagram
Many engineers prioritize layout work over creating a schematic diagram. However, the schematic diagram plays a crucial role in the subsequent circuit debugging process. It helps in identifying issues, communicating with colleagues, and providing a visual aid. Developing the habit of labeling the schematic diagram and marking areas that require attention during layout is beneficial for self-reminders and for others. Use a hierarchical schematic diagram to divide the circuit into different pages based on functionality and modules. This reduces workload and facilitates circuit reading or reuse in the future. Utilizing a proven design is less risky than creating a new circuit. Seeing all circuits densely packed on a drawing can be overwhelming.
(2) Set Rules
It is essential to set wiring rules in advanced PCB design software as well as in simple and user-friendly PCB tools. Humans are prone to errors, so setting rules to address common mistakes can prevent them. Proper rule setting enhances workflow regulation. As the complexity of the board increases, rule setting becomes more critical. Many EDA tools offer automatic wiring functions. Detailed rule settings allow the tools to design for you, leaving you time to enjoy a cup of coffee.
(3) Properly Arrange the Circuit Layout
Impatient engineers may rush to place components and start routing wires after importing the netlist into the PCB. However, a well-planned PCB layout makes wire routing easier and improves PCB performance. Follow the signal path when arranging the layout to ensure smooth signal transmission. Divide the board into different areas based on functional modules. Separate analog and digital components, power supply signals, heating devices, and susceptible devices. Avoid placing large components near the board’s edge and consider shielding radio frequency signals. Spending extra time optimizing the layout can save time during wire routing.