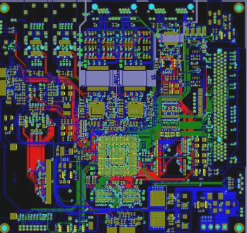
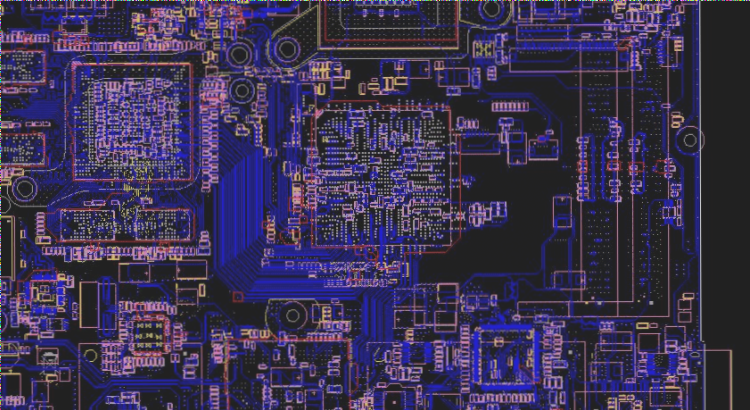
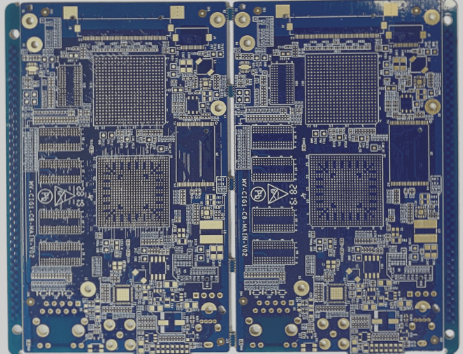
PCB Layout Rules
1. Under normal circumstances, all components should be arranged on the same surface of the printed circuit board. Only if the top layer is too dense, should some highly constrained and small heat-sensitive devices, such as chip resistors, chip capacitors, or chip ICs, be placed on the bottom layer.
2. To ensure electrical performance, components should be placed on a grid and arranged either parallel or perpendicular to each other for a neat and organized appearance. Overlapping components are generally not allowed. The arrangement of components should be compact, with components evenly distributed and uniform in density throughout the layout.
3. The spacing between adjacent pads of different components on the circuit board should be at least 1 mm.

4. Generally, the distance from the edge of the circuit board should not be less than 2 mm. The optimal shape for the circuit board is rectangular, with a length-to-width ratio of 3:2 or 4:3. For circuit boards larger than 200 mm by 150 mm, the mechanical strength must be considered.
PCB Design and Setup Skills
PCB design requires different point settings at various stages. During the layout stage, large grid points are used for device placement. For large components like ICs and non-positioning connectors, grid points of 50–100 mils are suitable, while for smaller passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, grid points of 25 mils are preferable. Larger grid points aid in device alignment and layout aesthetics.
PCB Design Layout Skills
In PCB layout design, analyze the unit of the circuit board and design the layout according to its function. When laying out all circuit components, follow these principles:
a. Position each functional circuit unit according to the circuit process to facilitate signal flow, and keep signals aligned in the same direction whenever possible.
b. Center the layout around each functional unit. Components should be arranged uniformly, integrally, and compactly on the PCB to minimize and shorten leads and connections between components.
c. For high-frequency circuits, consider distribution parameters between components. Arrange circuit components in parallel where possible to enhance aesthetics, ease installation, and facilitate mass production.
When designing PCB wiring, consider the following:
(1) Keep wire lengths as short as possible to minimize lead inductance. In low-frequency circuits, avoid multipoint grounding as all ground currents should flow through a common grounding impedance or plane. Place the public ground wire as close to the PCB edge as possible and use copper foil extensively as ground wire to enhance shielding.
(3) For double-layer boards, use a ground plane to provide low impedance grounding. In multilayer printed circuit boards, configure ground planes as a network. Ensure that ground grid spacing is not too large, as ground grids provide a signal backflow path. Large spacing can create large signal loop areas, leading to radiation and sensitivity issues. Small loop areas improve signal backflow and reduce radiation.
1. Under normal circumstances, all components should be arranged on the same surface of the printed circuit board. Only if the top layer is too dense, should some highly constrained and small heat-sensitive devices, such as chip resistors, chip capacitors, or chip ICs, be placed on the bottom layer.
2. To ensure electrical performance, components should be placed on a grid and arranged either parallel or perpendicular to each other for a neat and organized appearance. Overlapping components are generally not allowed. The arrangement of components should be compact, with components evenly distributed and uniform in density throughout the layout.
3. The spacing between adjacent pads of different components on the circuit board should be at least 1 mm.

4. Generally, the distance from the edge of the circuit board should not be less than 2 mm. The optimal shape for the circuit board is rectangular, with a length-to-width ratio of 3:2 or 4:3. For circuit boards larger than 200 mm by 150 mm, the mechanical strength must be considered.
PCB Design and Setup Skills
PCB design requires different point settings at various stages. During the layout stage, large grid points are used for device placement. For large components like ICs and non-positioning connectors, grid points of 50–100 mils are suitable, while for smaller passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, grid points of 25 mils are preferable. Larger grid points aid in device alignment and layout aesthetics.
PCB Design Layout Skills
In PCB layout design, analyze the unit of the circuit board and design the layout according to its function. When laying out all circuit components, follow these principles:
a. Position each functional circuit unit according to the circuit process to facilitate signal flow, and keep signals aligned in the same direction whenever possible.
b. Center the layout around each functional unit. Components should be arranged uniformly, integrally, and compactly on the PCB to minimize and shorten leads and connections between components.
c. For high-frequency circuits, consider distribution parameters between components. Arrange circuit components in parallel where possible to enhance aesthetics, ease installation, and facilitate mass production.
When designing PCB wiring, consider the following:
(1) Keep wire lengths as short as possible to minimize lead inductance. In low-frequency circuits, avoid multipoint grounding as all ground currents should flow through a common grounding impedance or plane. Place the public ground wire as close to the PCB edge as possible and use copper foil extensively as ground wire to enhance shielding.
(3) For double-layer boards, use a ground plane to provide low impedance grounding. In multilayer printed circuit boards, configure ground planes as a network. Ensure that ground grid spacing is not too large, as ground grids provide a signal backflow path. Large spacing can create large signal loop areas, leading to radiation and sensitivity issues. Small loop areas improve signal backflow and reduce radiation.