PCB Assembly and Soldering Processes
After the production of printed circuit boards, various electronic components need to be assembled onto the PCB. In order to connect these components to the circuits, soldering processes are essential.
Types of Soldering Methods
- Wave Soldering: Pin type components are typically soldered using this method.
- Reflow Soldering: Surface mount components are commonly soldered using reflow technology.
- Manual Soldering: Individual components, installation processes, and maintenance welding are manually soldered with an electric soldering iron.
Solder Resistance of Copper Clad Laminates
During soldering, copper clad laminates (CCL) are subjected to high temperatures, testing their heat resistance. To enhance CCL reliability, additional performance measurement tests have been introduced in recent years.
These tests include the hygroscopic heat resistance test and the hygroscopic reflow soldering test. Manufacturers should conduct strict dip solder resistance tests before mass-producing PCBs for final assembly.
It is important to follow national standards and industry guidelines for determining the dip solder resistance of CCLs. The accuracy of temperature measurement during testing significantly impacts the evaluation of a board’s dip solder resistance level.
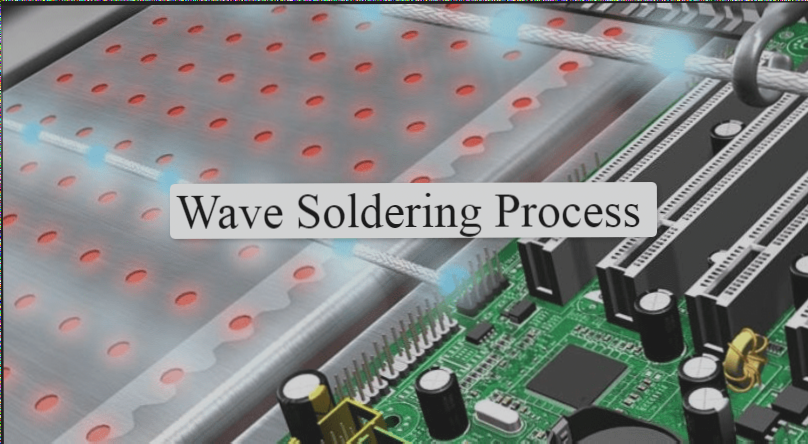
Wave Soldering Process
In wave soldering, maintaining a soldering temperature below 250°C is crucial for ensuring soldering quality. Temperature control is essential to prevent issues like blistering, delamination, or warping of the circuit.
Reflow Soldering
Reflow soldering temperatures are slightly lower than those used in wave soldering. The setting of reflow soldering temperature depends on various factors such as equipment type, line speed, substrate material, and PCB size.
Reflow Soldering and Manual Welding in PCB Manufacturing
During the process of reflow soldering in PCB manufacturing, the temperature limit for the substrate surface where copper foil bulges (blistering) occurs can vary based on the preheating temperature and moisture absorption of the PCB. A lower preheating temperature leads to a lower heat resistance limit for bulging on the substrate surface. Additionally, if the reflow soldering temperature setting and preheating temperature remain constant, moisture absorption by the substrate can result in a decrease in surface temperature.
Reflow Soldering
- Preheating temperature impacts heat resistance limit
- Moisture absorption can lower surface temperature
Manual Welding
For manual repair welding or individual manual welding of special components on PCBs, it is crucial to consider the surface temperature of the electrochromic ferrochrome. The recommended temperature is below 260°C for paper-based copper clad laminates and below 300°C for glass fiber cloth-based copper clad laminates. It is advisable to keep the welding time to a minimum, with a general requirement of less than 3 seconds for paper substrates and less than 5 seconds for glass fiber cloth substrates.
- Surface temperature guidelines for manual welding
- Optimal welding time for different substrate types