The Electric Wheelchair PCBA: Ensuring Optimal Performance and Reliability
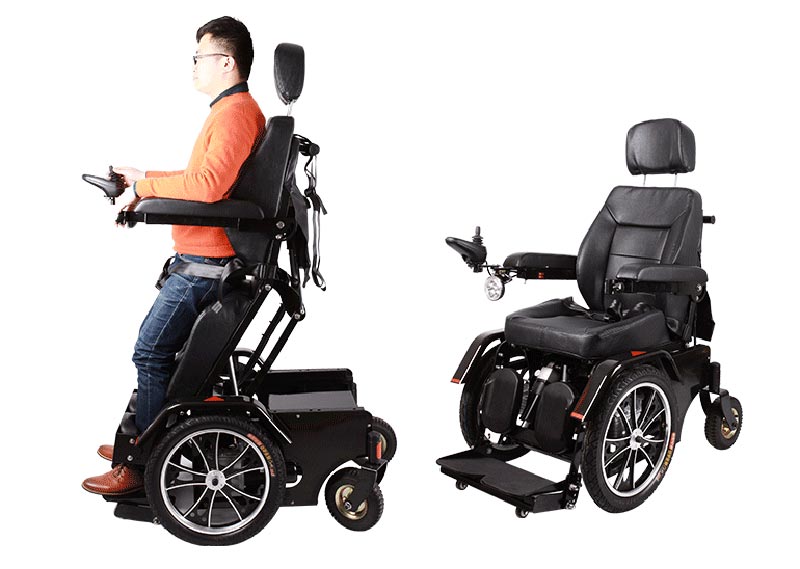
The Electric Wheelchair PCBA is a crucial component that houses essential functions like control systems, power management, and motor drive in electric wheelchairs. To guarantee optimal performance and reliability, it is vital to focus on technical specifications, design considerations, manufacturing processes, and testing procedures.
I. Technical Specifications and Operating Environment:
- Electric Wheelchair Parameters:
- Maximum Load: 100 kg to 150 kg.
- Maximum Speed: 6 km/h to 10 km/h.
- Maximum Driving Range: 20 km to 30 km.
- Charging Time: 6 to 8 hours.
- Battery Types: Lead-acid or lithium batteries.
- Operating Environment:
- Suitable for flat indoor and outdoor surfaces.
- Temperature Range: 0°C to 40°C.
- Humidity Range: 20% to 80%.
II. Design and Manufacturing Characteristics:
- Versatility:
- Integration of functional modules (motor drive, battery management, control system) for comprehensive electric wheelchair functionality.
- Stability and Reliability:
- Ensuring stable performance and reliable operation for the safety of electric wheelchair users.
- Rational design and component selection to enhance stability and reliability.
- Low Power and High Performance:
- Balancing power consumption and performance to extend battery life and improve driving range.
- Size and Layout:
- Accommodating structural and space limitations in the electric wheelchair.
- Planning module positions and connections for compactness and maintainability.
III. Production Process Considerations:
- PCB Design:
- Considering size, layout, and circuit board levels to isolate key circuits from noise sources.
- Preventing interference and crosstalk to ensure signal integrity.
- Component Selection:
- Choosing quality components, such as motor driver chips and sensors, for reliability and safety.
- Welding Process:
- Monitoring welding temperature, time, and quality to ensure reliable solder joints and circuit board stability.
- Circuit Protection:
- Incorporating over-current, over-voltage, and low voltage protection for safe operation.
- Testing and Quality Control:
- Rigorous testing during production, including functional, performance, and reliability testing.
PCBA Testing for Electric Wheelchair
- Circuit Connectivity Test:
- Ensuring proper connections between components, including checking solder joint quality.
- Functional Test:
- Validating the functionality of motor drive, battery management, and control system.
- Performance Test:
- Assessing performance metrics such as speed, mileage, and load capacity.
- Reliability Test:
- Evaluating PCBA reliability under different conditions through vibration, temperature cycle, and humidity assessments.
Designing and producing Electric Wheelchair PCBA involves meticulous attention to technical specifications, design aspects, manufacturing processes, and comprehensive testing protocols to ensure top-notch performance, dependability, and user safety.