How are high-quality flex PCBs made? This concern is not only shared by customers but also occupies the minds of PCB manufacturers.
During the proofing production of circuit boards, engineers often encounter various issues such as short circuits, open circuits, pad detachment, and inadequate soldering. Hence, engineers tend to prefer manufacturers known for superior production quality and speed when selecting circuit board proofing factories. This proactive choice helps avoid unnecessary complications. So, how can you determine if the boards produced by a circuit board proofing factory qualify as high-quality flex PCB products?
Flex printed circuit boards (PCBs) are a distinct type of PCB designed to be flexible and bendable. Their ability to accommodate intricate geometries and confined spaces has made them increasingly popular across diverse industries. In this blog post, we will delve into the process of manufacturing high-quality flex PCBs.
The first crucial step in creating a high-quality flex PCB is the design phase. Designers must meticulously consider factors like required flexibility, board thickness, and overall functionality. It is imperative to design the PCB while carefully addressing electrical and mechanical constraints to ensure optimal performance.

Choosing the right materials is crucial for creating high-quality flex PCBs. These materials typically include a flexible substrate, such as polyimide or polyester, and a layer of copper conductor patterns. The substrate is selected based on criteria like flexibility, resistance to harsh chemicals, and ability to withstand temperature variations. Copper conductor patterns are created using techniques such as photolithography or etching.
Flex PCBs may consist of multiple layers, depending on the application. Layer configuration aims to minimize overall board thickness while meeting functional requirements. Layers are interconnected using flexible joints like vias or traces, ensuring the PCB remains stable even under bending or twisting.
Given that flex PCBs often endure high temperatures, which can impact performance and stability, effective thermal management techniques are essential in their design. Methods such as heat sinks, thermal vias, or thermal pads are employed to dissipate heat and prevent thermal degradation.

Once the design is finalized and materials have been chosen, the flex PCB enters the assembly and testing phase. During assembly, electronic components like resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits are mounted onto the board. Subsequently, rigorous testing verifies the board’s functionality, electrical stability, and compliance with specifications.
Quality control is pivotal in ensuring the production of high-quality flex PCBs. Various tests—including visual inspection, electrical testing, and thermal cycling—are conducted to identify defects or issues. Maintaining stringent quality control measures guarantees the reliability and durability of the PCBs.
Finally, the flex PCBs are carefully packaged and dispatched to clients or manufacturers. Effective packaging is essential for safeguarding the PCBs from transportation and storage-related damage. Packaging must shield the boards from mechanical stress, moisture, and environmental factors that could compromise their integrity.

6. In conclusion, high-quality flex PCBs are manufactured through a meticulous process involving design, materials selection, layer configuration, thermal management, assembly, testing, quality control, and packaging. By meticulously following these steps and adhering to strict quality standards, manufacturers can produce flex PCBs that meet the specific requirements and demands of various applications.
During the proofing production of circuit boards, engineers often encounter various issues such as short circuits, open circuits, pad detachment, and inadequate soldering. Hence, engineers tend to prefer manufacturers known for superior production quality and speed when selecting circuit board proofing factories. This proactive choice helps avoid unnecessary complications. So, how can you determine if the boards produced by a circuit board proofing factory qualify as high-quality flex PCB products?
Flex printed circuit boards (PCBs) are a distinct type of PCB designed to be flexible and bendable. Their ability to accommodate intricate geometries and confined spaces has made them increasingly popular across diverse industries. In this blog post, we will delve into the process of manufacturing high-quality flex PCBs.
The first crucial step in creating a high-quality flex PCB is the design phase. Designers must meticulously consider factors like required flexibility, board thickness, and overall functionality. It is imperative to design the PCB while carefully addressing electrical and mechanical constraints to ensure optimal performance.
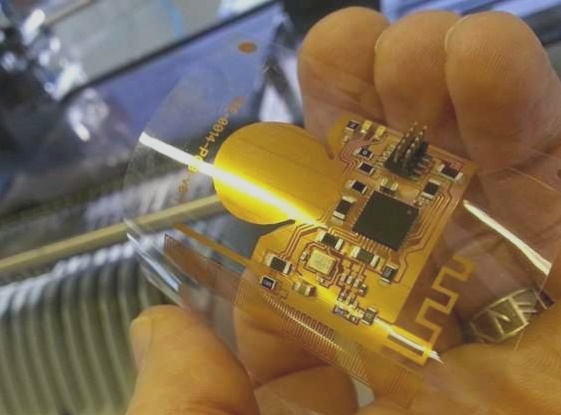

Choosing the right materials is crucial for creating high-quality flex PCBs. These materials typically include a flexible substrate, such as polyimide or polyester, and a layer of copper conductor patterns. The substrate is selected based on criteria like flexibility, resistance to harsh chemicals, and ability to withstand temperature variations. Copper conductor patterns are created using techniques such as photolithography or etching.
Flex PCBs may consist of multiple layers, depending on the application. Layer configuration aims to minimize overall board thickness while meeting functional requirements. Layers are interconnected using flexible joints like vias or traces, ensuring the PCB remains stable even under bending or twisting.
Given that flex PCBs often endure high temperatures, which can impact performance and stability, effective thermal management techniques are essential in their design. Methods such as heat sinks, thermal vias, or thermal pads are employed to dissipate heat and prevent thermal degradation.

Once the design is finalized and materials have been chosen, the flex PCB enters the assembly and testing phase. During assembly, electronic components like resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits are mounted onto the board. Subsequently, rigorous testing verifies the board’s functionality, electrical stability, and compliance with specifications.
Quality control is pivotal in ensuring the production of high-quality flex PCBs. Various tests—including visual inspection, electrical testing, and thermal cycling—are conducted to identify defects or issues. Maintaining stringent quality control measures guarantees the reliability and durability of the PCBs.
Finally, the flex PCBs are carefully packaged and dispatched to clients or manufacturers. Effective packaging is essential for safeguarding the PCBs from transportation and storage-related damage. Packaging must shield the boards from mechanical stress, moisture, and environmental factors that could compromise their integrity.
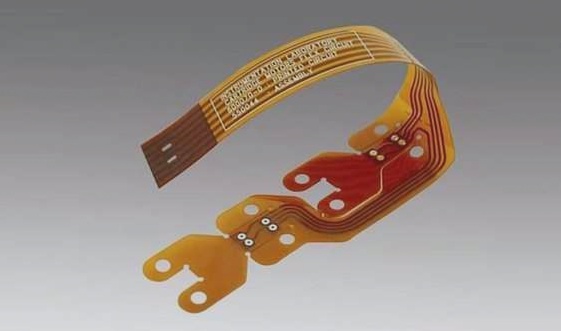
6. In conclusion, high-quality flex PCBs are manufactured through a meticulous process involving design, materials selection, layer configuration, thermal management, assembly, testing, quality control, and packaging. By meticulously following these steps and adhering to strict quality standards, manufacturers can produce flex PCBs that meet the specific requirements and demands of various applications.