1. As electronic products demand increasingly sophisticated functionalities, the structure of PCB circuit boards is becoming progressively complex. Due to space constraints on PCBs, they are evolving from single-layer to double-layer and now, multilayer configurations. So, what sets apart the manufacturing processes of multilayer PCB circuit boards from their double-layer counterparts? Let’s delve into it below.
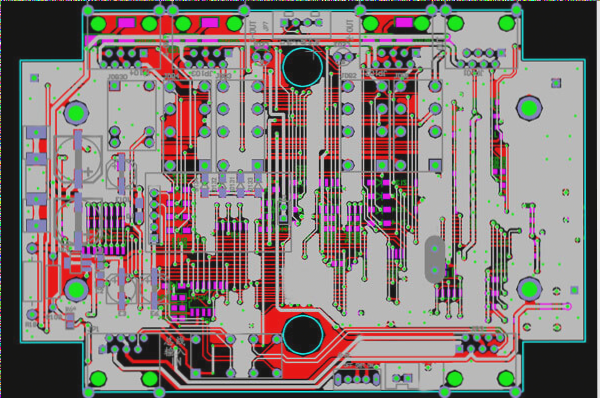
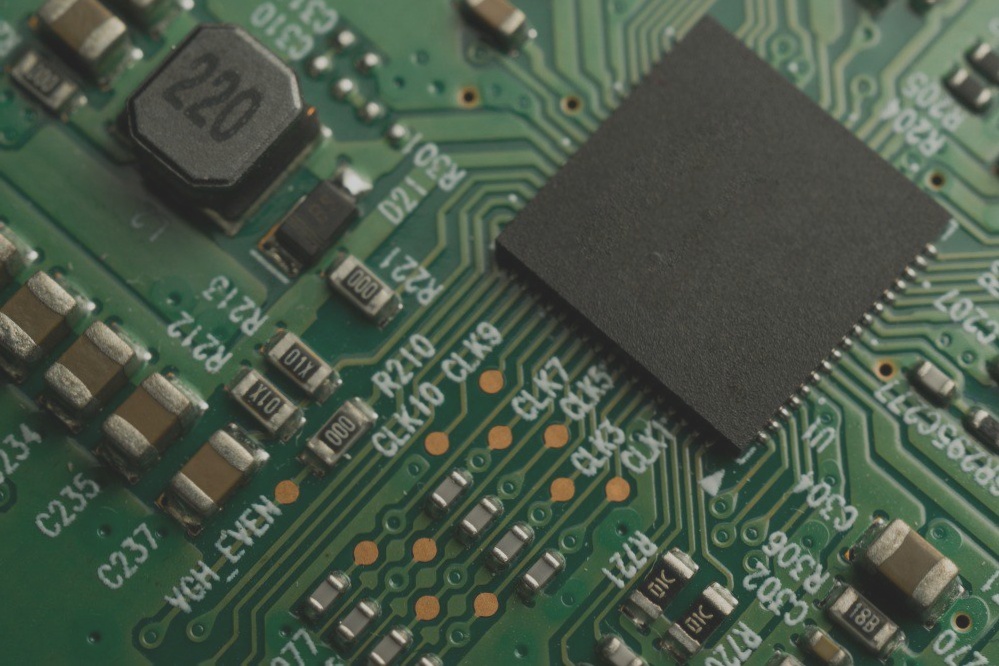
2. A multilayer PCB circuit board is a type of printed circuit board comprised of alternating layers of conductive patterns and insulating materials, bonded together through lamination. The number of conductive pattern layers exceeds three, and electrical interconnections between these layers are facilitated through metallized holes.
3. When one double-sided board serves as the inner layer, paired with two single-sided boards as the outer layers, or when two double-sided boards are utilized as inner layers along with two single-sided boards as outer layers, the positioning system and insulating bonding material are laminated together. This results in the compression of the conductive patterns, forming either a four-layer or six-layer printed circuit board, also known as a multilayer PCB circuit board.
4. Multilayer PCB circuit boards are typically fabricated using epoxy glass cloth copper-clad laminates, with their manufacturing process evolving from that of plated-through double-sided boards. The general procedure involves initially etching the inner layer board graphics, followed by a blackening treatment. Prepreg is then applied according to the predetermined design for lamination, after which copper foil is added to the upper and lower surfaces. Subsequently, the boards are subjected to heat pressing. This process yields a “double-sided copper-clad laminate” with an inner layer pattern ready for use.
2. A multilayer PCB circuit board is a type of printed circuit board comprised of alternating layers of conductive patterns and insulating materials, bonded together through lamination. The number of conductive pattern layers exceeds three, and electrical interconnections between these layers are facilitated through metallized holes.
3. When one double-sided board serves as the inner layer, paired with two single-sided boards as the outer layers, or when two double-sided boards are utilized as inner layers along with two single-sided boards as outer layers, the positioning system and insulating bonding material are laminated together. This results in the compression of the conductive patterns, forming either a four-layer or six-layer printed circuit board, also known as a multilayer PCB circuit board.
4. Multilayer PCB circuit boards are typically fabricated using epoxy glass cloth copper-clad laminates, with their manufacturing process evolving from that of plated-through double-sided boards. The general procedure involves initially etching the inner layer board graphics, followed by a blackening treatment. Prepreg is then applied according to the predetermined design for lamination, after which copper foil is added to the upper and lower surfaces. Subsequently, the boards are subjected to heat pressing. This process yields a “double-sided copper-clad laminate” with an inner layer pattern ready for use.