The Process of Copper Plate Production and Mastering PCB Core Technology
- Prepare a solution containing resin, filler, and organic solvents like acetone and methyl ethyl ketone.
- Soak glass fiber cloth in the resin solution and dry it to create a PP sheet.
- Stack PP sheets with copper foil on top and bottom based on required thickness.
- Align and press layers in a constant-temperature press for curing.
- Remove the laminate after the curing process.
Characteristics of Copper-Clad Laminate
- Excellent temperature resistance with a high glass transition temperature (Tg) for stiffness.
- High peel strength of copper foil to prevent tearing.
- Good flame resistance, high breakdown voltage, and low dielectric constant.
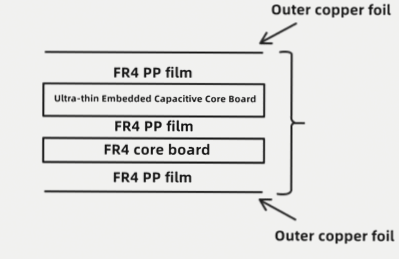
Core Technology of Copper-Clad Laminate
- Selection of critical resin, filler, and curing agent components.
- Layering process to create the copper-clad laminate.
The industry commonly uses bisphenol A epoxy resin for its performance, with options for phenolic resin or modified bisphenol A epoxy resin for higher temperature resistance. Domestic resin manufacturers have narrowed the technology gap with imported products, but high-end fields still rely on technologies from Europe, the U.S., and Japan.
While bisphenol A epoxy resin is widely used, there is a gap in special resin technologies compared to Europe and the U.S. Domestic manufacturers typically use polytetrafluoroethylene resin in electronic products for its flame resistance.
Filler

Fillers like silica (SiO2) and aluminum oxide (Al2O3) are commonly used in copper-clad laminate formulations, with little difference between domestic and imported fillers.
Hardener
The curing agent for bisphenol A epoxy resin is self-sufficiently produced in China. Specialized resins, like phenolic resins, often source curing agents from Europe, the U.S., and Japan.
Laminating Technology
A PCB rigid board cannot be folded, while a foldable circuit board is known as an FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit). PCBs are primary boards with soldered chips, whereas FPCs connect components like flat cables in electronic products. FPCs are lighter, more compact, and flexible compared to PCBs.
Domestic companies have invested in R&D and production of copper-clad laminate technologies, minimizing the technological gap with foreign manufacturers.