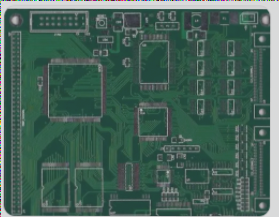
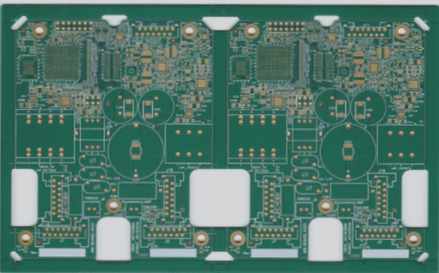
What are Mounting Holes?
Mounting holes are openings drilled through a PCB to provide points for securely attaching the board to a chassis or enclosure. These holes are typically larger in diameter than other holes on the board and are commonly located at the corners or other critical areas. Mounting holes are often surrounded by a copper pad or annular ring, which ensures a stable connection between the PCB and the mounting hardware.

Figure 1: Mounting Holes
Two Types of Mounting Holes
Mounting holes can be classified into two types: plated and un-plated, depending on whether they have a conductive layer.
Plated mounting holes are essential when electrical connections between different PCB layers are required. For example, if a PCB has a ground plane on a separate layer from the top layer, plated mounting holes may be necessary to link the top layer to the ground plane. Additionally, plated mounting holes offer a reliable anchor point for screws, bolts, or other hardware, ensuring that components stay securely attached to the board.
In contrast, un-plated mounting holes, which are primarily used for mechanical purposes, are not intended to carry electrical signals. These holes are usually isolated from other components and traces on the PCB and may require a keep-out zone to prevent interference with the circuit’s functionality.
Mounting Holes Surrounded by Vias
In many cases, mounting holes are surrounded by small vias. What is the purpose of these vias? Typically, these vias are positioned within the annular ring or thermal relief pads of the mounting holes and serve three main functions.
First, they help distribute the mechanical stress from mounting the PCB across a larger area. Vias provide additional support and prevent the mounting holes from loosening or being damaged over time due to mechanical stress or vibration.
Second, they establish a grounding connection between different layers of the PCB. This improves electromagnetic shielding and reduces noise, which is particularly critical for sensitive or high-frequency circuits.
Third, the vias can be used to connect a copper plane or heatsink to the mounting hole, aiding in heat dissipation. The vias create a direct thermal pathway between the PCB and the heatsink, allowing for more efficient heat transfer and better thermal management.

Figure 2: Mounting Holes with Vias Surrounding
If you have any questions regarding PCBs or PCBA, please feel free to contact me at info@wellcircuits.com