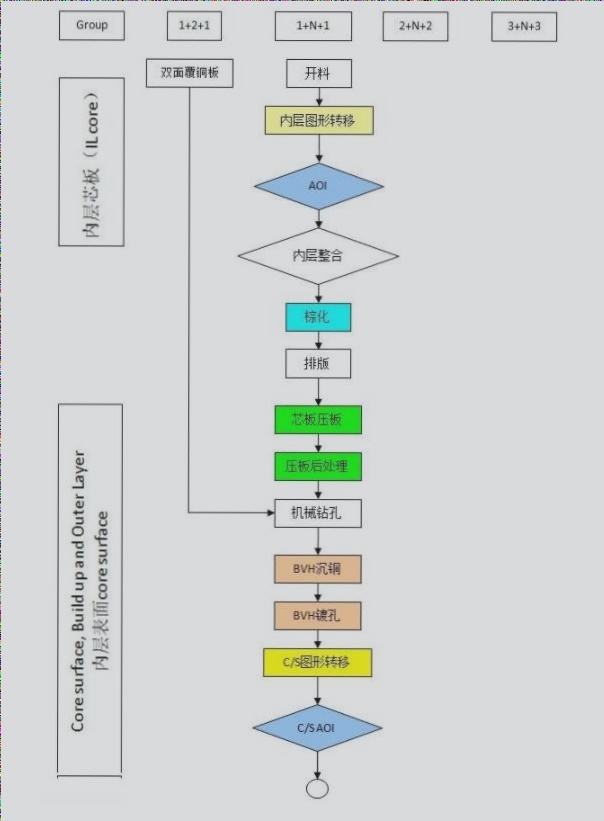
Multilayer PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) are composed of multiple layers of substrates, conductive layers, and insulating layers stacked alternately. Here are their advantages and disadvantages compared to single-layer PCBs:
1. Higher density and smaller size: Multilayer PCBs can accommodate more components and circuits in the same area, resulting in increased density and reduced size.
2. Better electrical performance: Each layer in a multilayer PCB is interconnected through plated copper holes, which effectively lowers resistance and inductance. This configuration enhances signal transmission speed and stability.
3. Higher reliability: Multilayer PCBs exhibit improved resistance to interference and noise. Additionally, they can efficiently dissipate heat, thereby enhancing circuit reliability and stability.
4. Greater flexibility: Multilayer PCBs offer flexibility in circuit layout design. Different circuits can be arranged in separate layers as needed, providing greater customization options.

Higher cost: Multilayer PCBs incur greater production costs due to increased processes and materials. Additionally, their design necessitates more time and labor, further escalating expenses.
More complex designs: Designing multilayer PCBs demands advanced technology, expertise, and considerable effort. These boards require multiple layers and must address complexities such as signal and power interfaces, wiring, and electromagnetic compatibility.
Greater manufacturing complexity: Manufacturing multilayer PCBs involves sophisticated technologies and equipment like drilling, layer stacking, and via pressing. Quality control and rigorous inspections are also essential to ensure electrical performance and reliability.
Challenges in debugging and maintenance: Detecting and repairing faults in multilayer PCBs is more challenging due to intricate layer connections. Troubleshooting and maintenance tasks are correspondingly more demanding, particularly when disassembly is necessary for component replacement.
Increased electromagnetic radiation: Multilayer PCBs conduct current across different layers, resulting in heightened electromagnetic radiation that can potentially interfere with nearby electronics.

1. In general, multilayer PCBs offer higher density, better electrical performance, reliability, and flexibility compared to single-layer PCBs. However, they also come with disadvantages such as increased cost, complex design, and challenging maintenance. Therefore, when selecting a PCB, it’s essential to consider various factors based on specific requirements to choose the most suitable solution.
2. **Higher density:** Multilayer PCBs achieve higher board density by increasing the number of circuits while reducing board size.
3. **Improved reliability:** Layering in multilayer PCBs reduces board crosspoints, minimizing interference and noise.
4. **Enhanced impedance control:** Inner layer routing in multilayer PCBs reduces signal transmission delay and impedance changes, thereby enhancing signal stability.
5. **Better heat dissipation:** Multilayer PCBs enhance circuit board heat dissipation by incorporating dedicated heat dissipation layers within the board.
6. **Expanded functionality:** By incorporating specialized layers such as power, ground, and signal layers internally, multilayer PCBs can achieve additional functions like protection, isolation, and filtering.

1. Higher density and smaller size: Multilayer PCBs can accommodate more components and circuits in the same area, resulting in increased density and reduced size.
2. Better electrical performance: Each layer in a multilayer PCB is interconnected through plated copper holes, which effectively lowers resistance and inductance. This configuration enhances signal transmission speed and stability.
3. Higher reliability: Multilayer PCBs exhibit improved resistance to interference and noise. Additionally, they can efficiently dissipate heat, thereby enhancing circuit reliability and stability.
4. Greater flexibility: Multilayer PCBs offer flexibility in circuit layout design. Different circuits can be arranged in separate layers as needed, providing greater customization options.

Higher cost: Multilayer PCBs incur greater production costs due to increased processes and materials. Additionally, their design necessitates more time and labor, further escalating expenses.
More complex designs: Designing multilayer PCBs demands advanced technology, expertise, and considerable effort. These boards require multiple layers and must address complexities such as signal and power interfaces, wiring, and electromagnetic compatibility.
Greater manufacturing complexity: Manufacturing multilayer PCBs involves sophisticated technologies and equipment like drilling, layer stacking, and via pressing. Quality control and rigorous inspections are also essential to ensure electrical performance and reliability.
Challenges in debugging and maintenance: Detecting and repairing faults in multilayer PCBs is more challenging due to intricate layer connections. Troubleshooting and maintenance tasks are correspondingly more demanding, particularly when disassembly is necessary for component replacement.
Increased electromagnetic radiation: Multilayer PCBs conduct current across different layers, resulting in heightened electromagnetic radiation that can potentially interfere with nearby electronics.

1. In general, multilayer PCBs offer higher density, better electrical performance, reliability, and flexibility compared to single-layer PCBs. However, they also come with disadvantages such as increased cost, complex design, and challenging maintenance. Therefore, when selecting a PCB, it’s essential to consider various factors based on specific requirements to choose the most suitable solution.
2. **Higher density:** Multilayer PCBs achieve higher board density by increasing the number of circuits while reducing board size.
3. **Improved reliability:** Layering in multilayer PCBs reduces board crosspoints, minimizing interference and noise.
4. **Enhanced impedance control:** Inner layer routing in multilayer PCBs reduces signal transmission delay and impedance changes, thereby enhancing signal stability.
5. **Better heat dissipation:** Multilayer PCBs enhance circuit board heat dissipation by incorporating dedicated heat dissipation layers within the board.
6. **Expanded functionality:** By incorporating specialized layers such as power, ground, and signal layers internally, multilayer PCBs can achieve additional functions like protection, isolation, and filtering.