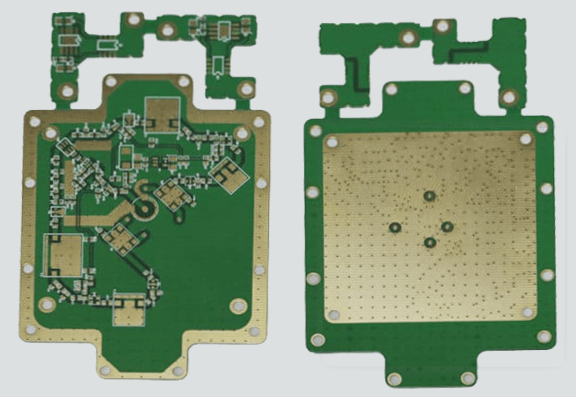
PCB Board Design Explained
In this section, we delve into the crucial aspect of PCB online testing during the PCBA processing phase. Understanding the intricacies of In-Circuit Testing (ICT) is vital for assessing device and circuit network characteristics.
- Detection of open circuits, short circuits, and connection failures
- Identification of missing or faulty parts
- Parameter testing for analog devices
- Functional testing of integrated circuits
- Identification of soldering failures
- Programming error detection

When designing PCBA for ICT testing, considerations for the test needle bed are essential to meet production and testing requirements.
- Designing non-metallized positioning holes on the PCB
- Specifying test points for probe testing
- Setting requirements for test points
- Determining test point size specifications
Choosing PCB Board Materials
For multilayer PCBs, the selection of dielectric materials significantly impacts circuit performance. Key considerations include the Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) and the choice of appropriate prepregs and core boards.
The Importance of Tg in PCB Selection
Tg, or glass transition temperature, is a critical property of polymers that plays a key role in determining the behavior of materials. It serves as a crucial factor in choosing the right substrate materials for PCBs.
- When the PCB temperature surpasses the Tg threshold, the thermal expansion coefficient increases.
- PCBs are typically categorized into low Tg (around 135°C), medium Tg (around 150°C), and high Tg (around 170°C) boards based on their Tg values.
- For scenarios involving multiple pressing cycles, more than 14 layers, soldering temperatures above 230°C, or working temperatures exceeding 100°C, it is recommended to opt for high Tg materials.
The Significance of Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE)
The CTE is crucial for soldering reliability and overall usage of PCBs. It is essential to select materials with an expansion coefficient that aligns with copper to minimize thermal deformation during soldering processes.
Considerations for PCB Material Selection
- Heat Resistance: Ability to withstand soldering temperatures and cycles. Welding tests are usually conducted under stringent conditions, considering parameters like Td, T260, and T288.
- Thermal Conductivity
- Dielectric Constant (Dk)
- Volume Resistance and Surface Resistance
- Moisture Absorption: Impacts shelf life and assembly processes. Moisture absorption can lead to delamination during soldering.
If you require PCB manufacturing services, feel free to contact us.