2. PCBA stands for Printed Circuit Board Assembly, often translated as PCB Assembly. This process involves passing a PCB blank board through SMT (Surface Mount Technology) soldering, DIP (Dual In-line Package) insertion, testing, and other procedures to create a finished product, known as PCBA.
3. A PCB can transform a program that cannot independently function into a unit capable of independent operation. Excellent circuit design in PCBA can achieve optimal circuit and heat dissipation performance. PCBA generally refers to the manufacturing process, which results in a finished circuit board where the PCB is fully processed. A PCB itself is a physical printed circuit board without any components soldered onto it.

—
Image 1: PCB Assembly
Integrated circuits (ICs) generally refer to chips that integrate functions such as the northbridge chip on motherboards or within CPUs. They are also known as integrated blocks. Printed circuit boards (PCBs), on the other hand, are the platforms where ICs are soldered and serve as their carriers.
PCBs can be found in nearly every electronic device. They provide the foundation for soldering various electronic components, facilitating electrical connections among them.
Simply put, an integrated circuit integrates a complete circuit into a chip, where any internal damage to the IC results in damage to the entire chip. In contrast, PCBs allow for the soldering and replacement of individual components as needed.
—
Image 2: IC Packaging on PCB
1. PCB circuit boards are among the most critical hardware components in electronic equipment, serving as vital elements in various electronic devices. PCBs are typically connected to equipment to provide power for its operation.
A. Over the past 100 years, the development of high-density printed circuit boards has progressed alongside advancements in integrated circuit integration and installation technologies.
B. High reliability is ensured through a series of inspections, tests, and aging tests, guaranteeing long-term functionality of PCBs.
C. Design flexibility is achieved through standardization and design methodologies, enabling efficient realization of various PCB performance requirements within short timeframes.
D. Production efficiency is enhanced through modern management practices, enabling standardized, large-scale, and automated production processes to maintain consistent product quality.
E. Testability: Comprehensive test methods, standards, and equipment have been established to assess and validate the quality and longevity of PCB products.
—
These edits aim to improve readability and clarity while maintaining the original meaning of each point.
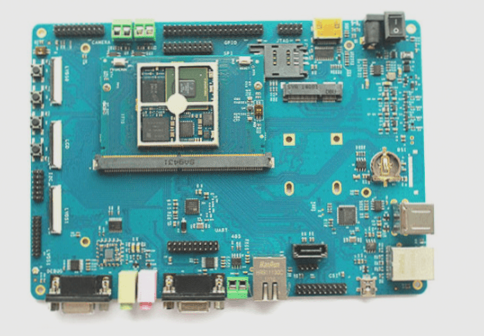
Image 3: Automotive PCB Assembly
F. Assemblability: PCB products not only facilitate the standardized assembly of various components but also support automated and large-scale mass production. Moreover, PCBs can integrate with various component assembly parts to form larger components, systems, and even complete machines.
G. Maintainability: Due to the standardized design and production of PCB products and various component assembly components on a large scale, these components can be quickly, easily, and flexibly replaced in case of system failure, thereby enabling swift system restoration.