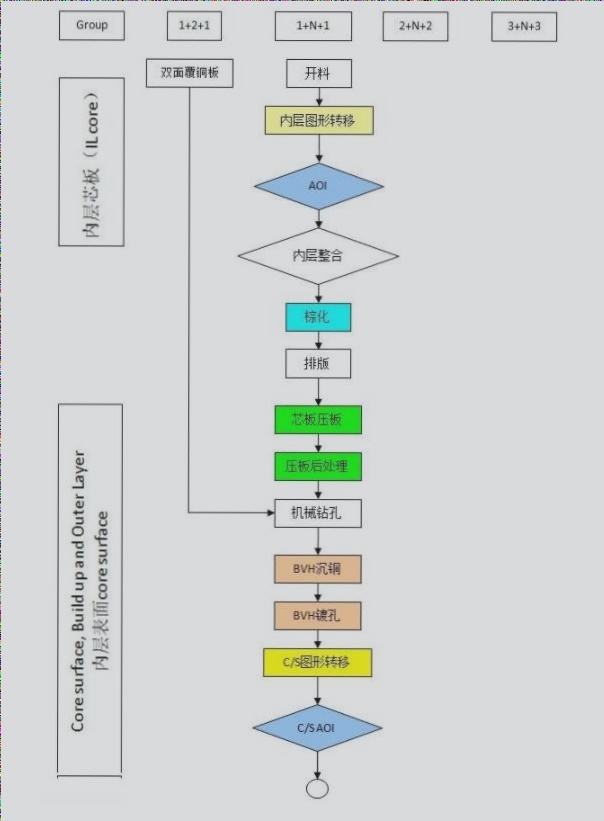
There are two different processes for selective soldering: drag soldering and dip soldering.
The selective drag soldering process is carried out on a single small soldering tip wave. It is suitable for soldering in very tight spaces on the PCB, such as individual solder joints or pins. The PCB moves on the solder wave at different speeds and angles to achieve the best quality. To ensure the stability of the process, the inner diameter of the soldering tip is kept under 6mm. Soldering tips are installed and optimized in different directions based on the soldering requirements. The manipulator can approach the solder wave from various angles, with a recommended tilt angle of 10° for most devices.
Compared to dip soldering, the drag soldering process has better heat conversion efficiency due to the solder solution and PCB movement. However, only a small solder tip wave can transfer the heat required for the weld connection. The solder wave temperature for drag soldering is usually set between 275℃ to 300℃, with a pulling speed range of 10mm/s to 25mm/s. Nitrogen is supplied to prevent oxidation. The solder wave eliminates oxidation, preventing bridging defects and increasing stability and reliability.
The machine offers high precision and flexibility. The modular design allows for customization according to specific production requirements and upgrades for future needs. The manipulator’s motion radius covers the flux nozzle, preheating, and soldering nozzle, allowing for different welding processes. The unique synchronization process significantly shortens the single board process cycle. The manipulator’s capabilities ensure high-precision and high-quality welding with stable and precise positioning (±0.05mm) and 5-dimensional movement for optimized contact angles. The tin wave height stylus is made of titanium alloy and can be controlled under program regulation by adjusting the tin pump speed for stability.
The selective drag soldering process is carried out on a single small soldering tip wave. It is suitable for soldering in very tight spaces on the PCB, such as individual solder joints or pins. The PCB moves on the solder wave at different speeds and angles to achieve the best quality. To ensure the stability of the process, the inner diameter of the soldering tip is kept under 6mm. Soldering tips are installed and optimized in different directions based on the soldering requirements. The manipulator can approach the solder wave from various angles, with a recommended tilt angle of 10° for most devices.
Compared to dip soldering, the drag soldering process has better heat conversion efficiency due to the solder solution and PCB movement. However, only a small solder tip wave can transfer the heat required for the weld connection. The solder wave temperature for drag soldering is usually set between 275℃ to 300℃, with a pulling speed range of 10mm/s to 25mm/s. Nitrogen is supplied to prevent oxidation. The solder wave eliminates oxidation, preventing bridging defects and increasing stability and reliability.
The machine offers high precision and flexibility. The modular design allows for customization according to specific production requirements and upgrades for future needs. The manipulator’s motion radius covers the flux nozzle, preheating, and soldering nozzle, allowing for different welding processes. The unique synchronization process significantly shortens the single board process cycle. The manipulator’s capabilities ensure high-precision and high-quality welding with stable and precise positioning (±0.05mm) and 5-dimensional movement for optimized contact angles. The tin wave height stylus is made of titanium alloy and can be controlled under program regulation by adjusting the tin pump speed for stability.