With advancements in science and technology and the enhancement of living standards, PCB boards primarily serve as connections for electronic components and electrical energy. They significantly contribute to increasing automation levels and production efficiency. Are you aware of the cleaning procedures for PCB boards? What are the maintenance techniques? Let’s explore this topic together. Below is an introduction to the “PCB Cleaning Process and Maintenance Measures.”
**Steps to Clean Residues After Soldering on the PCB Board Wire Module**
After soldering the wireless data transmission module PCB board to the antenna SMA connector, residues such as flux and rosin will remain on the surface. At this stage, you can use board washing solution (commonly referred to as circuit board cleaner) to effectively clean the wireless module. To ensure thorough cleaning, follow these steps:
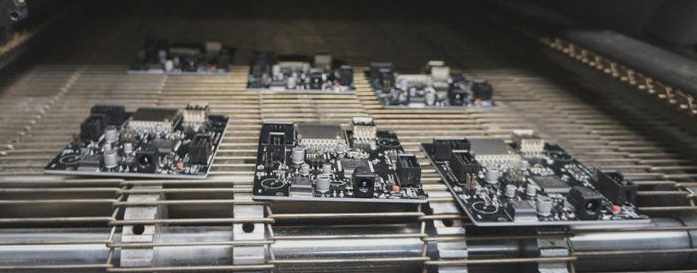
1. Prepare specialized cotton swabs, cleaning solution, rubber gloves, and masks. Since the cleaning solution is a volatile chemical that can irritate the respiratory tract and lungs upon inhalation, and it is also corrosive to the skin, ensure you wear a mask and silicone gloves along with other protective equipment before commencing the cleaning process.
2. Dip the specialized cotton swab into the opening of the bottle containing the cleaning solution. Squeeze gently to release some of the solution. Note: an appropriate amount will suffice.
3. Use the cotton swab to gently wipe the area with rosin residue around the soldering SMA head. If residue remains, repeat the procedure until the area is clean.
4. Place the cleaned wireless module into the designated container. If there is dust or debris on the shielding cover of the wireless module, fold a specialized paper towel into approximately three layers. Use the folded paper towel to press against the opening of the small bottle containing the cleaning solution and dispense an appropriate amount. Wipe the top of the shielding cover from left to right in a single motion. If it remains dirty, feel free to wipe it again.
**Introduction to PCB Maintenance and Composition**
After etching and cleaning the PCB, it is essential to apply a coating to protect the surface and enhance the reliability of the solder joints. Applying a solder mask in non-soldering areas prevents solder overflow and potential bridging while providing moisture protection post-soldering. Coating the pad surface helps prevent oxidation.
(1) **Solder Mask.** There are two main types of solder mask graphic structures: one defined by the solder mask (SMD) and the other by the non-solder mask (NSMD). Typically, the solder mask for NSMD pads is automatically generated in computer CAD designs and covers all graphics except the pads. The solder mask margin from the soldering area should be between 0.1 and 0.25 mm, and the area between QFP soldering zones should be covered as much as possible. The solder mask should be applied on a clean and dry bare copper board; otherwise, defects like bubbles, wrinkles, and cracks may occur during soldering. The design for SMD pads can be slightly enlarged, allowing for an increased area covered by the solder mask, which is commonly used in lead-free processes.
(2) **Pad Coating Layer.** To protect the pads and ensure good solderability with a longer shelf life (up to 6 months), it is necessary to add a coating on the pad surface. The pad coating layer typically follows specific processes.
The above information regarding “Cleaning Steps for Residues after Soldering the Wireless Module PCB Board” and “Introduction to PCB Maintenance and Composition” aims to enhance your understanding of the “PCB cleaning process and maintenance measures.”
If you have any PCB manufacturing needs, please do not hesitate to contact me.Contact me