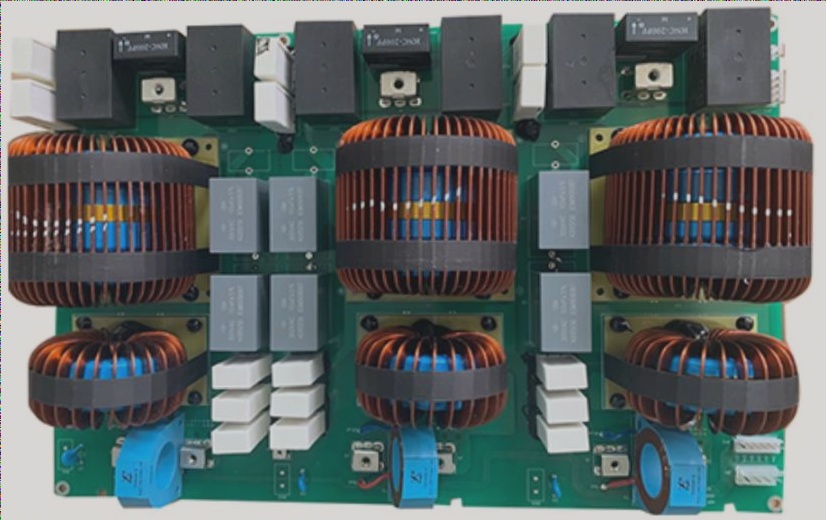
PCB Design Best Practices
- Follow a structured order when designing PCBs, moving from left to right and top to bottom.
- Optimize the width of PCB traces and trace spacing, maintaining consistent gaps between capacitor pads.
- Minimize trace bends for a simple and clear routing layout.
- Ensure a reasonable pin placement sequence with appropriate component pin spacing.

PCB Wiring Direction
Align component placement with the schematic diagram for easier inspection, debugging, and maintenance. Wiring should follow the circuit diagram layout to meet system requirements.
Design Considerations
Prioritize efficient wiring, minimize jumpers, and route wires smoothly for intuitive installation, maintenance, and repair.
Component Arrangement
Distribute components evenly for a neat and structurally sound PCB layout.
Orientation of Input and Output Terminals
- Minimize the distance between lead terminals for optimal routing.
- Cluster input and output terminals on one or two sides to avoid excessive dispersion.
Placement Guidelines for Potentiometers and IC Holders
- Potentiometers: Ensure correct positioning for adjusting output voltage and charging current.
- IC Holders: Carefully position IC holders with proper orientation and pin alignment.
Resistor and Diode Placement
- Horizontal Placement: Preferred for fewer components in larger PCBs with specific pad distances.
- Vertical Installation: Suitable for larger components or smaller PCBs with different pad distances.