1. We have introduced a new section dedicated to designing and creating our own PCB boards for electronic products and Arduino projects.
2. Until recently, outsourcing PCB manufacturing was an expensive process, requiring long lead times and hundreds of euros in investment. Consequently, it was often beyond the reach of families and hobbyists.
3. Fortunately, this situation has changed significantly in recent years. Online services for custom PCB manufacturing have become increasingly common, enabling us to obtain professional-quality small batches (5 pieces) at very low costs. Now, we can purchase 5-10 boards for just a few euros, with each board costing less than one euro.
4. Advances in PCB design software have also played a role. Previously, these tools were fully commercialized, with license fees reaching thousands of euros. Today, we have access to powerful free and even open-source solutions for layout design.
5. Thanks to these developments, we can now produce custom PCBs of our own design with industrial-quality standards for less than one euro per board! These can be incorporated into our projects within 2-3 weeks.

1. This was unthinkable a few years ago. It not only delights all electronics enthusiasts but also elevates your projects, making them more professional, powerful, and easy to assemble.
2. Therefore, we will create a new section for designing and fabricating our own PCBs, starting from scratch and obtaining the files needed for manufacturing.
3. We will explore these topics in detail in future posts. But let’s not get ahead of ourselves and start from the beginning (as we prefer on the blog). So, what exactly is a PCB?
4. What is a PCB?
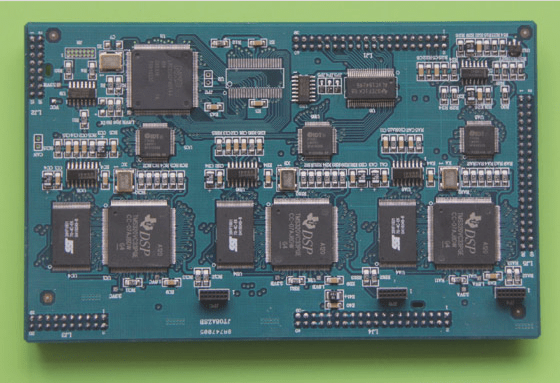
5. A printed circuit board (PCB) is a compact circuit configuration system that reduces the need for cables and produces a durable and compact circuit.
6. The printed circuit board was invented by Austrian engineer Paul Eisler in 1936 and was quickly adopted, largely due to the technological advancements spurred by World War II.
7. Today, PCBs are ubiquitous. From small modules in home electronics to large ones in your smartphone or computer motherboard.
8. PCB Design Tutorial: What is a PCB?
9. PCBs are often regarded as complex components, typically used by electronics professionals. Indeed, they can be intricate. However, in this section, we will demystify PCBs and see if anyone can design their own.
10. A PCB consists of copper layers that are insulated from each other. These copper layers form the circuit. In the next article in this series, we will examine each of these aspects in detail, but for now, this summary will suffice.
11. We will mount and solder electronic components onto the PCB, which can be either PTH (Plated Through Hole) or SMD (Surface Mount Device). Both types of components include resistors, capacitors, coils, transistors, and integrated circuits.
12. The conductive tracks on the PCB and the mounted components together form the final circuit. Without a PCB, we would need to connect the components using a breadboard or manual soldering, which is less organized. The PCB streamlines this process.
13. It helps avoid cable confusion, such as connecting and disconnecting cables, dealing with bent pins, tracking cable origins, and addressing issues like solder bridges or electrical noise. Most importantly, it prevents these issues from rendering your project non-functional.
14. Logically, the greatest challenge lies in designing the circuit. The more knowledgeable you are about electronics, the more complex and useful the PCB you create will be (this also applies to breadboards).
15. However, as we’ve seen, despite its complexity, a PCB is fundamentally a simple concept. Its conductive tracks replace numerous cables, offering a powerful and reliable way to build electronic circuits.
16. In conclusion
17. So far, we have introduced the basics of PCB design and why there is no need to fear them. Today, anyone can create custom PCBs.
2. Until recently, outsourcing PCB manufacturing was an expensive process, requiring long lead times and hundreds of euros in investment. Consequently, it was often beyond the reach of families and hobbyists.
3. Fortunately, this situation has changed significantly in recent years. Online services for custom PCB manufacturing have become increasingly common, enabling us to obtain professional-quality small batches (5 pieces) at very low costs. Now, we can purchase 5-10 boards for just a few euros, with each board costing less than one euro.
4. Advances in PCB design software have also played a role. Previously, these tools were fully commercialized, with license fees reaching thousands of euros. Today, we have access to powerful free and even open-source solutions for layout design.
5. Thanks to these developments, we can now produce custom PCBs of our own design with industrial-quality standards for less than one euro per board! These can be incorporated into our projects within 2-3 weeks.

1. This was unthinkable a few years ago. It not only delights all electronics enthusiasts but also elevates your projects, making them more professional, powerful, and easy to assemble.
2. Therefore, we will create a new section for designing and fabricating our own PCBs, starting from scratch and obtaining the files needed for manufacturing.
3. We will explore these topics in detail in future posts. But let’s not get ahead of ourselves and start from the beginning (as we prefer on the blog). So, what exactly is a PCB?
4. What is a PCB?
5. A printed circuit board (PCB) is a compact circuit configuration system that reduces the need for cables and produces a durable and compact circuit.
6. The printed circuit board was invented by Austrian engineer Paul Eisler in 1936 and was quickly adopted, largely due to the technological advancements spurred by World War II.
7. Today, PCBs are ubiquitous. From small modules in home electronics to large ones in your smartphone or computer motherboard.
8. PCB Design Tutorial: What is a PCB?
9. PCBs are often regarded as complex components, typically used by electronics professionals. Indeed, they can be intricate. However, in this section, we will demystify PCBs and see if anyone can design their own.
10. A PCB consists of copper layers that are insulated from each other. These copper layers form the circuit. In the next article in this series, we will examine each of these aspects in detail, but for now, this summary will suffice.
11. We will mount and solder electronic components onto the PCB, which can be either PTH (Plated Through Hole) or SMD (Surface Mount Device). Both types of components include resistors, capacitors, coils, transistors, and integrated circuits.
12. The conductive tracks on the PCB and the mounted components together form the final circuit. Without a PCB, we would need to connect the components using a breadboard or manual soldering, which is less organized. The PCB streamlines this process.
13. It helps avoid cable confusion, such as connecting and disconnecting cables, dealing with bent pins, tracking cable origins, and addressing issues like solder bridges or electrical noise. Most importantly, it prevents these issues from rendering your project non-functional.
14. Logically, the greatest challenge lies in designing the circuit. The more knowledgeable you are about electronics, the more complex and useful the PCB you create will be (this also applies to breadboards).
15. However, as we’ve seen, despite its complexity, a PCB is fundamentally a simple concept. Its conductive tracks replace numerous cables, offering a powerful and reliable way to build electronic circuits.
16. In conclusion
17. So far, we have introduced the basics of PCB design and why there is no need to fear them. Today, anyone can create custom PCBs.