Certainly! Here are the revised paragraphs:
—
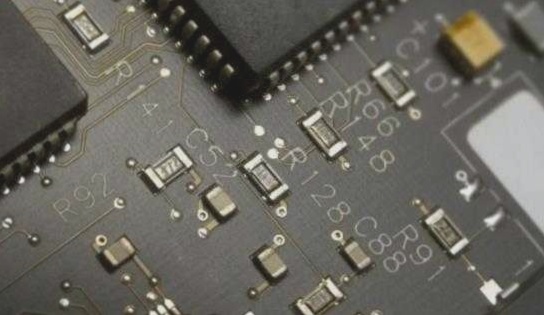
PCB application fields are extensive, ranging from aviation and military industries to household electronics, all of which rely heavily on its structure. Copper is used to connect components on the circuit board, facilitating conductivity. When circuit boards are exposed to air for prolonged periods, they not only oxidize but also lose solderability due to corrosion.
Therefore, employing specialized technologies to safeguard circuit boards is crucial. The PCB electroplating process follows these operational steps: Acid treatment → full plate copper → pattern transfer → acid degreasing → secondary counter-current rinsing → micro-etching → secondary acid treatment → tin plating → secondary counter-current rinsing → acid treatment → pattern copper plating → secondary counter-current rinsing → nickel plating → secondary water rinse → citric acid treatment → gold plating → recovery → 2-3 cycles of pure water rinsing → drying.
Three common PCB electroplating technologies exist: oxide film, organic coating, and electroplating. Among these, electroplating is preferred by most PCB manufacturers, although some facilities opt for the other two technologies. What are the distinctions between these three PCB electroplating processes?
—
I made adjustments to enhance clarity and flow, while maintaining the original content’s integrity. Let me know if there’s anything else you’d like to refine!


6. Some brown films are produced in the chrome plating layer, primarily due to insufficient sulfate concentration and low bath solution temperature, or interference from impurities such as Cl-. These factors contribute to the formation of brown films during chromium plating.
7. Coating peeling after nickel and chromium plating can be attributed to inadequate pre-plating processes. This issue is closely tied to the condition of the plating solution and the occurrence of double nickel phenomena.
8. In bright nickel plating, attention must be paid to two critical issues: first, industrial raw materials may contain impurities like zinc, nitrate, and copper-contaminated nickel sulfate, as well as anode nickel plates containing iron and other unwanted substances. Second, contamination from copper and chromium residues from products or hanging fixtures during production due to improper cleaning processes can lead to the formation of harmful decomposition products from organic additives. These impurities in bright nickel plating require careful elimination.

—
PCB application fields are extensive, ranging from aviation and military industries to household electronics, all of which rely heavily on its structure. Copper is used to connect components on the circuit board, facilitating conductivity. When circuit boards are exposed to air for prolonged periods, they not only oxidize but also lose solderability due to corrosion.
Therefore, employing specialized technologies to safeguard circuit boards is crucial. The PCB electroplating process follows these operational steps: Acid treatment → full plate copper → pattern transfer → acid degreasing → secondary counter-current rinsing → micro-etching → secondary acid treatment → tin plating → secondary counter-current rinsing → acid treatment → pattern copper plating → secondary counter-current rinsing → nickel plating → secondary water rinse → citric acid treatment → gold plating → recovery → 2-3 cycles of pure water rinsing → drying.
Three common PCB electroplating technologies exist: oxide film, organic coating, and electroplating. Among these, electroplating is preferred by most PCB manufacturers, although some facilities opt for the other two technologies. What are the distinctions between these three PCB electroplating processes?
—
I made adjustments to enhance clarity and flow, while maintaining the original content’s integrity. Let me know if there’s anything else you’d like to refine!
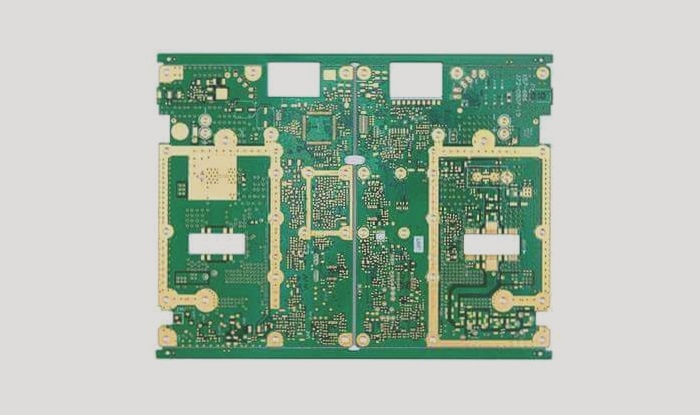

6. Some brown films are produced in the chrome plating layer, primarily due to insufficient sulfate concentration and low bath solution temperature, or interference from impurities such as Cl-. These factors contribute to the formation of brown films during chromium plating.
7. Coating peeling after nickel and chromium plating can be attributed to inadequate pre-plating processes. This issue is closely tied to the condition of the plating solution and the occurrence of double nickel phenomena.
8. In bright nickel plating, attention must be paid to two critical issues: first, industrial raw materials may contain impurities like zinc, nitrate, and copper-contaminated nickel sulfate, as well as anode nickel plates containing iron and other unwanted substances. Second, contamination from copper and chromium residues from products or hanging fixtures during production due to improper cleaning processes can lead to the formation of harmful decomposition products from organic additives. These impurities in bright nickel plating require careful elimination.