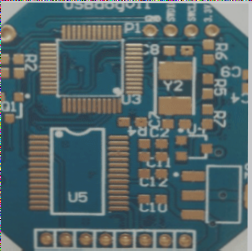
1. With the rapid advancement of integrated circuit technology, the layers of circuit boards have progressed from the initial single-layer and double-layer designs to multi-layer boards with a dozen or more layers.
2. This evolution presents significant challenges for many individuals when it comes to identifying the number of PCB layers.
3. As the number of layers increases, the difficulty in distinguishing the layer count also rises.
4. Therefore, it is essential for professionals in the circuit board industry to master an efficient method for quickly identifying the number of PCB layers.
5. The substrate of the circuit board is composed of insulating and heat-resistant materials that are not easily bent.
6. The small circuit elements visible on the surface are made of copper foil.
7. Initially, the copper foil covered the entire circuit board, but portions were etched away during the manufacturing process, leaving behind a network of small circuits.
8. These lines are referred to as traces or wiring, and they facilitate electrical connections between components on the circuit board.

1. Typically, the color of a circuit board is green or brown, which represents the solder mask.
2. This solder mask acts as an insulating protective layer that safeguards the copper traces and prevents components from being incorrectly soldered.
3. Multilayer boards are now prevalent in motherboards and graphics cards, significantly expanding the wiring area.
4. These boards incorporate multiple single or double-sided wiring layers, with an insulating layer pressed between each to enhance functionality.
5. The number of layers in a PCB indicates the number of independent wiring layers present, usually in an even count, including the two outermost layers.
6. Common PCB structures typically consist of 4 to 8 layers, and while one might identify the number of layers by examining the cut edge of the PCB, it requires keen eyesight.
7. Therefore, let me share a technique for assessing the number of PCB layers effectively.
8. The circuit connections in multilayer boards utilize buried and blind via technologies.
9. Most motherboards and graphics cards feature 4-layer PCBs, while some utilize 6, 8, or even 10 layers.
10. To distinguish the number of layers, observe the via holes: in a 4-layer board, the vias connect the first and fourth layers for wiring, with the remaining layers allocated for ground and power.
11. If vias appear on the front of the PCB but are absent on the reverse, it indicates a 6 or 8-layer board.
12. Conversely, if the same via holes are visible on both sides, it is likely a 4-layer board.
13. A tip for determining the number of PCB layers: position the motherboard or display card toward a light source; if light passes through the guide holes, it suggests a 6 or 8-layer board; otherwise, it is a 4-layer board.
2. This evolution presents significant challenges for many individuals when it comes to identifying the number of PCB layers.
3. As the number of layers increases, the difficulty in distinguishing the layer count also rises.
4. Therefore, it is essential for professionals in the circuit board industry to master an efficient method for quickly identifying the number of PCB layers.
5. The substrate of the circuit board is composed of insulating and heat-resistant materials that are not easily bent.
6. The small circuit elements visible on the surface are made of copper foil.
7. Initially, the copper foil covered the entire circuit board, but portions were etched away during the manufacturing process, leaving behind a network of small circuits.
8. These lines are referred to as traces or wiring, and they facilitate electrical connections between components on the circuit board.

1. Typically, the color of a circuit board is green or brown, which represents the solder mask.
2. This solder mask acts as an insulating protective layer that safeguards the copper traces and prevents components from being incorrectly soldered.
3. Multilayer boards are now prevalent in motherboards and graphics cards, significantly expanding the wiring area.
4. These boards incorporate multiple single or double-sided wiring layers, with an insulating layer pressed between each to enhance functionality.
5. The number of layers in a PCB indicates the number of independent wiring layers present, usually in an even count, including the two outermost layers.
6. Common PCB structures typically consist of 4 to 8 layers, and while one might identify the number of layers by examining the cut edge of the PCB, it requires keen eyesight.
7. Therefore, let me share a technique for assessing the number of PCB layers effectively.
8. The circuit connections in multilayer boards utilize buried and blind via technologies.
9. Most motherboards and graphics cards feature 4-layer PCBs, while some utilize 6, 8, or even 10 layers.
10. To distinguish the number of layers, observe the via holes: in a 4-layer board, the vias connect the first and fourth layers for wiring, with the remaining layers allocated for ground and power.
11. If vias appear on the front of the PCB but are absent on the reverse, it indicates a 6 or 8-layer board.
12. Conversely, if the same via holes are visible on both sides, it is likely a 4-layer board.
13. A tip for determining the number of PCB layers: position the motherboard or display card toward a light source; if light passes through the guide holes, it suggests a 6 or 8-layer board; otherwise, it is a 4-layer board.