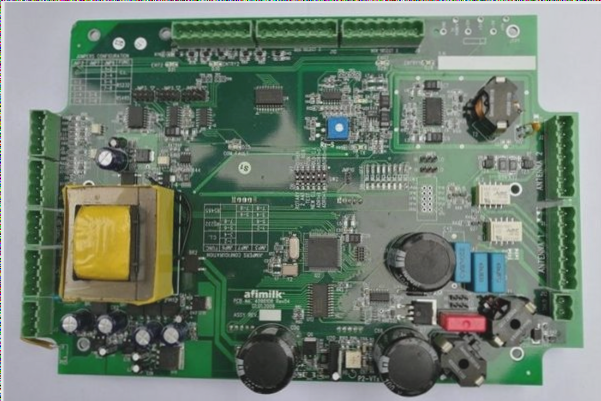
**PCB Performance Specification**
1. FPC, or flexible printed circuit board, is a highly reliable type of PCB constructed from polyimide or polyester film as its substrate. It is characterized by high wiring density, lightweight, thin profile, and excellent flexibility.
The Chinese term for flexible circuit board, often abbreviated as soft board, highlights features such as lightweight and thinness, along with various pre-production modifications. Throughout the manufacturing process, care must be taken to prevent excessive openings and short circuits, which can lead to low yield rates or complications in drilling and laminating. Issues like rough cutting techniques and material replenishment can render FPC boards unusable, necessitating a careful evaluation of material choices to meet customer specifications for their flexible circuit boards.
Pre-production treatment is crucial. There are three key aspects of pre-production treatment that must be addressed, all handled by engineers. The first is the engineering evaluation of the FPC board, which primarily assesses whether the customer’s design can be manufactured and if the company’s production capabilities align with the customer’s requirements and cost expectations.
If the project evaluation is approved, the next step is to immediately prepare materials and ensure the supply of raw materials for each production stage. The engineer will then process the customer’s CAD design, Gerber files, and other engineering documents to align with the production environment and the specifications of the manufacturing equipment. Subsequently, the production drawings, along with the MI (Engineering Process Card) and other relevant documents, will be transferred to the production, document control, procurement, and related departments, entering the standard production workflow.
**Modification of the production process:** Double-sided panel cutting – drilling – PTH – electroplating – pre-treatment – dry film application – alignment – exposure – development – pattern plating – film removal – pre-processing – dry film application – alignment – exposure – development – etching – film stripping – surface treatment – masking film application – restriction – curing – immersion nickel gold – character printing – cutting – electrical testing – punching – final inspection – packaging – shipment.
2. Let’s discuss the characteristics of the FPC sub-board machine:
1. Compact structure with robust rigidity, designed for simple and safe operation;
2. Multiple molds can be replaced easily, facilitating convenient mold changes;
3. The lower mold automatically adjusts, making it easy to place and retrieve products, with finished items dropping directly into a drawer;
4. Reduces internal stress during board cutting, preventing tin cracking;
5. Offers extremely high efficiency for punching semi-finished PCBs and FPCs.
**Solutions to challenges faced by circuit boards:**
Firstly, it is essential to understand the corrosion process of PCB circuit boards. The corrosive solution typically consists of ferric chloride and water. Ferric chloride is a solid that readily absorbs moisture from the air, so it should be stored in a sealed container. When preparing the ferric chloride solution, a common ratio is 40% ferric chloride to 60% water. Increasing the amount of ferric chloride or using warm water (not hot, to prevent paint detachment) can accelerate the reaction. It is important to note that ferric chloride is corrosive, so avoid direct contact with skin and clothing. A basic plastic basin can be used as a reaction vessel, just large enough to accommodate the circuit board.
Begin the corrosion process from the edge of the PCB. Once the uncoated copper foil starts to corrode, promptly remove the circuit board to prevent the paint from eroding essential circuits. At this stage, rinse the board and gently scrape off the paint using bamboo sticks (the paint tends to float out of the liquid, making it easier to remove).
If scraping is difficult, rinse the board with warm water instead. Then dry it thoroughly and polish it with sandpaper to reveal the shiny copper foil, completing the printed circuit board. To preserve the results, polished PCB circuit boards are often coated with a rosin solution, which aids in soldering and prevents oxidation.
If you have any PCB manufacturing needs, please do not hesitate to contact me.Contact me