The Advantages of Selective Soldering in PCB Fabrication
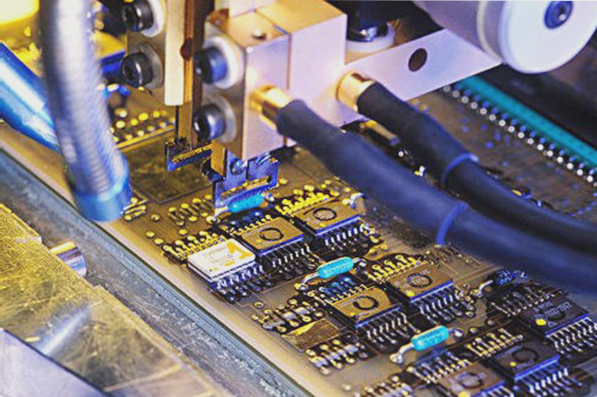
Selective soldering offers unique benefits compared to traditional wave soldering techniques. In wave soldering, the entire PCB is submerged in liquid solder, while selective soldering targets specific areas, preventing overheating and ensuring precise solder joints.
One key advantage of selective soldering is its ability to apply flux only to targeted areas, reducing waste and improving efficiency. This method is ideal for soldering through-hole components, making it a valuable technique in modern PCB manufacturing.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, PCB manufacturers face both challenges and opportunities. By embracing environmentally friendly practices, such as using FPC flexible circuit boards, manufacturers can stay ahead of the curve and meet market demands.
The rise of the Internet has revolutionized marketing and accelerated the adoption of FPC flexible circuit boards. This shift towards digital platforms has also highlighted the importance of environmental sustainability in PCB production.
With the integration of environmental data centers and green procurement practices, PCB factories can navigate the evolving landscape of environmental protection and contribute to a greener, more sustainable future.
- Selective soldering offers precise soldering of specific areas on the PCB.
- Flux is applied only to targeted areas, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
- Environmental regulations present challenges and opportunities for PCB manufacturers.
- Embracing FPC flexible circuit boards can lead to further development opportunities.
- The Internet era has accelerated the adoption of FPC flexible circuit boards.
- Environmental information data centers and green procurement practices are shaping the future of PCB production.