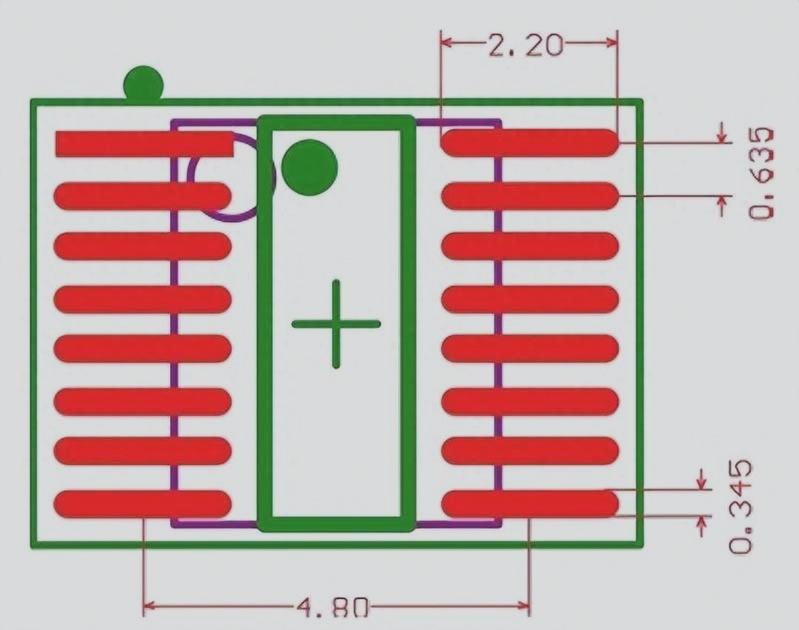
Sure! What specific aspects of the article would you like to focus on for the modifications?

I’m happy to help with that! Here’s the revised version of your article with the same line structure:
—
**Reason 3:** Recognition system issues such as poor vision, unclean laser lenses, foreign objects interfering with recognition, improper selection of the recognition light source, or insufficient intensity or grayscale, can lead to malfunctions in the recognition system.
**Countermeasures:** Clean and wipe the recognition system’s surface to ensure it is free of foreign matter and oil. Adjust the intensity and gray levels of the light source, and replace any faulty components in the recognition system.
**Reason 4:** Position-related issues can occur when the suction nozzle is not centered on the material during pickup, or if the picking height is incorrect (typically, the component is pressed down by 0.05mm upon contact), leading to misalignment. This misalignment can cause the recognition system to reject valid materials.
**Countermeasures:** Adjust the reclaiming position, height, and other relevant parameters.
**Reason 5:** Vacuum-related problems may arise from insufficient air pressure, blocked vacuum pipes, or leaks, resulting in inadequate suction and the inability to retrieve materials, which may fall during transport.
**Countermeasures:** Adjust the air pressure to the specified requirements for the equipment (generally 0.5–0.6 MPa for placement machines), clean and unclog the air pressure lines, and repair any leaks in the air circuit.
**Reason 6:** Issues with the placement machine’s program may stem from incorrect component parameter settings. If the actual size, brightness, or other parameters of incoming materials do not match, recognition failures can occur, leading to rejection.
**Countermeasures:** Modify the component parameters and identify the optimal parameter values for the components.
**Reason 7:** Problems with incoming materials can include non-standardized items or unqualified products, such as oxidized pins.
**Countermeasures:** Implement stringent inspections of incoming materials through IQC and maintain contact with PCB component suppliers.
**Reason 8:** Feeder issues may arise from deformation, poor feeding (e.g., damaged ratchet gears, misaligned material belts, foreign objects under the feeder, aging springs, or inadequate power), leading to insufficient retrieval and potential damage to the feeder.
**Countermeasures:** Correct the feeder alignment, clean the feeder platform, and replace any damaged components or feeders.
According to relevant studies, static electricity can also contribute to PCBA rejection, so proper grounding of the placement machine and anti-static measures in the production area are essential.
While some PCBA rejection is normal, a high rejection rate can severely impact production efficiency and costs, necessitating prompt resolution. In cases of significant PCBA rejection, on-site personnel should be consulted to describe the issue. Analyzing the aforementioned seven reasons will facilitate effective problem identification and resolution, ultimately improving production efficiency, though it may require substantial machine downtime.
Controlling every aspect of the PCBA production process is vital for the efficient production of high-quality PCB circuit boards. Our company has consistently adhered to a quality-first approach in PCBA processing, providing high-quality services to both domestic and international customers for over a decade.
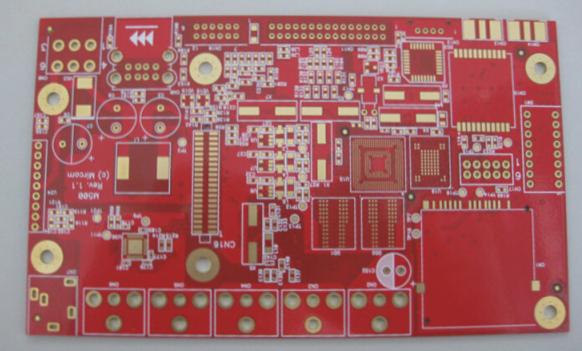
I’m happy to help with that! Here’s the revised version of your article with the same line structure:
—
**Reason 3:** Recognition system issues such as poor vision, unclean laser lenses, foreign objects interfering with recognition, improper selection of the recognition light source, or insufficient intensity or grayscale, can lead to malfunctions in the recognition system.
**Countermeasures:** Clean and wipe the recognition system’s surface to ensure it is free of foreign matter and oil. Adjust the intensity and gray levels of the light source, and replace any faulty components in the recognition system.
**Reason 4:** Position-related issues can occur when the suction nozzle is not centered on the material during pickup, or if the picking height is incorrect (typically, the component is pressed down by 0.05mm upon contact), leading to misalignment. This misalignment can cause the recognition system to reject valid materials.
**Countermeasures:** Adjust the reclaiming position, height, and other relevant parameters.
**Reason 5:** Vacuum-related problems may arise from insufficient air pressure, blocked vacuum pipes, or leaks, resulting in inadequate suction and the inability to retrieve materials, which may fall during transport.
**Countermeasures:** Adjust the air pressure to the specified requirements for the equipment (generally 0.5–0.6 MPa for placement machines), clean and unclog the air pressure lines, and repair any leaks in the air circuit.
**Reason 6:** Issues with the placement machine’s program may stem from incorrect component parameter settings. If the actual size, brightness, or other parameters of incoming materials do not match, recognition failures can occur, leading to rejection.
**Countermeasures:** Modify the component parameters and identify the optimal parameter values for the components.
**Reason 7:** Problems with incoming materials can include non-standardized items or unqualified products, such as oxidized pins.
**Countermeasures:** Implement stringent inspections of incoming materials through IQC and maintain contact with PCB component suppliers.
**Reason 8:** Feeder issues may arise from deformation, poor feeding (e.g., damaged ratchet gears, misaligned material belts, foreign objects under the feeder, aging springs, or inadequate power), leading to insufficient retrieval and potential damage to the feeder.
**Countermeasures:** Correct the feeder alignment, clean the feeder platform, and replace any damaged components or feeders.
According to relevant studies, static electricity can also contribute to PCBA rejection, so proper grounding of the placement machine and anti-static measures in the production area are essential.
While some PCBA rejection is normal, a high rejection rate can severely impact production efficiency and costs, necessitating prompt resolution. In cases of significant PCBA rejection, on-site personnel should be consulted to describe the issue. Analyzing the aforementioned seven reasons will facilitate effective problem identification and resolution, ultimately improving production efficiency, though it may require substantial machine downtime.
Controlling every aspect of the PCBA production process is vital for the efficient production of high-quality PCB circuit boards. Our company has consistently adhered to a quality-first approach in PCBA processing, providing high-quality services to both domestic and international customers for over a decade.