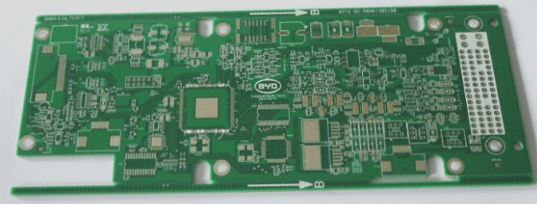
PCBA Processing: A Comprehensive Overview
Design Phase
PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) begins with the design phase, which involves schematic and PCB design. The schematic design creates circuit diagrams, determining component connections and placements. PCB design transforms these diagrams into PCB layouts, organizing components and establishing circuit connections while considering size, shape, and layer requirements.
Procurement Process
During PCBA processing, various components, circuit boards, and materials need to be procured. Factors such as component quality, pricing, delivery time, and supplier reliability must be carefully evaluated. It is crucial to ensure purchased components meet design specifications and provide reliable performance.
Manufacturing Stage
PCBA manufacturing involves transforming PCBs into printed circuit boards. This includes cutting, punching, surface treatments like gold plating and solder resist, copper lamination for conductivity, and screen printing for solder paste application in preparation for component soldering.
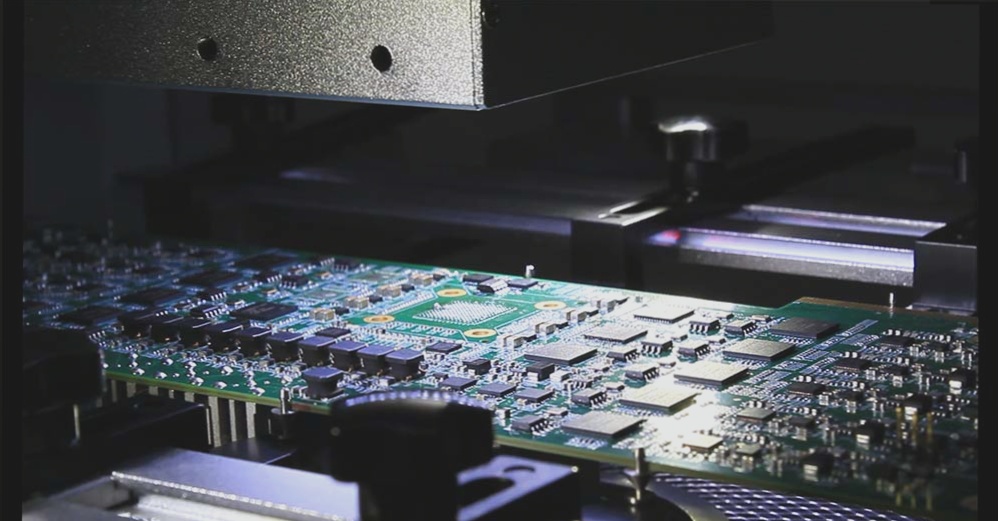
Assembly Process
Assembly integrates components and circuit boards to create a complete circuit system. SMT (surface mount technology) and THT (through-hole technology) are used, with SMT being the primary method. Components are accurately placed using automated equipment and soldered to the board to ensure reliability and stability.
Testing and Quality Assurance
Testing is essential to assess PCBA function and reliability. This includes appearance inspection, functional testing, performance evaluation, and environmental testing. These tests ensure the PCBA meets requirements and performs reliably under various conditions.
Conclusion
The PCBA processing journey involves meticulous control in design, procurement, manufacturing, assembly, and testing phases to guarantee quality and reliability. Continuous improvement and optimization are crucial for enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. By focusing on quality control at each stage, high-quality PCBA products can be consistently produced.