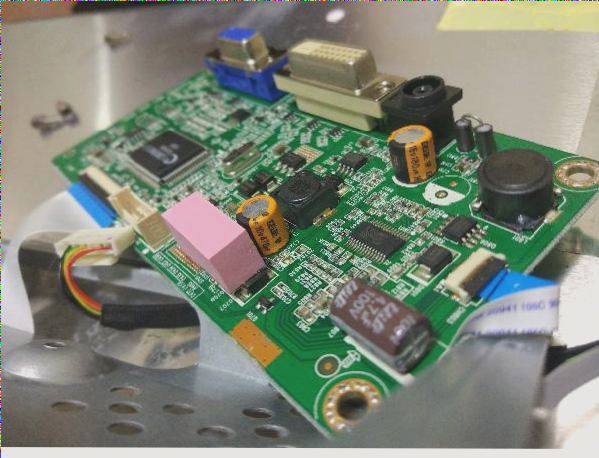
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) Design Guidelines for Optimal Performance
Layout
- Consider PCB board size carefully to balance impedance, anti-noise ability, and cost.
- Strategically place special components to optimize performance.
- Arrange circuit components by functional units to minimize interference.
- Ensure proper spacing between components to prevent short circuits.
- Secure heavier components with brackets for stability.
- Position heat-generating components away from thermal-sensitive elements for efficient dissipation.
- Integrate adjustable components structurally within the machine for ease of access.
Wiring
- Minimize parallel runs for input and output terminals to prevent feedback coupling.
- Determine wire width based on current load and circuit requirements.
- Use arc-shaped bends to maintain electrical performance in high-frequency circuits.
Pad
- Ensure proper pad dimensions to prevent virtual solder formation.
- Design for Anti-Interference Measures
Power Cord Design
- Adjust power line width based on current for enhanced loop resistance.
- Align ground wire direction with data transmission for improved anti-noise capabilities.
Ground Design
- Segregate digital and analog grounds to minimize interference.
- Use thicker ground wires for stability against current variations.
Decoupling Capacitor Configuration
- Bridge power input with electrolytic capacitors for noise mitigation.
- Place ceramic capacitors strategically for stable operation.
- Connect decoupling capacitors for devices with power fluctuations.
By adhering to these PCB design principles, you can ensure optimal performance, reduce interference, and enhance the overall functionality of your electronic circuits.