The Significance of Copper Clad Printed Circuit Boards in Electronics
Copper clad printed circuit boards (PCBs) are essential in the electronics industry, known for their copper-clad laminates that are crucial for high-frequency applications. These laminated boards, made by soaking copper-clad laminates and reinforcing materials in resin, find wide usage in computers, televisions, and various electronic devices.
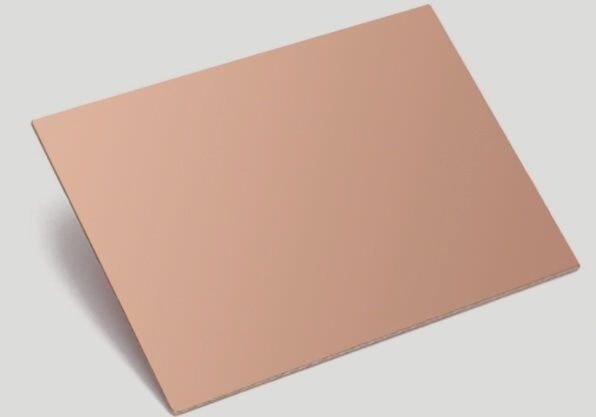

The Role of Copper Coating in PCBs
- Enhanced Functionality: Copper coating on PCBs improves anti-interference, reduces ground wire impedance, and decreases voltage drop, enhancing the performance of circuit boards.
- Material Composition: Copper clad circuit boards, comprising non-conductive substrates like FR4 and copper foil layers, provide conductive paths for electronic circuits.
The Function of Copper Clad Circuit Boards
- Crucial Substrate: Copper clad circuit boards play a vital role in interconnecting, conducting, insulating, and supporting PCBs, influencing signal transmission speed and energy loss.
- Usage: These boards are used in manufacturing PCBs, facilitating circuit connections, soldering, and electronic component integration.
The Role of PCB Copper Coating
- Grounding and Shielding: PCB copper coating aids in grounding, EMI shielding, heat dissipation, and copper balance for efficient circuit operation.
- Heat Dissipation: Copper grounding helps dissipate heat from high-power components, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
- Circuit Path Optimization: Surface-grounded copper coating provides shorter return paths for high-current equipment, improving circuit efficiency.
The Importance of Copper Clad Circuit Boards in PCB Manufacturing
Copper clad circuit boards play a crucial role in the manufacturing process of printed circuit boards (PCBs). These boards are essentially plate-like materials that are created by immersing electronic fiberglass cloth or other reinforcing materials in resin. One or both sides of the material are then covered with copper foil and hot pressed.
- Conductivity: The copper on the circuit board allows for the flow of electrical currents, making it an essential component for the functionality of the PCB.
- Insulation: The materials used in the board provide insulation to prevent short circuits and ensure the proper functioning of the electronic components.
- Support: Copper clad circuit boards offer structural support to the PCB, ensuring its durability and longevity.
Latest Developments in PCB Manufacturing
Recent advancements in PCB manufacturing include the use of advanced materials such as flexible substrates and high-density interconnects, leading to smaller and more efficient electronic devices. Additionally, the integration of automated assembly processes has improved production efficiency and consistency in PCB manufacturing.
Overall, copper clad circuit boards remain an essential component in the production of PCBs, providing the necessary foundation for the functionality and reliability of electronic devices.