1. The material used in the current PCB manufacturing process is metal-clad copper, known for its excellent heat dissipation function.
2. Generally speaking, single-layer LED PCB boards are composed of three layers: the circuit layer, ceramic layer, and insulation layer.

LEDs are positioned directly on the circuit layer where they are mounted. The heat generated by the LEDs swiftly conducts to the substrate layer for dissipation, passing through the insulation layer before dissipating through the substrate. Copper, aluminum, and iron are commonly utilized as thermal conductive layer materials, with iron cores predominantly employed in high-end PCBs for motors requiring significant heat dissipation. LEDs are affixed onto the surface of the circuit layer, and heat generated during PCB operation efficiently transfers through the insulation layer to the metal substrate. This heat is subsequently dissipated through the metal substrate to achieve effective device cooling.
Type of LED PCB boards
1) Single-layer LED PCB board
This comprises a substrate layer and a conductive layer, protected by solder mask and screen printing. This type of LED PCB lacks circuit layers on the reverse side, making it exceptionally thin and lightweight.
2) Double-layer LED PCB board
In comparison to single-layer PCBs, this variant features two copper layers, resulting in increased weight due to the additional conductive layer. Double-layer PCBs exhibit robust durability, capable of withstanding higher currents and offering superior heat dissipation.
LED stands for light-emitting diode, a semiconductor diode soldered onto printed circuit boards, where electrical connections enable light emission. Chips are integrated with heat sinks and ceramic bases for efficient heat dissipation.
Two types of circuit boards are commonly used for LED fluorescent lamps: aluminum substrate and fiberglass board.
The aluminum substrate structure comprises a circuit board layer, thermal insulation layer, and aluminum base layer.
1) Circuit board layer: This layer primarily utilizes copper foil with high current-carrying capacity, and its thickness directly influences the aluminum substrate’s cost due to the relatively high price of copper.
2) Thermal insulation layer: Optimal thermal insulation is achieved with specialized ceramic polymers.
3) Aluminum substrate: Typically composed of aluminum sheet as a robust structural support, although copper plate may be used for enhanced thermal conductivity. Essential qualities include excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to bending.
4) Fiberglass board: Available in several types, including glass fiber board, single-sided copper foil glass fiber board, double-sided copper foil laminated fiberglass board, and perforated glass copper foil laminated fiberglass board.
a: Single-sided copper foil fiberglass board: Features copper foil on one side to augment heat dissipation area, priced slightly higher than standard fiberglass boards.
b: Double-sided copper foil laminated fiberglass board: Copper foil on both sides enhances performance and cost, surpassing single-sided copper foil boards.
c: Perforated glass copper foil laminated fiberglass board: Specialized structure with copper foil on both sides and numerous small holes facilitating front-to-back copper foil connectivity for efficient heat dissipation via aluminum profiles.
LED PCB boards are versatile, with widespread applications and promising market prospects due to advantages such as high brightness, low power consumption, long lifespan, and flexibility.
2. Generally speaking, single-layer LED PCB boards are composed of three layers: the circuit layer, ceramic layer, and insulation layer.
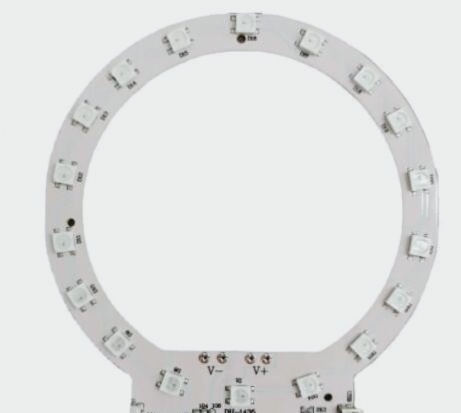

LEDs are positioned directly on the circuit layer where they are mounted. The heat generated by the LEDs swiftly conducts to the substrate layer for dissipation, passing through the insulation layer before dissipating through the substrate. Copper, aluminum, and iron are commonly utilized as thermal conductive layer materials, with iron cores predominantly employed in high-end PCBs for motors requiring significant heat dissipation. LEDs are affixed onto the surface of the circuit layer, and heat generated during PCB operation efficiently transfers through the insulation layer to the metal substrate. This heat is subsequently dissipated through the metal substrate to achieve effective device cooling.
Type of LED PCB boards
1) Single-layer LED PCB board
This comprises a substrate layer and a conductive layer, protected by solder mask and screen printing. This type of LED PCB lacks circuit layers on the reverse side, making it exceptionally thin and lightweight.
2) Double-layer LED PCB board
In comparison to single-layer PCBs, this variant features two copper layers, resulting in increased weight due to the additional conductive layer. Double-layer PCBs exhibit robust durability, capable of withstanding higher currents and offering superior heat dissipation.
LED stands for light-emitting diode, a semiconductor diode soldered onto printed circuit boards, where electrical connections enable light emission. Chips are integrated with heat sinks and ceramic bases for efficient heat dissipation.
Two types of circuit boards are commonly used for LED fluorescent lamps: aluminum substrate and fiberglass board.
The aluminum substrate structure comprises a circuit board layer, thermal insulation layer, and aluminum base layer.
1) Circuit board layer: This layer primarily utilizes copper foil with high current-carrying capacity, and its thickness directly influences the aluminum substrate’s cost due to the relatively high price of copper.
2) Thermal insulation layer: Optimal thermal insulation is achieved with specialized ceramic polymers.
3) Aluminum substrate: Typically composed of aluminum sheet as a robust structural support, although copper plate may be used for enhanced thermal conductivity. Essential qualities include excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to bending.
4) Fiberglass board: Available in several types, including glass fiber board, single-sided copper foil glass fiber board, double-sided copper foil laminated fiberglass board, and perforated glass copper foil laminated fiberglass board.
a: Single-sided copper foil fiberglass board: Features copper foil on one side to augment heat dissipation area, priced slightly higher than standard fiberglass boards.
b: Double-sided copper foil laminated fiberglass board: Copper foil on both sides enhances performance and cost, surpassing single-sided copper foil boards.
c: Perforated glass copper foil laminated fiberglass board: Specialized structure with copper foil on both sides and numerous small holes facilitating front-to-back copper foil connectivity for efficient heat dissipation via aluminum profiles.
LED PCB boards are versatile, with widespread applications and promising market prospects due to advantages such as high brightness, low power consumption, long lifespan, and flexibility.