Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs): Essential Components in Electronic Devices
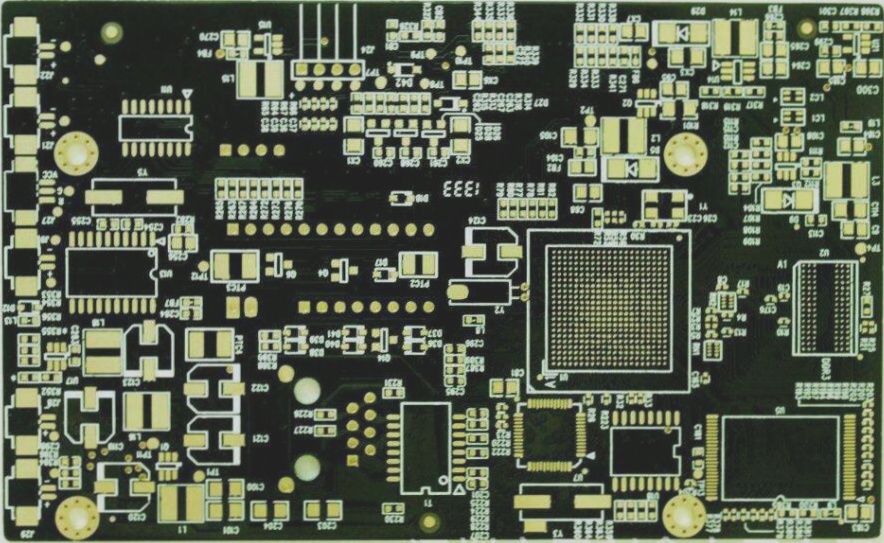
A printed circuit board (PCB) is a crucial element found in almost every electronic device. It serves as the foundation for mounting electronic components and establishing electrical connections among them. With the advancement of technology, PCBs have evolved to accommodate a higher number of components, resulting in more intricate circuit arrangements.
Key Features of a Standard PCB
- PCBs consist of a base material made from insulating and rigid materials, with a surface layer of copper foil.
- The copper foil is etched to form conductor patterns or traces, enabling electrical connections.
- The bare board, known as a “Printed Wiring Board” (PWB), is the initial form of a PCB without mounted components.
PCB Components and Connections

Components on a PCB can be easily installed or removed using sockets, such as the ZIF socket, which allows for effortless component insertion and removal. Additionally, edge connectors, known as “golden fingers,” facilitate connections between PCBs, enabling the integration of various interface cards with the motherboard.
Understanding PCB Design Types
- Single-Sided Boards: Basic PCBs with components on one side and routing on the other, suitable for simpler circuit designs.
- Double-Sided Boards: Feature traces on both sides interconnected by vias, offering more flexibility for routing complex circuits.
- Multi-Layer Boards: Stack multiple single- or double-sided boards with insulating layers in between, allowing for high-capacity routing and intricate designs.
The evolution of PCB technology has led to the development of multi-layer boards with advanced routing capabilities, making them indispensable in modern electronic devices.