The Importance of Quality Management in PCBA Electronic Manufacturing
1. PCB Production
Quality PCB production is crucial for electronic manufacturing. Factors such as substrate material, dust-free exposure, and copper coating play a significant role in ensuring high-quality PCBs. When selecting a PCB manufacturer, consider their adherence to quality standards and cleanliness in the production environment.
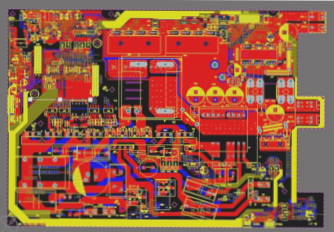
2. Component Procurement
Sourcing components from reputable brands is essential to avoid batch defects. Implementing Incoming Quality Control (IQC) processes can help verify the consistency and quality of incoming materials, ensuring a smooth production process.
3. Surface Mount Technology (SMT) Chip Processing
During the SMT chip processing phase, uniform solder paste printing and precise programming of SMT machines are critical for high-precision ICs and BGAs placement. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) and In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) inspections are necessary to maintain quality standards.
4. Test Points and Analysis
Design engineers designate test points on PCBs for ICT and FCT tests. Analyzing circuit voltage, current curves, and product functionality test results are essential for establishing acceptance criteria and improving products continuously.
5. Human Management in Manufacturing
Effective human management is as crucial as advanced equipment in PCBA manufacturing. Developing standardized production procedures and continuous optimization of production management processes are vital for meeting market demands and ensuring success.