In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, effective communication tools have become one of the cornerstones of success across all industries. As new devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops are introduced almost daily, the printed circuit board (PCB) industry has adapted by advancing its electronic and design solutions. These innovations aim to streamline the communication tool manufacturing process, meeting the growing demand for high-performance devices. Among these advancements, microwave and radio frequency (RF) PCBs have emerged as crucial components in the production of modern electronic equipment. This article explores the technical aspects of microwave and RF PCBs, while also highlighting the latest PCB manufacturing techniques that enable high-speed signal transmission and enhanced performance in electronic systems.
### Advancements in RF and Microwave PCB Manufacturing
The ongoing modernization of communication equipment, which plays a vital role in business operations, has spurred significant growth across various industries. In response to this demand, PCB manufacturers and experts have developed a new generation of RF and microwave PCBs, creating innovative products that cater to the specific needs of electronic manufacturers worldwide. These specialized PCBs are designed to deliver reliable performance under challenging conditions, offering enhanced stability even as environmental factors such as amplitude, current levels, and voltage fluctuations come into play.
Microwave PCBs, in particular, have become a specialized field of expertise. They are crafted to meet the rigorous requirements of high-frequency applications, such as wireless communication, radar systems, and satellite technology. The RF PCB, on the other hand, is designed to withstand environmental stress while ensuring minimal signal loss and maximum efficiency in high-speed data transmission.
To optimize the performance of RF and microwave PCBs, manufacturers employ advanced design techniques and materials. These innovations enable the creation of PCBs that support faster signal speeds, improved signal integrity, and reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI). As a result, these PCBs are crucial in the production of devices that require high-frequency performance, such as smartphones, communication satellites, and other cutting-edge electronic instruments.
In conclusion, the continuous evolution of communication tools and the increasing demands of modern electronics have driven significant advancements in PCB technology. Microwave and RF PCBs are at the forefront of these innovations, offering the precise electronic and design solutions required to meet the high-performance standards of today’s electronic devices. By leveraging new manufacturing methods, the industry is poised to further enhance the capabilities of communication tools, ensuring they remain reliable and efficient in an ever-changing technological landscape.

The term “microwave circuit” is derived from the Greek word “micros,” meaning very small. In microwave or radio frequency (RF) circuits, the wavelength is significantly smaller than the physical dimensions of the circuit. This results in high-speed signals that interact with circuit components. Microwave PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) use specialized laminated materials with unique mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties, unlike traditional FR4 materials. These materials were introduced in the 20th century, facilitating advancements such as microwave integrated circuits (MIC), waveguide and coaxial technologies, and monolithic microwave integrated circuits (MMIC).
Microwave PCBs are primarily used in avionics, wireless communication applications, and devices that operate in medium- to high-frequency ranges for signal control. These PCBs are key in applications such as military radars, mobile phones, laptops, and more. There is often confusion between standard PCBs and microwave PCBs, but the distinction mainly lies in the physical and electrical characteristics of the dielectric material used. RF circuits typically operate in the range of 500 MHz to 2 GHz. A layout above 100 MHz is considered an RF PCB, while anything over 2 GHz is classified as microwave frequency.
To understand these differences, it’s helpful to consider signal speed. High-performance microwave PCBs require advanced manufacturing methods to optimize performance, enabling high-frequency output for RF and microwave applications. The materials selected for PCB manufacturing must have specific properties, such as dielectric constant (ER), coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), and loss tangent, to ensure efficient signal transmission with minimal impedance. This leads to stable, durable PCBs that can withstand extreme temperatures and climates, while also ensuring precise placement of fine-pitch components.
Multilayer PCBs are commonly used in RF and microwave applications. Key design considerations for these PCBs include low-impedance ground planes, which help minimize signal distortion, and maintaining sufficient spacing between RF signal lines to prevent crosstalk. Additionally, effective thermal management is essential, with copper shapes and flatness being critical factors for heat dissipation. A solid ground plane is necessary to reduce inductance, which can interfere with signal integrity.
The packaging technologies for microwave circuits can be broadly divided into two categories: circuit card components and hybrid circuits. Hybrid circuit packaging, which combines different technologies in a single unit, is particularly effective in high-reliability applications, such as military and aerospace systems. In contrast, circuit card components are more cost-effective and are suitable for standard, quality RF solutions. It is crucial for PCB manufacturers to have a deep understanding of RF and microwave technologies before starting a project.
When designing or reworking an RF or microwave PCB, it’s important to consult with experts in the field to optimize both cost and performance. This ensures the project stays on schedule and within budget. To deliver high-performance microwave PCBs, manufacturers rely on advanced PCB engineering technologies, coupled with an experienced team of experts. A focus on quality and strong customer relationships is vital to success, as is providing excellent technical support and fast turnaround times to meet the needs of diverse industries.
In conclusion, the manufacturing of RF and microwave PCBs involves complex considerations such as material selection, signal integrity, and thermal management. Expert guidance and an in-depth understanding of these factors are essential to producing high-quality, reliable products. By leveraging the latest technologies and best practices, manufacturers can ensure the success of their projects and meet the demanding requirements of modern communication and defense systems.
### Advancements in RF and Microwave PCB Manufacturing
The ongoing modernization of communication equipment, which plays a vital role in business operations, has spurred significant growth across various industries. In response to this demand, PCB manufacturers and experts have developed a new generation of RF and microwave PCBs, creating innovative products that cater to the specific needs of electronic manufacturers worldwide. These specialized PCBs are designed to deliver reliable performance under challenging conditions, offering enhanced stability even as environmental factors such as amplitude, current levels, and voltage fluctuations come into play.
Microwave PCBs, in particular, have become a specialized field of expertise. They are crafted to meet the rigorous requirements of high-frequency applications, such as wireless communication, radar systems, and satellite technology. The RF PCB, on the other hand, is designed to withstand environmental stress while ensuring minimal signal loss and maximum efficiency in high-speed data transmission.
To optimize the performance of RF and microwave PCBs, manufacturers employ advanced design techniques and materials. These innovations enable the creation of PCBs that support faster signal speeds, improved signal integrity, and reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI). As a result, these PCBs are crucial in the production of devices that require high-frequency performance, such as smartphones, communication satellites, and other cutting-edge electronic instruments.
In conclusion, the continuous evolution of communication tools and the increasing demands of modern electronics have driven significant advancements in PCB technology. Microwave and RF PCBs are at the forefront of these innovations, offering the precise electronic and design solutions required to meet the high-performance standards of today’s electronic devices. By leveraging new manufacturing methods, the industry is poised to further enhance the capabilities of communication tools, ensuring they remain reliable and efficient in an ever-changing technological landscape.
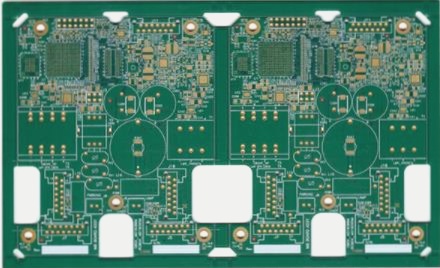
The term “microwave circuit” is derived from the Greek word “micros,” meaning very small. In microwave or radio frequency (RF) circuits, the wavelength is significantly smaller than the physical dimensions of the circuit. This results in high-speed signals that interact with circuit components. Microwave PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) use specialized laminated materials with unique mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties, unlike traditional FR4 materials. These materials were introduced in the 20th century, facilitating advancements such as microwave integrated circuits (MIC), waveguide and coaxial technologies, and monolithic microwave integrated circuits (MMIC).
Microwave PCBs are primarily used in avionics, wireless communication applications, and devices that operate in medium- to high-frequency ranges for signal control. These PCBs are key in applications such as military radars, mobile phones, laptops, and more. There is often confusion between standard PCBs and microwave PCBs, but the distinction mainly lies in the physical and electrical characteristics of the dielectric material used. RF circuits typically operate in the range of 500 MHz to 2 GHz. A layout above 100 MHz is considered an RF PCB, while anything over 2 GHz is classified as microwave frequency.
To understand these differences, it’s helpful to consider signal speed. High-performance microwave PCBs require advanced manufacturing methods to optimize performance, enabling high-frequency output for RF and microwave applications. The materials selected for PCB manufacturing must have specific properties, such as dielectric constant (ER), coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), and loss tangent, to ensure efficient signal transmission with minimal impedance. This leads to stable, durable PCBs that can withstand extreme temperatures and climates, while also ensuring precise placement of fine-pitch components.
Multilayer PCBs are commonly used in RF and microwave applications. Key design considerations for these PCBs include low-impedance ground planes, which help minimize signal distortion, and maintaining sufficient spacing between RF signal lines to prevent crosstalk. Additionally, effective thermal management is essential, with copper shapes and flatness being critical factors for heat dissipation. A solid ground plane is necessary to reduce inductance, which can interfere with signal integrity.
The packaging technologies for microwave circuits can be broadly divided into two categories: circuit card components and hybrid circuits. Hybrid circuit packaging, which combines different technologies in a single unit, is particularly effective in high-reliability applications, such as military and aerospace systems. In contrast, circuit card components are more cost-effective and are suitable for standard, quality RF solutions. It is crucial for PCB manufacturers to have a deep understanding of RF and microwave technologies before starting a project.
When designing or reworking an RF or microwave PCB, it’s important to consult with experts in the field to optimize both cost and performance. This ensures the project stays on schedule and within budget. To deliver high-performance microwave PCBs, manufacturers rely on advanced PCB engineering technologies, coupled with an experienced team of experts. A focus on quality and strong customer relationships is vital to success, as is providing excellent technical support and fast turnaround times to meet the needs of diverse industries.
In conclusion, the manufacturing of RF and microwave PCBs involves complex considerations such as material selection, signal integrity, and thermal management. Expert guidance and an in-depth understanding of these factors are essential to producing high-quality, reliable products. By leveraging the latest technologies and best practices, manufacturers can ensure the success of their projects and meet the demanding requirements of modern communication and defense systems.