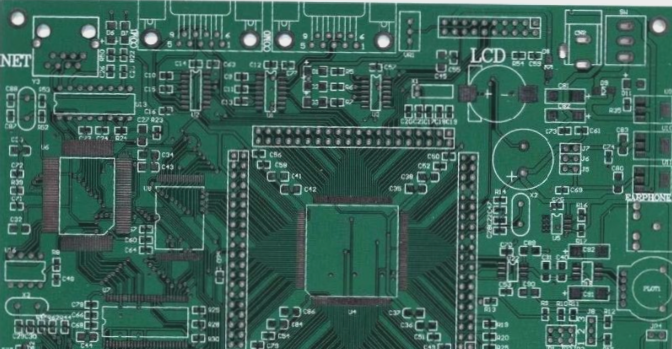
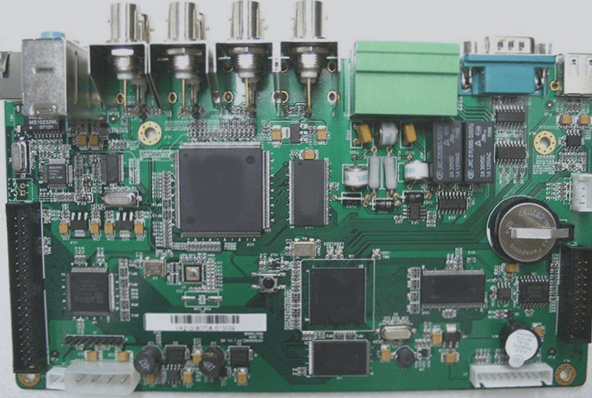
Rigid-flex PCB is a hybrid printed circuit board that integrates both flexible and rigid circuit boards. This combination leverages the strengths of each to meet the requirements of applications with space constraints or demanding high-density integration.
Flexible circuit boards, constructed from materials like polyimide film, offer the ability to bend and fold, accommodating various shapes. Conversely, rigid circuit boards utilize substrates such as fiberglass, providing structural support for electronic components.
Rigid-flexible PCBs are typically composed by connecting flexible and rigid circuit boards into a unified unit. This structure allows for the synergistic utilization of flexible and rigid board advantages, enhancing design flexibility and integration capabilities. For instance, flexible circuit boards can facilitate connections between different rigid boards in complex circuit layouts. Additionally, they can conform to curved shapes to fit specific spatial limitations.
Commonly employed in premium electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, rigid-flex PCBs are favored for their design versatility and reliability. Consequently, they have emerged as a prominent technology in the realm of printed circuit boards.

Design: Designers need to create the circuit layout and shape of the rigid-flex PCB based on the electronic product’s requirements and space constraints.
Manufacturing rigid circuit boards: The manufacturing process for rigid circuit boards closely follows the traditional PCB manufacturing process, involving steps such as cutting, drilling, copper plating, and more.
Fabrication of flexible circuit boards: The fabrication process of flexible circuit boards utilizes specialized substrates and technologies, including coating, exposure, and etching of thin film materials.
Circuit connection: Rigid circuit boards and flexible circuit boards are interconnected through soldering, gluing, or plugging to form a rigid-flex PCB.
Testing and quality control: Rigorous testing and quality control procedures are implemented for rigid-flex PCBs to ensure they meet electronic product requirements and standards.

Design flexibility: Rigid-flex PCBs enable more complex circuit layouts and shapes, accommodating various electronic product requirements and space constraints.
High-density integration: These PCBs achieve higher circuit integration levels without enlarging the board’s size.
Reliability: By connecting rigid and flexible circuit boards in diverse configurations, rigid-flex PCBs enhance circuit board stability and reliability.
Cost savings: They streamline assembly steps and reduce parts in electronic products, cutting costs and boosting production efficiency.
In conclusion, rigid-flex PCB technology is crucial for high-end electronic products due to its powerful, flexible design and high reliability.
However, rigid-flexible PCBs also present challenges such as high manufacturing costs, complex processes, and maintenance difficulties. Therefore, it’s essential to thoroughly consider actual needs and manufacturing costs when opting for rigid-flex PCBs.

1. With the continuous development and popularization of electronic products, the integration of hardware and software in PCB technology is advancing and expanding.
2. In the future, this integration will play a crucial role across various fields including smart wearable devices, smart homes, and medical equipment.
3. Concurrently, advancing rigid-flex PCB technology requires continuous innovation and technological advancement to meet the diverse needs and challenges in these fields.
Flexible circuit boards, constructed from materials like polyimide film, offer the ability to bend and fold, accommodating various shapes. Conversely, rigid circuit boards utilize substrates such as fiberglass, providing structural support for electronic components.
Rigid-flexible PCBs are typically composed by connecting flexible and rigid circuit boards into a unified unit. This structure allows for the synergistic utilization of flexible and rigid board advantages, enhancing design flexibility and integration capabilities. For instance, flexible circuit boards can facilitate connections between different rigid boards in complex circuit layouts. Additionally, they can conform to curved shapes to fit specific spatial limitations.
Commonly employed in premium electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, rigid-flex PCBs are favored for their design versatility and reliability. Consequently, they have emerged as a prominent technology in the realm of printed circuit boards.
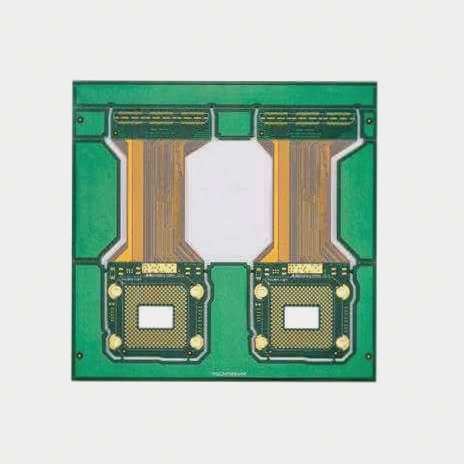
Design: Designers need to create the circuit layout and shape of the rigid-flex PCB based on the electronic product’s requirements and space constraints.
Manufacturing rigid circuit boards: The manufacturing process for rigid circuit boards closely follows the traditional PCB manufacturing process, involving steps such as cutting, drilling, copper plating, and more.
Fabrication of flexible circuit boards: The fabrication process of flexible circuit boards utilizes specialized substrates and technologies, including coating, exposure, and etching of thin film materials.
Circuit connection: Rigid circuit boards and flexible circuit boards are interconnected through soldering, gluing, or plugging to form a rigid-flex PCB.
Testing and quality control: Rigorous testing and quality control procedures are implemented for rigid-flex PCBs to ensure they meet electronic product requirements and standards.

Design flexibility: Rigid-flex PCBs enable more complex circuit layouts and shapes, accommodating various electronic product requirements and space constraints.
High-density integration: These PCBs achieve higher circuit integration levels without enlarging the board’s size.
Reliability: By connecting rigid and flexible circuit boards in diverse configurations, rigid-flex PCBs enhance circuit board stability and reliability.
Cost savings: They streamline assembly steps and reduce parts in electronic products, cutting costs and boosting production efficiency.
In conclusion, rigid-flex PCB technology is crucial for high-end electronic products due to its powerful, flexible design and high reliability.
However, rigid-flexible PCBs also present challenges such as high manufacturing costs, complex processes, and maintenance difficulties. Therefore, it’s essential to thoroughly consider actual needs and manufacturing costs when opting for rigid-flex PCBs.
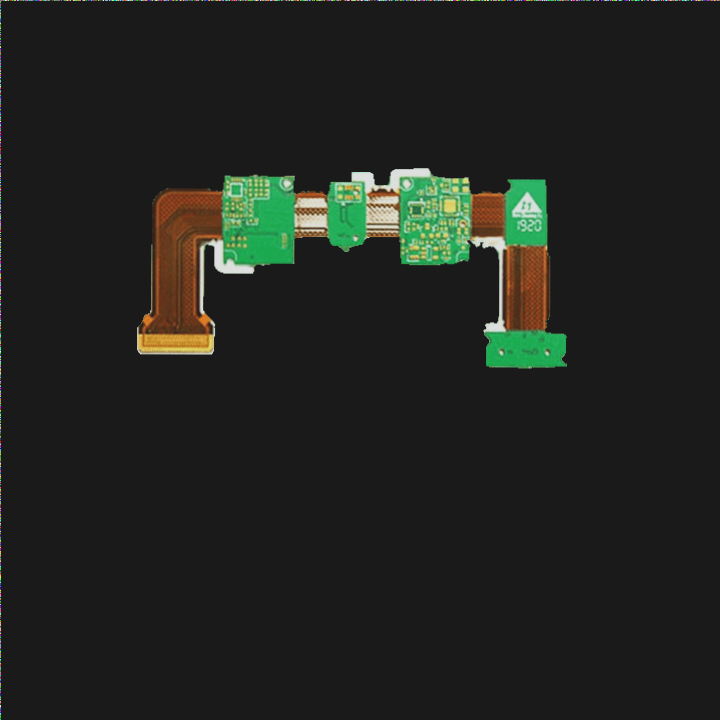
1. With the continuous development and popularization of electronic products, the integration of hardware and software in PCB technology is advancing and expanding.
2. In the future, this integration will play a crucial role across various fields including smart wearable devices, smart homes, and medical equipment.
3. Concurrently, advancing rigid-flex PCB technology requires continuous innovation and technological advancement to meet the diverse needs and challenges in these fields.