The Evolution of PCB Colors: Exploring Beyond Green
Traditionally, green has been the go-to color for PCBs. However, with technological advancements and creative innovations, the spectrum of available PCB colors has broadened significantly.
Every electronic circuit is constructed on a printed circuit board (PCB), which serves as the fundamental backbone of modern electronics.
Understanding the significance of PCB colors is often underestimated but holds great importance.
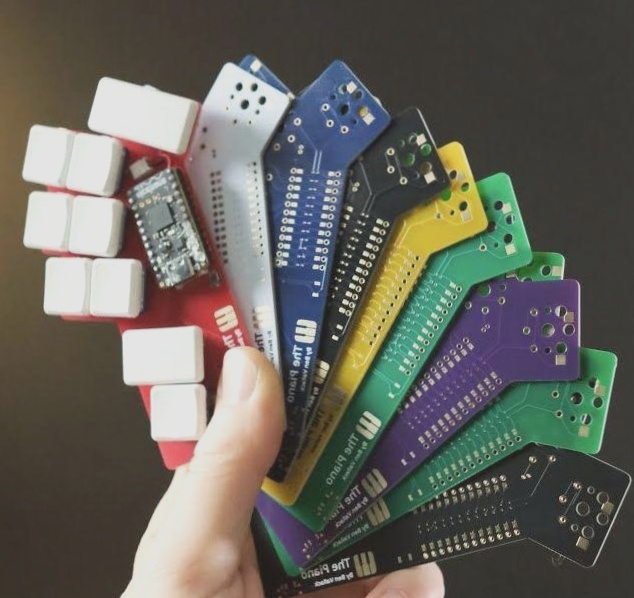

Wellcircuits provides a diverse array of colors to elevate your design aesthetics.
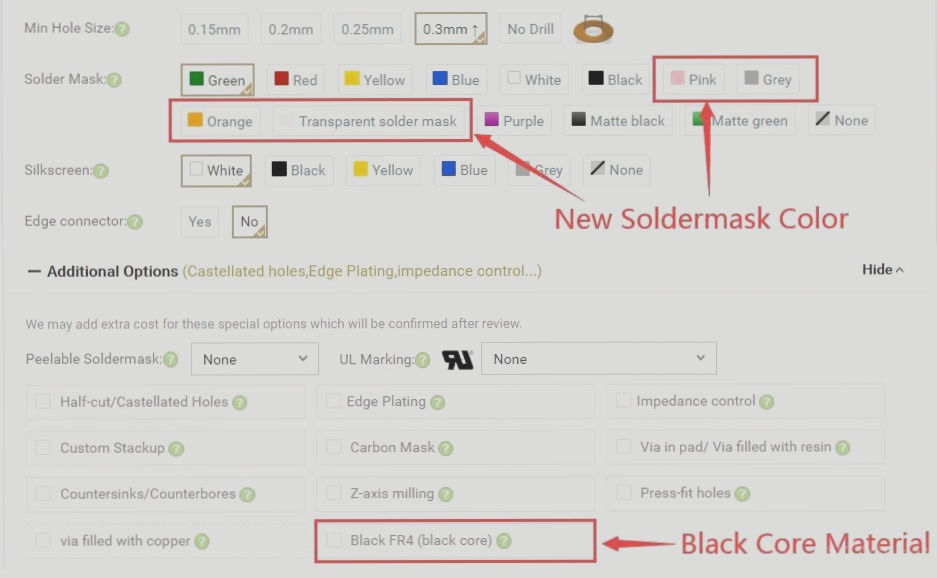
Enhancing Understanding: The Significance of PCB Board and Solder Mask Colors
Comprehending the basics of PCB boards and solder mask colors is simplified with this informative guide.
The color of the solder mask is typically influenced by the PCB’s color. This colored lacquer mask conceals the copper traces beneath, protecting the circuit board from short circuits. The final PCB color, derived from glass and epoxy, mirrors the solder mask color.
While green has been the conventional choice for PCBs, the expanding range of colors is driven by technological progress and innovative trends, leading many manufacturers to opt for non-green PCBs.
Reasons to Opt for Non-Green PCBs:
- Different colors aid in identifying revision changes, ensuring users are alerted to crucial updates.
- Non-green colors can enhance the design’s vibrancy and compactness, considering the impact of assembly equipment’s light properties on the design.
- Distinct colors help prevent errors in complex assemblies and facilitate the identification of lead-free components during production.
Wellcircuits offers a variety of solder mask colors, including white, blue, black, yellow, and red, among others, providing flexibility and customization options for your PCB designs.

While green remains a staple in PCB manufacturing, modern PCBs come in a plethora of colors and styles. For instance, green epoxy is still prevalent in PC motherboard production.
Although the solder mask color doesn’t impact PCB performance, the resolution of the board may vary based on the color chosen. Red and blue solder masks typically have lower resolution than yellow or black variants, with transparent masks offering the highest resolution.
Diving Deeper: The Role of Solder Mask Colors
Various solder mask colors are available, each serving specific purposes. For example, black solder masks, containing cobalt and carbon, are conductive due to their carbon content, shielding signals from external interference.
White PCBs are common in LED applications, while blue masks are favored in LCD displays for reducing distractions. Red PCBs are often used for board differentiation, especially in precision equipment like oscilloscopes and analog meters.
Green’s dominance in PCBs is acknowledged globally for its soldering compatibility with component pitches. Japan leans towards green PCBs for their reliability, while Germany explores non-traditional colors in engineering sectors.
Exploring Color Options at Wellcircuits
Choosing the Right Solder Mask Color for Your PCB
When selecting printed circuit boards, one crucial consideration is the color of the solder mask. While green is the most common choice, options like yellow, white, black, and even new colors like PINK, ORANGE, GRAY, and TRANSPARENT are available at no extra cost. Deciding on the best color can be challenging, so it’s essential to weigh the pros and cons of each option.
Red Solder Mask
Red solder masks offer a bold and professional look with excellent contrast. However, compared to green PCBs, the contrast is less distinct, requiring higher magnification for inspection. Keep in mind that red backgrounds may make flux residue removal more challenging.
Blue Solder Mask
The blue solder mask is often linked to Arduino projects. While it has lower contrast than green or red PCBs, it provides strong contrast with the silkscreen layer. Blue is a good choice for designs with heavy components and can complement your Arduino design well.
Black Solder Mask
Black PCBs present challenges due to minimal contrast, making inspection difficult. They also absorb heat during soldering and are harder to clean. Despite these issues, black solder masks offer clear separation between silkscreen and pads without additional lighting.
White Solder Mask
White solder masks are considered the most challenging to work with, as they have low contrast and visibility issues. Cleaning white PCBs can be tough due to trace spotting difficulties. While they offer similar silkscreen contrast to black, white solder masks are generally not recommended for most applications.
Yellow Solder Mask
Although rarely chosen, yellow solder masks provide excellent contrast and can be a great choice for well-routed and visually appealing designs. Pairing yellow with black silkscreen offers superior contrast and performance without significant cleaning challenges.
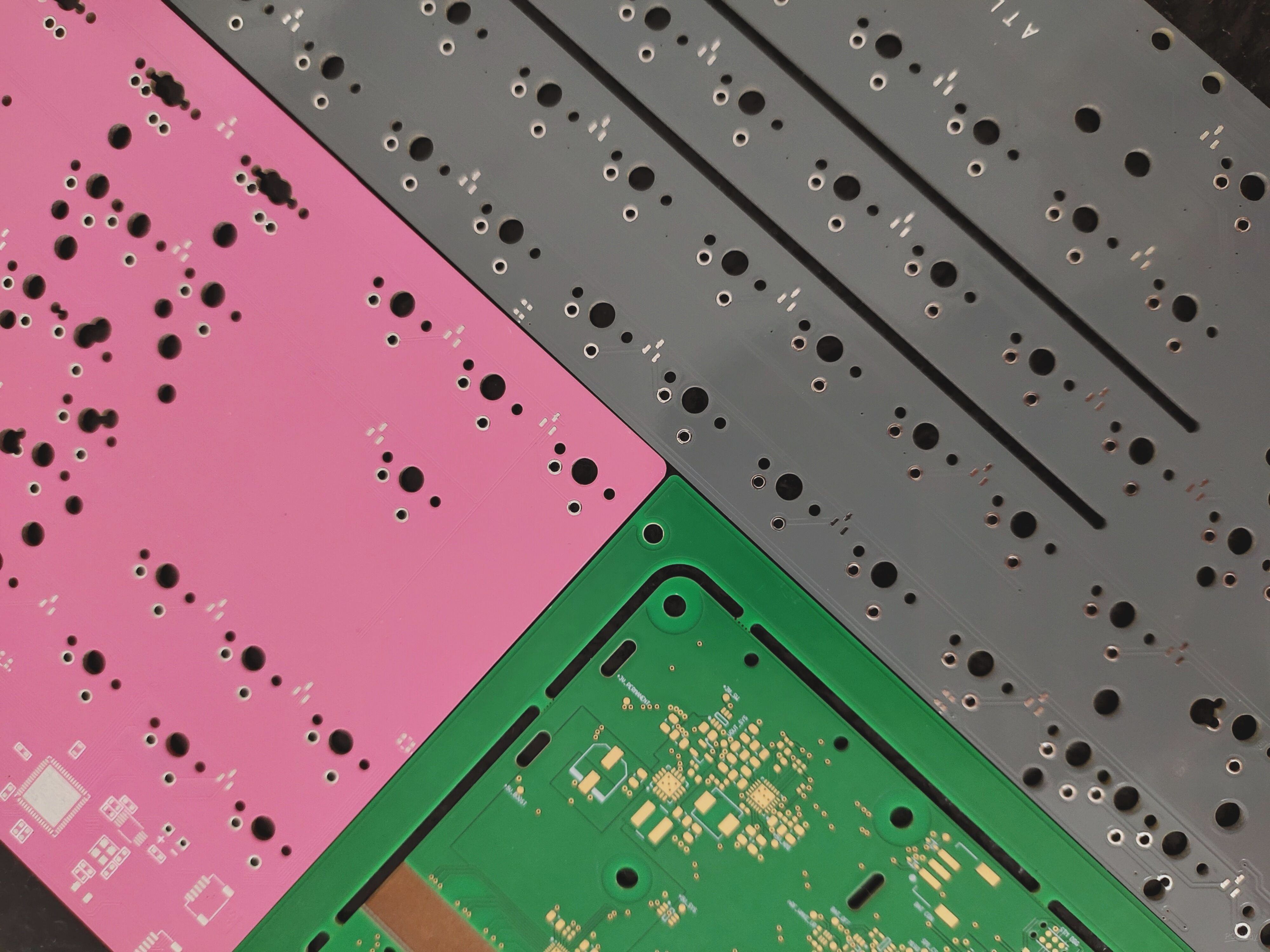
For more color options and high-quality PCB solutions, explore new solder mask colors like PINK, ORANGE, GRAY, and TRANSPARENT at Wellcircuits!
Author: Stack Thomas
For any inquiries about PCBs or PCBA, contact me at info@wellcircuits.com.