Introduction to Flexible Circuit Boards (FPCBs)
In today’s fast-paced electronics industry, Flexible Circuit Boards (FPCBs) have emerged as essential components due to their adaptability and versatility. These boards play a crucial role in meeting the requirements of modern electronics, providing solutions for applications that demand compact, lightweight, and flexible designs. Among the various manufacturing methods for FPCBs, Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a standout technique. This article explores the significance of the SMT process specifically for FPCBs, covering its importance, procedural steps, and the benefits it brings.
What are Flexible Circuit Boards (FPCBs)?
Flexible Circuit Boards are a type of printed circuit board designed to bend and flex without damage. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs, FPCBs are crafted from flexible materials like polyimide or polyester, allowing them to conform to diverse shapes and sizes. This flexibility makes them ideal for applications where rigid circuit boards would not suffice. FPCBs find extensive use across various industries, including consumer electronics, medical devices, automotive systems, and wearable technology. Their lightweight and compact nature make them particularly well-suited for modern devices that prioritize efficiency and space-saving designs.
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) for FPCBs
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a technique where electronic components are directly mounted onto the surface of a printed circuit board, eliminating the need for insertion into holes. This method is especially advantageous when working with flexible circuit boards. SMT enables a higher component density, optimizing space utilization. It enhances the reliability of the final product and significantly reduces manufacturing time compared to traditional methods like Through-Hole Technology (THT). Additionally, SMT supports automated assembly processes, enhancing precision and reducing labor costs.
Benefits of SMT for FPCBs
- Higher Component Density: SMT allows for placing more components in a smaller area, enhancing the functionality of the final product.
- Improved Reliability: Direct component mounting reduces the risk of solder joint failure, boosting the overall reliability of the device.
- Reduced Manufacturing Time: SMT streamlines the assembly process by eliminating manual component insertion, leading to faster production.
- Cost Efficiency: Automation in the SMT process reduces labor costs by minimizing manual interventions.
Challenges and Considerations
While SMT offers numerous advantages, it also poses challenges, especially when applied to flexible circuit boards. The bending and flexing characteristics of FPCBs can make ensuring reliable solder joints challenging. Moreover, the thermal properties of materials like polyimide used in FPCBs differ from those of traditional rigid PCBs, which can complicate the reflow soldering process. Overcoming these challenges requires meticulous process optimization and precise control during manufacturing to achieve high-quality outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a crucial method for manufacturing Flexible Circuit Boards (FPCBs), offering benefits such as higher component density, enhanced reliability, and reduced production time. Despite challenges related to FPCB flexibility and material properties, these obstacles can be overcome through careful design and manufacturing practices. With the increasing demand for flexible and compact electronic devices, SMT remains a pivotal technology for meeting the evolving needs of modern electronics.
Summary
This article emphasizes the significance of Surface Mount Technology (SMT) in the production of Flexible Circuit Boards (FPCBs). FPCBs play a vital role in modern electronics due to their flexibility, compactness, and versatility. SMT brings several advantages to FPCB manufacturing, including higher component density, improved reliability, and cost efficiency. Despite challenges associated with FPCB flexibility, meticulous process optimization ensures the production of efficient, reliable, and cost-effective flexible circuit boards for diverse applications.
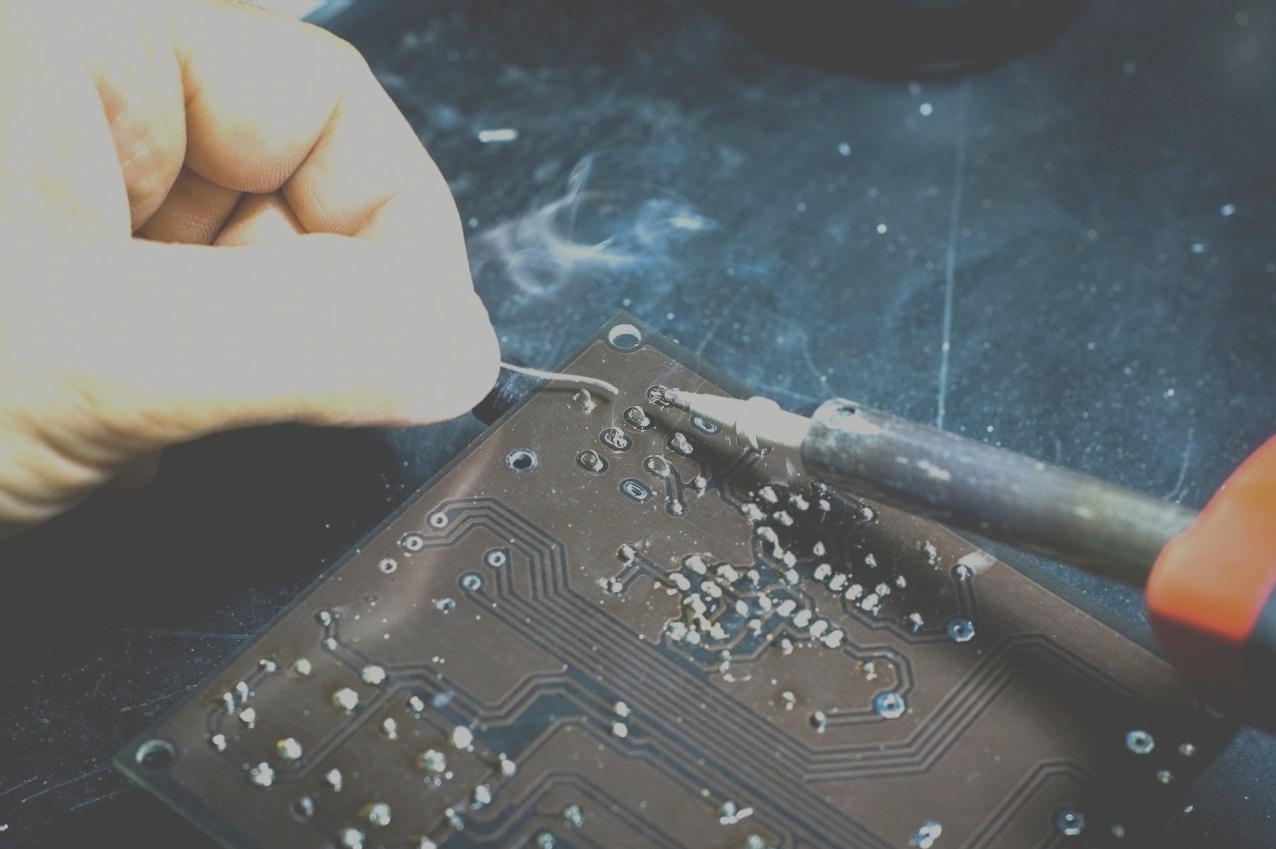

Designing Flexible Printed Circuit Boards (FPCBs)
- Design Preparation: Engineers use specialized software to create the schematic and layout, ensuring components fit the flexible substrate for optimal functionality and performance.
- Material Selection: Choosing materials like polyimide and polyester ensures flexibility and thermal stability, while surface-mounted devices (SMDs) are preferred for easy assembly.
- Solder Paste Application: Precision application of solder paste minimizes risks like solder bridges or insufficient joints, crucial for avoiding defects.
- Component Placement: Automated machines accurately place SMDs on the board, requiring precision to prevent poor connections or component failure.
- Reflow Soldering: Controlled heating melts solder paste to form solid connections between components and the board, ensuring reliable electrical pathways.
- Inspection and Testing: Automated systems detect defects, while functional testing verifies correct circuit operation for reliable performance.
- Final Processing: Post-production steps include cleaning, coating, and packaging the FPCB for integration into end products.
Key Benefits of Flexible PCB Manufacturing:
- Higher Component Density: SMT allows more components in a smaller space, ideal for compact devices requiring efficiency.
- Improved Reliability: SMT solder joints are stronger and more durable, crucial for flexible circuits prone to stress and movement.
- Reduced Manufacturing Time: Automation in SMT accelerates production, meeting fast-paced electronics market demands.
For more information on flexible PCB manufacturing and the latest industry trends, visit Well Circuits.
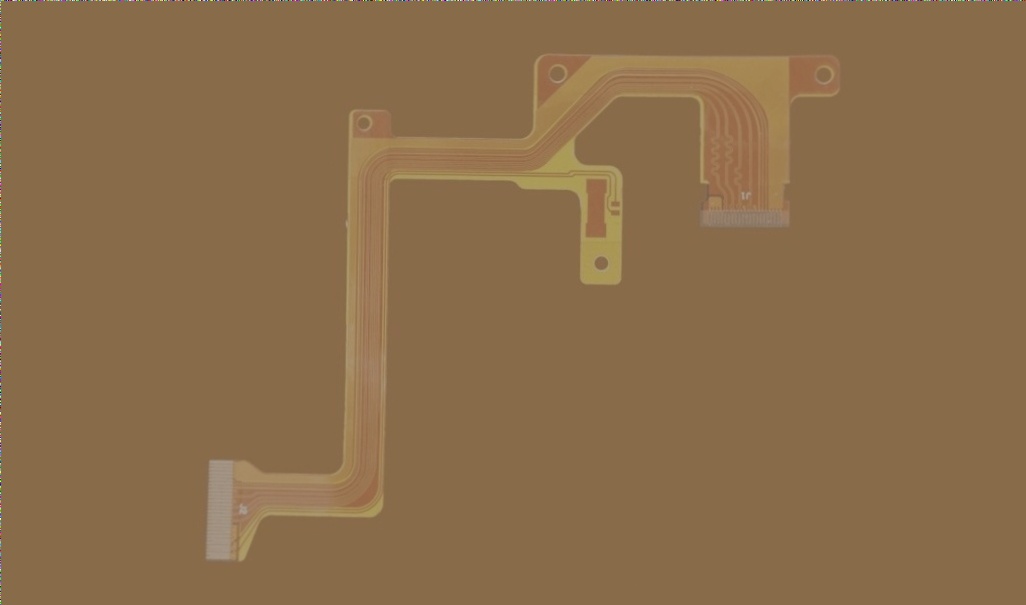

SMT Advantages in Flexible Circuit Production
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a crucial process that revolutionizes the production of flexible circuit boards by reducing manual labor and minimizing defects. This automation not only enhances efficiency but also lowers production costs significantly.
Key Benefits of SMT in Flexible Circuit Production
- Higher component density
- Improved reliability
- Faster production times
- Cost-effectiveness
As the electronics industry progresses, the importance of SMT in manufacturing top-quality, compact, and durable flexible circuits continues to grow. Ongoing advancements in SMT technology ensure that it remains a leading force in electronic design and Flexible Printed Circuit Board (FPCB) applications, facilitating the development of the next wave of technology-driven products.